Highlight: Sutra [Part 2] - Tentang Jalur Sutra #AlamSemenit
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the Silk Road's pivotal role in accelerating trade and cultural exchange, originating from China and Central Asia. It highlights how silk monopolized trade, influencing societies and economies. The script also touches on the spread of religions and ideas, the introduction of new maritime technologies, and the eventual decline of the Silk Road due to European exploration. It reflects on the impact of globalization on culture and economy, drawing parallels between historical trade routes and modern interconnectedness.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The Silk Road was not the beginning of human trade but it significantly helped in the exponential growth and diversification of trade activities.
- 🏺 Before the Silk Road, many civilizations were largely isolated due to geographical barriers and fear of the unknown.
- 🛣️ Around the 2nd century BCE, China and Central Asia began to explore and create land routes for trade, exchanging products and sometimes ideas.
- 🧵 Silk was the most commonly traded item along the Silk Road, having a significant impact on societies that received it.
- 📈 The demand for silk grew, leading to a shift in profession among the Chinese working class to silk production to meet the demands from various civilizations.
- 🌍 The Silk Road evolved into a complex network of land and sea trade routes, stretching from the Mediterranean to India and Southeast Asia.
- 🔥 The spread of gunpowder from China to the Middle East influenced the future of empires like the Ottoman, Safawi, and Mughal.
- 📚 Merchants from India brought Buddhism to China and Japan via the Silk Road, where it remains a dominant religion.
- 🕌 Arab traders brought Islam to Southeast Asia, introducing the religion to Malaysia, Indonesia, and surrounding countries.
- 🚢 The success of the Silk Road led to its own decline as the exchange of ideas introduced new maritime technologies like the magnetic compass.
- 🌟 Many historians believe the most significant impact of the Silk Road was not the spread of products but the spread of ideas and concepts.
Q & A
What was the significance of the Silk Road in terms of human activity?
-The Silk Road was significant because it facilitated the growth and diversity of trade activities exponentially, connecting civilizations and enabling the exchange of goods, ideas, languages, religions, and cultures.
How did the Silk Road impact the spread of Buddhism?
-The Silk Road allowed merchants from India to travel and bring Buddhism to China and Japan, where it remains a dominant religion to this day.
What was the initial monopoly that the Chinese had on the Silk Road?
-The Chinese initially had a monopoly on silk production, as they were the only ones who knew how to make it, which was a highly sought-after luxury fabric.
How did the demand for silk affect the working class in China?
-The growing demand for silk led to an increase in the working class in China shifting their profession to silk production to meet the demands from various civilizations.
What was one of the unintended consequences of the Silk Road?
-One of the unintended consequences of the Silk Road was its own decline, as the exchange of ideas led to new maritime technologies such as the magnetic compass, which eventually made long land routes obsolete.
How did the spread of gunpowder from China to the Middle East affect the future of empires like the Ottoman, Safawi, and Mughal?
-The spread of gunpowder influenced the military and political landscape, shaping the future of empires like the Ottoman, Safawi, and Mughal by altering warfare and strategies.
What role did the Silk Road play in the spread of Islam to Southeast Asia?
-Sailors from Arabia used the Silk Road to bring Islam to Southeast Asia, which opened the way for religious influence in countries like Malaysia, Indonesia, and surrounding nations.
What is the opinion of some historians regarding the greatest impact of the Silk Road?
-Some historians believe that the greatest impact of the Silk Road was not the spread of products but the spread of ideas or concepts, which were more beneficial for the rapid advancement in arts and technology of a civilization and diplomatic relations between nations.
How does the script suggest that globalization today is similar to the Silk Road?
-The script suggests that modern globalization, like the Silk Road, has both positive and negative impacts on culture and economy, and is not a new phenomenon but rather a continuation of historical patterns of exchange and influence.
What are the potential negative effects of globalization mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions that globalization can lead to the loss of cultural identity, tradition, and even language, with the example of the Euro adoption by European countries and the potential extinction of thousands of languages by the year 2100.
How did the Silk Road metaphorically become a 'car free day' for ideas and goods?
-The Silk Road metaphorically became a 'car free day' by originally being inaccessible and then being opened up for the exchange of goods and ideas, much like how a road might be closed for cars but open for pedestrians, leading to a bustling exchange of goods and interactions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Jalur Sutra | Jalur Perdagangan Berusia Ribuan Tahun

