Praktikum Korosi Pada Besi (Paku)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Dimas Reza Pradana, a student from UIN Raden Intan Lampung, conducts a simple chemistry experiment to demonstrate corrosion in iron. He immerses nails in five different liquids: soap water, boiled water, raw water, cooking oil, and saltwater. The experiment shows that nails in boiled and raw water corrode the most, while those in cooking oil remain unaffected due to the oil's isolating properties. The nails in saltwater and soap water show minimal corrosion. The video concludes that water exposure significantly accelerates iron corrosion, with cooking oil providing the best protection.
Takeaways
- 👋 The speaker introduces themselves as Dimas Reza Pradana, a student from UIN Raden Intan Lampung, conducting a simple chemistry experiment on iron corrosion.
- 🧪 Corrosion is defined as the damage or degradation of metals due to redox reactions between a metal and substances in its environment, producing unwanted compounds.
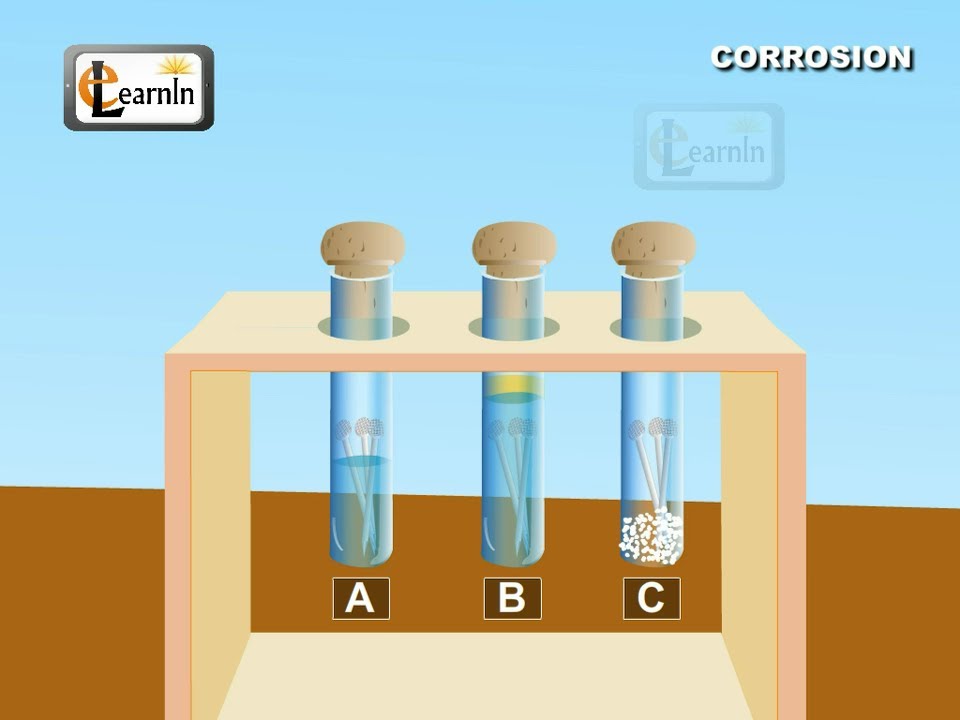
- 🔧 The experiment involves placing iron nails into five different solutions: soapy water, boiled water, raw water, cooking oil, and saltwater.
- 🧴 Each container with nails is tightly sealed with plastic and secured with a rubber band to prevent outside air from influencing the results.
- ⏳ After waiting for three days, the results of the experiment are observed.
- 🔍 Nails placed in raw water and boiled water show significant corrosion, demonstrating how iron reacts with water to cause rust.
- 🛢️ Nails placed in cooking oil do not corrode because the oil prevents water from reaching the iron, acting as a barrier.
- 🧂 The nail in saltwater shows minor corrosion due to the presence of sodium chloride, which inhibits the growth of bacteria like Gallionella that promote corrosion.
- 🧼 The nail in soapy water shows slight corrosion because soapy water is basic, not acidic, which slows down the corrosion process.
- 📊 The experiment concludes that nails in boiled and raw water experience the most corrosion, while those in oil experience the least.
Q & A
What is the main experiment discussed in the video?
-The main experiment is about observing corrosion on nails (iron) placed in different liquids, including soap water, boiled water, raw water, cooking oil, and saltwater.
What is corrosion, according to the script?
-Corrosion is the damage or degradation of metal due to a redox reaction between the metal and various substances in its environment, resulting in unwanted compounds.
What materials were used in the corrosion experiment?
-The materials used include nails (iron), soap water, boiled water, raw water, cooking oil, saltwater, plastic wrap, rubber bands, and glass containers.
Why are the glasses sealed with plastic and rubber bands during the experiment?
-The glasses are sealed with plastic and rubber bands to prevent exposure to air and external contaminants, ensuring that the experiment is controlled and focuses on the liquids inside.
Which liquid caused the most corrosion on the nails, and why?
-The nails placed in raw water and boiled water experienced the most corrosion because iron reacts with water, leading to corrosion over time.
Why didn’t the nail placed in cooking oil experience corrosion?
-The nail in cooking oil did not experience corrosion because oil acts as an isolator, preventing water from coming into contact with the nail and triggering the corrosion process.
What was the result of the nail placed in saltwater?
-The nail placed in saltwater experienced some corrosion, though less than in regular water. This is because the sodium chloride (salt) in the water can slow down bacterial activity that typically promotes corrosion.
Why did the nail in soap water only experience slight corrosion?
-The nail in soap water experienced slight corrosion because soap water is alkaline (basic) rather than acidic, which slows down the corrosion process.
What can be concluded from this experiment regarding the effect of different liquids on corrosion?
-The experiment concludes that nails in boiled water and raw water corrode the most, while nails in cooking oil do not corrode at all. Saltwater and soap water result in only slight corrosion.
Why is corrosion more severe in water compared to other liquids?
-Corrosion is more severe in water because the iron in the nail reacts with oxygen and moisture, leading to rust formation, which is less likely to happen in liquids like oil that isolate the nail from water.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)