Xylem and Phloem - Transport in Plants | Biology | FreeAnimatedEducation
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the transport systems in plants, focusing on xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem distributes water and minerals from roots to leaves, featuring cells like tracheids and vessels, and is strengthened by lignin. Phloem transports manufactured food like sucrose from leaves to other parts of the plant through sieve tubes and companion cells. The arrangement of these vascular tissues varies across roots, stems, and leaves. Xylem forms an 'X' shape in roots, while both tissues form clusters in stems and bundles in leaves. The video provides a detailed look at these essential plant structures and their functions.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Plants absorb water and minerals from the soil through their roots, while glucose is produced in the leaves via photosynthesis.
- 💧 Xylem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, playing a crucial role in plant nutrition.
- 🚰 Xylem vessels are long, hollow tubes, allowing continuous water flow from the roots to the leaves, while tracheids are connected by pitted walls.
- 🦴 The xylem is composed of tracheids, vessels, fibers for support, and living parenchyma cells for food storage.
- 🌀 Xylem cells are strengthened by lignin, which can form different patterns like rings, spirals, and pits depending on the plant's location.
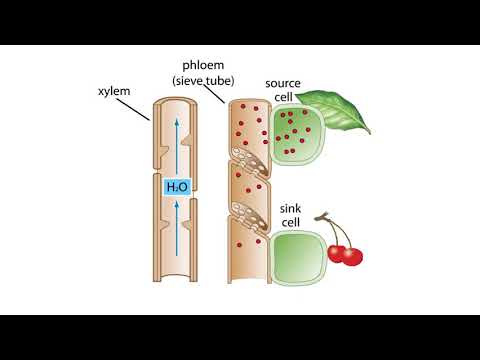
- 🍃 Phloem transports nutrients like sucrose and amino acids from the leaves to other parts of the plant, a process called translocation.
- 🍂 Phloem is made up of sieve tubes, companion cells, fibers for support, and parenchyma cells for food storage.
- 🌾 Sieve tube cells rely on companion cells for survival, as they have degenerated protoplasms and lack a nucleus.
- 🔄 In phloem, only the fiber cells are dead, while all other cells (sieve tubes, companion cells, parenchyma) are alive.
- 🌸 The arrangement of vascular tissues varies: in roots, xylem forms an X shape surrounded by phloem, while in stems, they cluster near the edges, and in leaves, xylem is positioned above phloem in vascular bundles.
Q & A
What are the two main vascular tissues in plants?
-The two main vascular tissues in plants are xylem and phloem.
What is the primary function of xylem in plants?
-Xylem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
What are the main components of xylem?
-Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, fibers, and parenchyma.
How do tracheids and vessels differ in xylem?
-Tracheids are narrow cells with pitted walls where water flows between cells, while vessels are long, wide, continuous hollow tubes that stretch from the roots to the leaves.
What role does lignin play in xylem cells?
-Lignin strengthens xylem cells and can appear in various patterns such as rings, spirals, reticulate, or pitted depending on the location.
What is the primary function of phloem?
-Phloem transports manufactured food, such as sucrose and amino acids, from the leaves to other parts of the plant, a process called translocation.
What are the components of phloem tissue?
-Phloem consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, fibers, and parenchyma.
Why do sieve tube cells need companion cells?
-Sieve tube cells have degenerated protoplasm and require companion cells to carry out vital processes. Companion cells have abundant cytoplasm and a nucleus to support the sieve tubes.
How is the vascular tissue arranged in the roots of dicot plants?
-In the roots of herbaceous dicot plants, the xylem forms an x-like shape in the middle, while the phloem surrounds the xylem.
Where are the xylem and phloem located in the leaf?
-In the leaf, xylem and phloem are located in the vascular bundle, with the xylem positioned above the phloem.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

8. Transport in Plants (Part 1) (Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)

7-1 Types of Dicotyledon Plant Tissues (Cambridge AS A Level Biology, 9700)

Xylem and Phloem - Transport in Plants | Biology | FuseSchool

Transportation in Plants
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant

Transportation in Plants
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)