FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SFTP, TFTP Explained.
Summary
TLDRThis video explains three file transfer protocols: FTP, SFTP, and TFTP. FTP is a standard protocol for transferring files over the internet but lacks security. SFTP, or Secure File Transfer Protocol, encrypts data during transfer, ensuring security. TFTP, or Trivial File Transfer Protocol, is a simple protocol used for transferring files within a local network without security features. The video also discusses how to use FTP with a browser or an FTP client like FileZilla.
Takeaways
- 🌐 FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a standard protocol for transferring files between computers and servers over a network like the internet.
- 💻 Users can upload files to an FTP server and others can download them from anywhere, or configure their own computer as an FTP server.
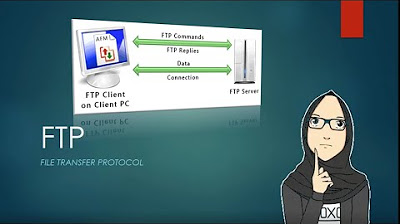
- 🔗 FTP can be accessed using a web browser by typing 'ftp://' followed by the server address, or through an FTP client like FileZilla for a more user-friendly experience.
- 📁 FTP clients provide a graphical interface to view and manage files on both local and remote servers, allowing easy file transfers with drag-and-drop functionality.
- 🔐 FTP is not secure as data is transferred in plaintext, making it unsuitable for sensitive data and best used on trusted networks.
- 🔒 SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) is a secure version of FTP that encrypts data during transfer, ensuring a safer file exchange.
- 🔑 SFTP uses secure shell for data encryption and port 22 for connections, providing authentication for both user and server.
- 📡 Both FTP and SFTP are connection-oriented protocols that use TCP, ensuring reliable file delivery.
- 📦 TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a simple protocol used for transferring files within a local area network, such as configuration files or firmware images.
- 🚫 Unlike FTP and SFTP, TFTP is connectionless and uses UDP, making it unreliable and insecure, suitable only for local network transfers where security is less of a concern.
Q & A
What does FTP stand for?
-FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol, which is a standard protocol used to transfer files between computers and servers over a network like the internet.
How can someone make their files available for others to download using FTP?
-To make files available for others to download via FTP, one would upload their files to an FTP server, allowing others to connect to that server and download the files.
Can a person set up their own computer as an FTP server?
-Yes, a person can configure their own computer to act as an FTP server, for example, using the Internet Information Services Manager in Microsoft Windows.
What are the different ways to transfer files using FTP?
-Files can be transferred using FTP through a standard internet browser or an FTP client like FileZilla.
How does one connect to an FTP server using a web browser?
-To connect to an FTP server using a browser, one would type the FTP server address into the URL bar, prefixed with 'ftp://' instead of 'http://'.
What is the role of authentication in accessing an FTP server?
-FTP servers may require a username and password for account authentication, or they may allow anonymous login, depending on the server's setup.
What benefits does using an FTP client like FileZilla offer over a web browser?
-Using an FTP client provides a graphical user interface and a better overall experience, allowing for easier file management and transfer.
How does SFTP differ from FTP in terms of security?
-SFTP, or Secure File Transfer Protocol, adds a layer of security by encrypting data during transfer using secure shell, unlike FTP which sends data in clear text.
What is the main drawback of using FTP?
-The main drawback of FTP is that it is not a secure protocol; data is sent in clear text, which can lead to security concerns.
What is TFTP and how is it typically used?
-TFTP, or Trivial File Transfer Protocol, is a simple protocol mainly used for transferring files within a local area network, such as configuration files and firmware images to devices like routers.
How does TFTP differ from FTP and SFTP in terms of reliability and security?
-TFTP is a connectionless protocol that uses UDP instead of TCP, making it unreliable and insecure, which is acceptable since it's only used on local networks and not over the internet.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Memahami Protokol Transfer File. FTP, SFTP dan TFTP.

4.3 File Transfer Enumeration

Common Ports - CompTIA Network+ N10-009 - 1.4

[HINDI] Networking Basics | Part #54 | Application Layer | File Transfer Protocol (FTP)

SSH vs SFTP Which is BETTER for Data Transfers?
FTP SERVER | PENJELASAN PENGERTIAN DAN FUNGSI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)