Cycles of Matter
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how matter and nutrients are recycled in ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of nutrient cycles such as the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. The discussion highlights how living organisms, along with geological processes, participate in these cycles. Examples include water evaporation, condensation, and the nitrogen fixation process. It also touches on the potential disruptions caused by human activities, like excess nutrients leading to algal blooms that can damage aquatic ecosystems by depleting oxygen and killing fish. The video underscores the delicate balance required for ecosystem health.
Takeaways
- 🌞 Matter is recycled in ecosystems, unlike energy which flows and exits as heat.
- ♻️ Elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus move between living organisms and non-living reservoirs called 'sinks'.
- 🏞️ Geologic processes can expose long-term sinks, such as carbon in coal or nitrogen in the air.
- 💧 Water cycles globally through processes like evaporation, transpiration, condensation, and precipitation, powered by the sun.
- 🌿 Nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus are essential for life, and are cycled through ecosystems via food chains and biochemical processes.
- 🍃 The carbon cycle involves photosynthesis and respiration, where plants absorb carbon dioxide to create sugars and animals release it back into the atmosphere.
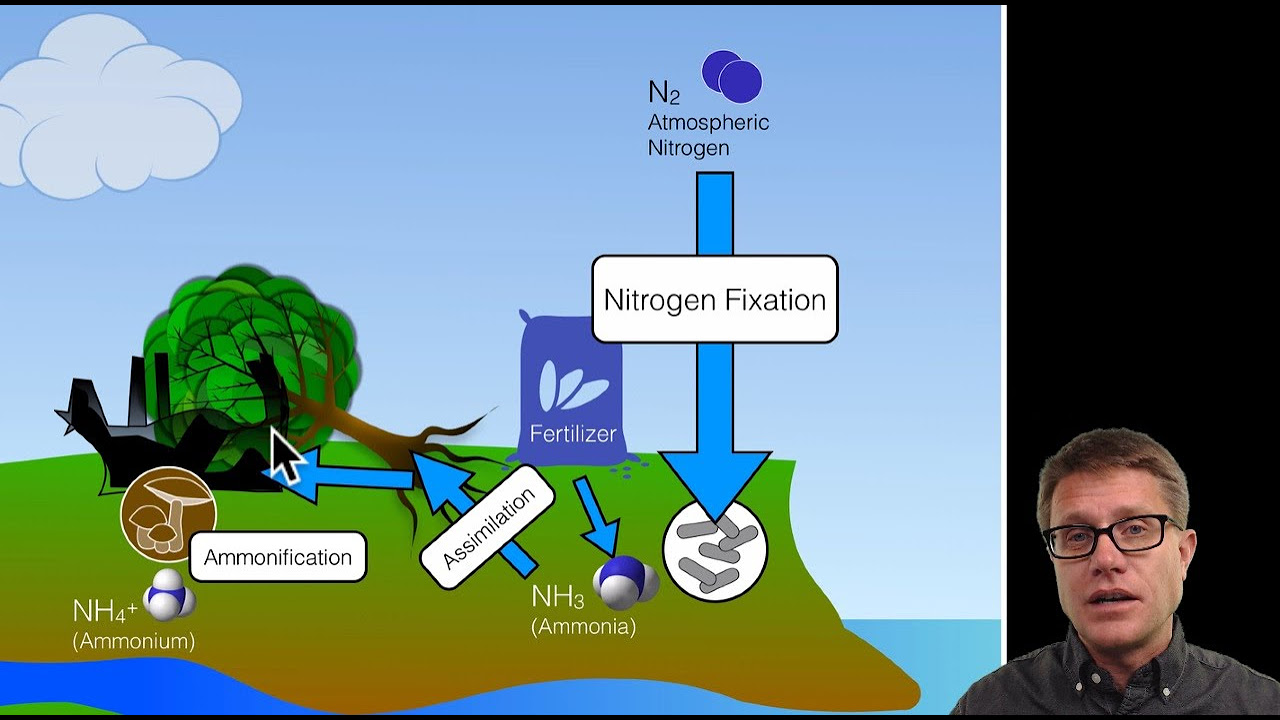
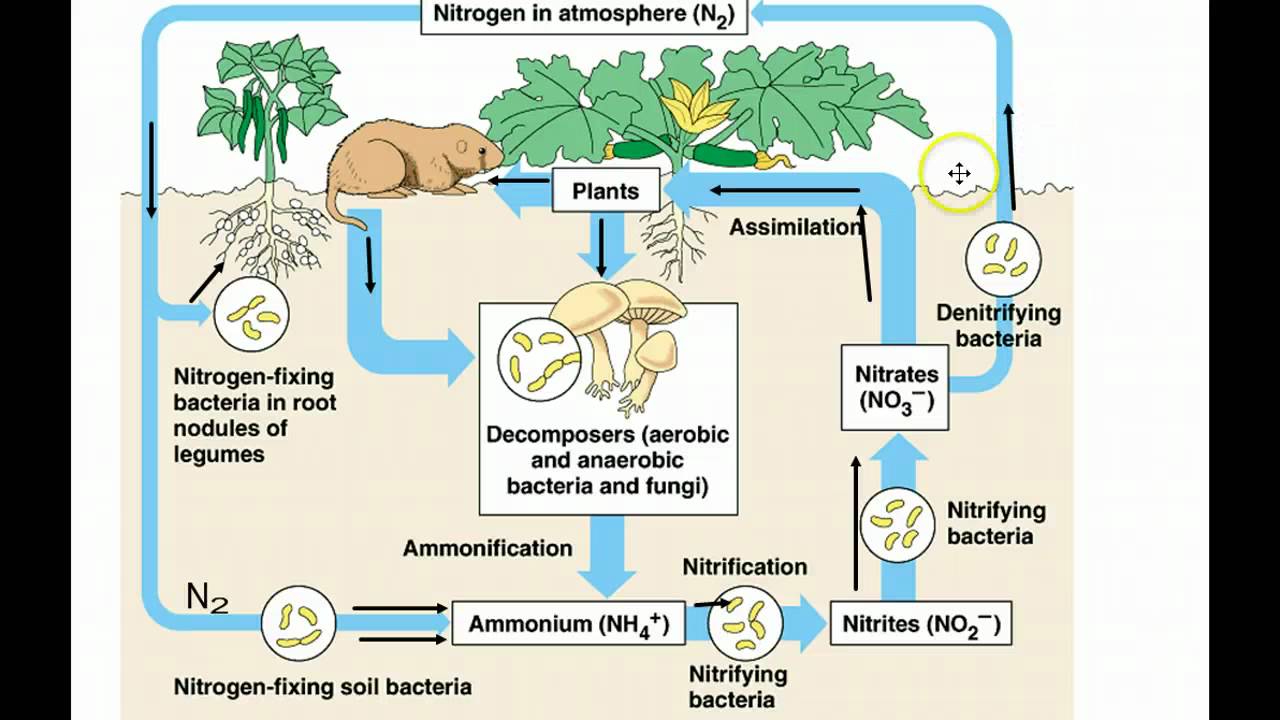
- 🐟 Nitrogen is cycled between air, soil, plants, and animals, with bacteria playing a crucial role in nitrogen fixation and denitrification.
- 🪨 The phosphorus cycle relies on the weathering of rocks and sedimentation, making it more local compared to the global water and carbon cycles.
- 🌊 Excess nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorus, can disrupt ecosystems, causing phenomena like algal blooms, which reduce oxygen levels and kill aquatic life.
- ⚖️ Nutrient limitations control primary productivity in ecosystems, keeping everything in balance, though human activity can cause nutrient imbalances.
Q & A
What is the main difference between how energy and matter are handled in ecosystems?
-Energy flows through ecosystems and is eventually lost as heat, while matter is recycled through different forms in ecosystems.
