Abdomen AP (KUB) View (Part - 2)
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the process of conducting a CT scan of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It explains the patient preparation, the use of contrast materials, and the positioning of the patient on the scanning table. The script also details the various types of scans, such as erect, supine, and flank positions, and the importance of minimal movement during the scan. The use of radiopaque markers and the role of gas in the intestines for visualizing the kidneys and bladder are also highlighted. The video aims to educate viewers on the intricacies of CT scans for urinary system diagnostics.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The video discusses the process of performing a CT scan of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, providing insights into the procedure and its importance.
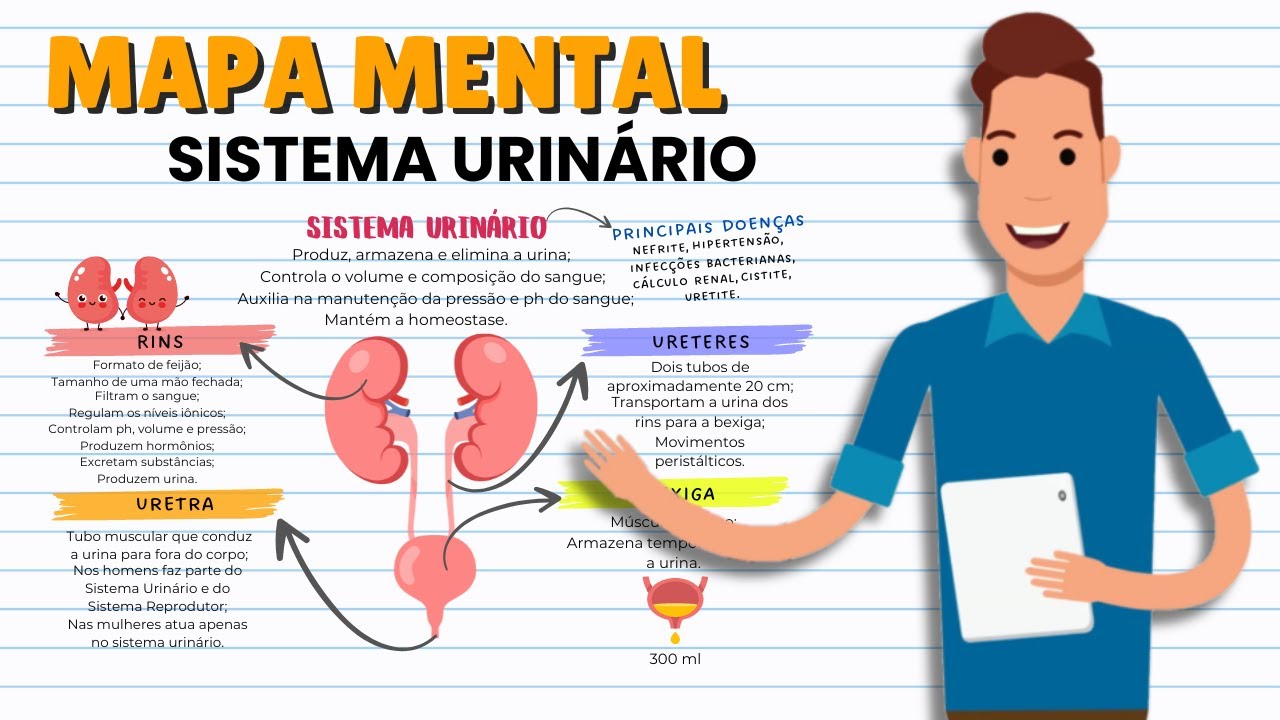
- 📍 Kidneys are located in the retroperitoneal cavity and are bean-shaped organs responsible for filtering blood and producing urine.
- 💧 The primary function of the kidneys is to filter blood, remove waste and excess water, and return essential minerals and water to the bloodstream.
- 🩸 The ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder, where it is stored until it is excreted through the urethra.
- 🏥 Preparation for a CT scan involves the removal of metallic materials from the patient's west region to avoid artifacts in the images.
- 👨⚕️ Patients are instructed to take laxatives and follow a clear liquid diet before the examination to ensure the digestive system is clear.
- 🛌 Patient positioning is crucial for the CT scan, with the patient lying flat on the scanning table, centered over the table's midpoint.
- 🔍 The use of contrast agents may be required for better visualization of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder during the scan.
- 📏 Specific attention is given to the lower abdomen and the area 2 inches below the public symphysis to include the bladder in the scan's field of view.
- 🎥 The radiographer must ensure that the patient remains still during the scan to prevent image blurriness or overlapping.
- 📊 The radiographic appearance includes visualization of the entire intestine, gas shadow of the intestine, and the lower ribs to ensure proper positioning and scanning.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The main focus of the video is to explain the process of performing a CT scan of the kidneys, ureter, and bladder.
What is the first step in preparing a patient for a CT scan?
-The first step in preparing a patient for a CT scan involves removing all metallic materials from the west region, which includes removing the patient's clothing and any items such as coins that may interfere with the image quality.
Why is it important to give the patient a low residue diet before the examination?
-A low residue diet is preferred before the examination to minimize the bowel movements and to clear the abdomen, which helps in obtaining clear images of the abdominal organs.
What are the different types of scans that can be performed using the CT scan?
-Different types of scans that can be performed using the CT scan include an acute intestinal scan, a forensic body scan, a gastro-intestinal pen, and a urological pen.
How is the patient positioned for the CT scan of the kidneys, ureter, and bladder?
-The patient is positioned supine on the scanning table, with their mid-sagittal plane overlapping the center of the scanning table and the table's center line overlapping the patient's mid-sagittal plane.
What is the significance of the lower end of the scanning range being 2 inches below the pubic symphysis?
-The lower end of the scanning range is placed 2 inches below the pubic symphysis to ensure that the bladder is included in the scan, as it is part of the urinary system being examined.
What is the role of the radiographer in the CT scan process?
-The radiographer plays a crucial role in the CT scan process by ensuring the patient is correctly positioned, setting the scanning parameters, and capturing the images without any movement that could affect the quality of the scan.
What are the key components of the CT scan settings?
-The key components of the CT scan settings include maintaining 200 mAs, a pitch of 30 to 40 mAs, a gantry speed of 0.15 to 0.2 seconds, a focus distance of 180 cm, and using a grid if necessary.
How does the radiographer ensure the patient remains still during the scan?
-The radiographer instructs the patient to remain completely still during the scan to avoid any movement that could cause blurring or overlapping of the images.
What are the structures visualized in the radiographs shown in the video?
-The structures visualized in the radiographs include the entire intestine, the gas shadow within the intestine, the iliac crest, the lower ribs, the pubic symphysis, the kidneys, the bladder, and the ureter.
Why is it important to have a clear understanding of the patient's anatomy before performing the CT scan?
-A clear understanding of the patient's anatomy is crucial for accurately positioning the patient and setting the correct scanning parameters to ensure high-quality images that can be effectively used for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)