India, China, and the Maritime Silk Road: More Than Just a Trade Route

Lalu Lintas Perdagangan Dunia Sebelum Era Kolonialisme dan Imperialisme Eropa

10 Signs You’re a MORE ATTRACTIVE MAN Than You Think

💀 중국이 중앙아시아에서 쫓겨난 이유…!! (feat.고구려) / 💀 탈라스 전투 총정리
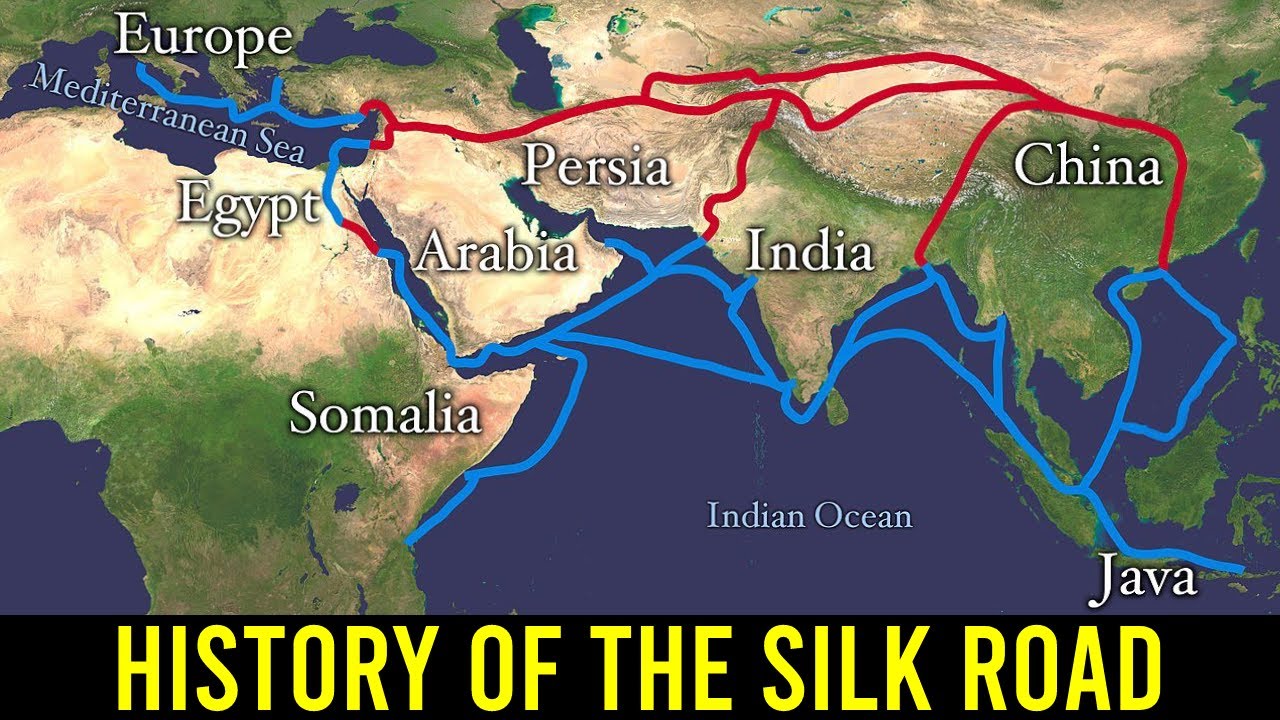
The Silk Road: A Story of Trade, Travel, and Cultural Exchange
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)