What are 'sinks' in the context of matter cycles, and can you give an example?
-Sinks are areas where matter is stored for long periods of time. An example is coal, which acts as a sink for carbon by trapping carbon dioxide underground for millions of years.
What are the four important cycles mentioned in the video?
-The four important cycles are the water cycle, carbon-oxygen cycle, nitrogen cycle, and phosphorus cycle.
How does water move through the ecosystem, and what are the key processes involved?
-Water moves through the ecosystem via evaporation (water turning into gas), transpiration (plants releasing water vapor), condensation (gas turning back into liquid), precipitation (rain, snow, etc.), and percolation (water seeping into the soil).
Why is nitrogen important for living organisms, and how do they acquire it?
-Nitrogen is essential for building proteins, especially in muscles. Organisms acquire nitrogen from plants, which absorb nitrogen through nitrogen fixation, a process carried out by bacteria in the soil.
What role do bacteria play in the nitrogen cycle?
-Bacteria help in nitrogen fixation by converting nitrogen gas from the air into forms that plants can use. They also perform denitrification, where they convert nitrogen compounds back into nitrogen gas.
What is the significance of phosphorus in living organisms?
-Phosphorus is vital for many functions, especially for forming DNA, which stores genetic information and passes it from one generation to the next.
What causes an algal bloom, and why is it harmful to aquatic ecosystems?
-An algal bloom is caused by excessive amounts of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus in the water, leading to rapid algae growth. It blocks sunlight, killing underwater plants, and when algae die, their decomposition consumes oxygen, leading to fish deaths.
How do nutrient limitations control primary productivity in ecosystems?
-Nutrient limitations determine how much energy is available at the base of the food chain. If key nutrients are limited, the overall productivity of the ecosystem is reduced.
What is the process of sedimentation in the phosphorus cycle?
-Sedimentation occurs when phosphorus accumulates at the bottom of lakes and streams, eventually compacting into rock. Over time, the rock weathers and releases phosphorus back into the ecosystem.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)