Design Sprint: Planning, Requirements, Overview.
Summary
TLDRGoogle's design sprint is a rapid, five-day process for solving critical business problems through design thinking. It involves understanding the problem, sketching solutions, deciding on a direction, prototyping, and validating with users. This method streamlines the design process, allowing teams to quickly iterate and gain valuable insights, potentially leading to efficient failures, flawed successes, or epic wins, and is adaptable for various product complexities.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Companies are hesitant to invest in large design projects without understanding their chances of success.
- 🏃♂️ Google Ventures has developed a 'design sprint' method to streamline the design process and provide valuable insights quickly.
- ⏱️ The design sprint process takes just five days, focusing on rapid design, prototyping, and user testing.
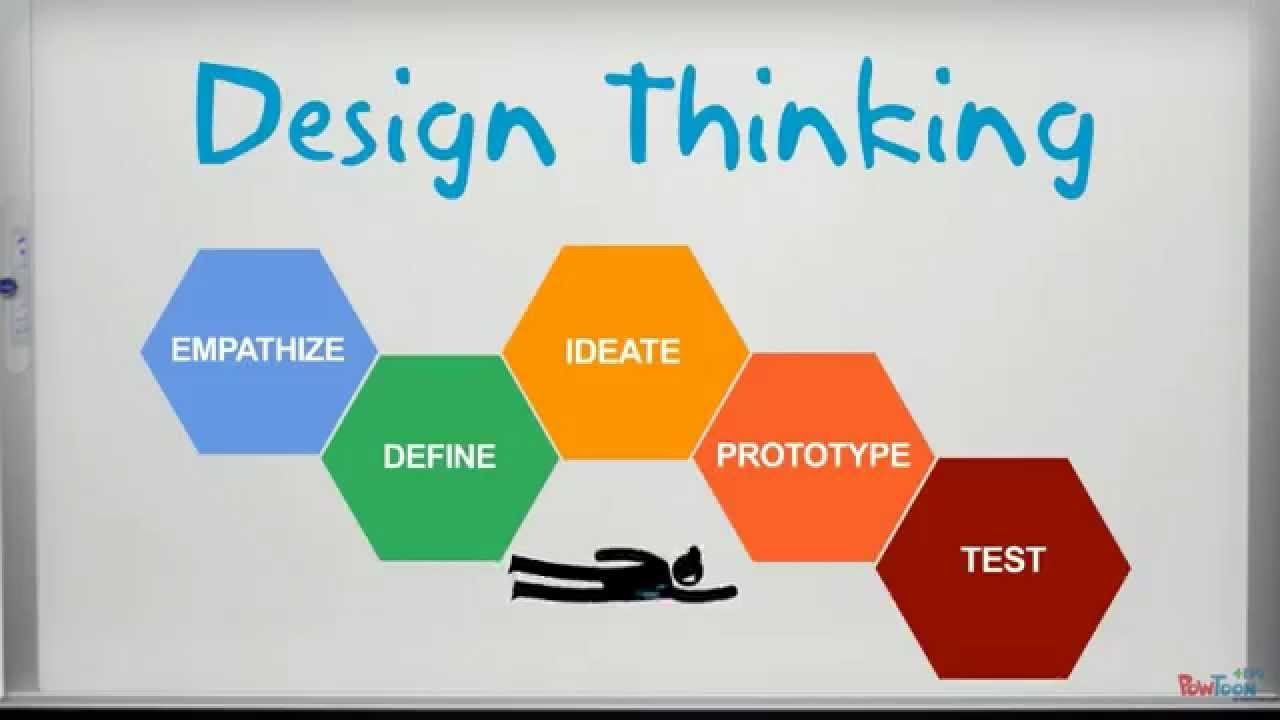
- 🤔 The sprint is based on design thinking and consists of five phases: Understand, Sketch, Decide, Prototype, and Validate.
- 📝 A successful sprint requires planning, including writing a brief, conducting user research, and assembling a diverse team.
- 👥 The ideal sprint team includes representatives from various functions and levels within the organization, and may also include external stakeholders.
- 📈 The Understand phase involves creating shared knowledge about the business problem and defining success metrics.
- ✏️ Sketch Day is an individual effort where team members brainstorm and sketch solutions on paper.
- 🗳️ Decide Day is about selecting the best ideas for prototyping, considering potential conflicts with objectives and abilities.
- 🛠️ Prototype Day involves creating a prototype that users can test, using familiar tools and involving the whole team.
- 📊 On the final day, the idea is validated through user testing, expert reviews, and team observations to decide if the design needs iterating or if it's ready for implementation.
- 🏆 The outcomes of a sprint can range from efficient failure (learning from mistakes), flawed success (partial wins), to an epic win (successful design).
Q & A
What is a design sprint?
-A design sprint is a method developed by Google Ventures to quickly gain insights into critical business questions through rapid design, prototype development, and user testing, all within a short timeframe of five days.
How long does a design sprint take?
-A design sprint is a five-phase process where each phase takes approximately one day or eight hours, allowing a sprint to be completed in five days.
What are the five phases of Google's design sprint?
-The five phases of Google's design sprint are Understand, Sketch, Decide, Prototype, and Validate.
What is the purpose of the Understand phase?
-The Understand phase aims to create shared knowledge about the business problem by bringing everyone together and unpacking all the team's knowledge about the problem.
What is a lightning talk and how does it fit into the Understand phase?
-A lightning talk is a short presentation, typically 10–15 minutes, where knowledge experts share their insights about the problem. It is an important part of the Understand phase to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Why is it important to involve the whole team during the Understand phase?
-Involving the whole team ensures everyone is on the same page and their insights are considered, preventing any individual or group from dominating the proceedings.
What is the main goal of Sketch Day?
-The main goal of Sketch Day is to generate as many detailed solutions to the problem as possible, allowing everyone to contribute ideas through sketching.
What is Decide Day and what happens during this phase?
-Decide Day is about making a decision on which idea to take to the Prototype phase. It also involves identifying conflicts with objectives and abilities, and creating storyboards for the chosen ideas.
How should a team approach Prototype Day?
-On Prototype Day, the team has one day to create a prototype that users can test. They should use familiar tools for rapid prototyping and leverage the whole team's skills.
What is the focus of the Validate phase?
-The Validate phase focuses on testing the prototype with end-users and observing their interactions. It also involves summarizing learnings and deciding if further iterations are needed.
What are the possible outcomes of a design sprint?
-The possible outcomes of a design sprint are an efficient failure, a flawed success, or an epic win. Each outcome provides valuable insights for the team to learn from or build upon.
How does a design sprint help in the design process?
-A design sprint helps by making the design process lean and efficient, allowing teams to ideate and test ideas incredibly fast, which can add significant business value.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)