Genetics Basics: Difference between Codominance and Incomplete Dominance
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the concepts of incomplete dominance and codominance in genetics are explained. Incomplete dominance results in a blend of traits, exemplified by the pink snapdragon flower, a mix of white and red. Codominance, however, allows both traits to be expressed together, as seen in spotted cows and speckled chickens. The video uses simple analogies and real-life examples to differentiate between these genetic phenomena, making complex science accessible.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Genetics is the study of heredity and how traits are passed from parents to offspring.
- 👨🔬 Gregor Mendel is known as the father of genetics and conducted experiments with pea plants.
- 🌿 In Mendel's pea plant experiments, traits were either dominant or recessive, with the recessive trait being masked by the dominant one.
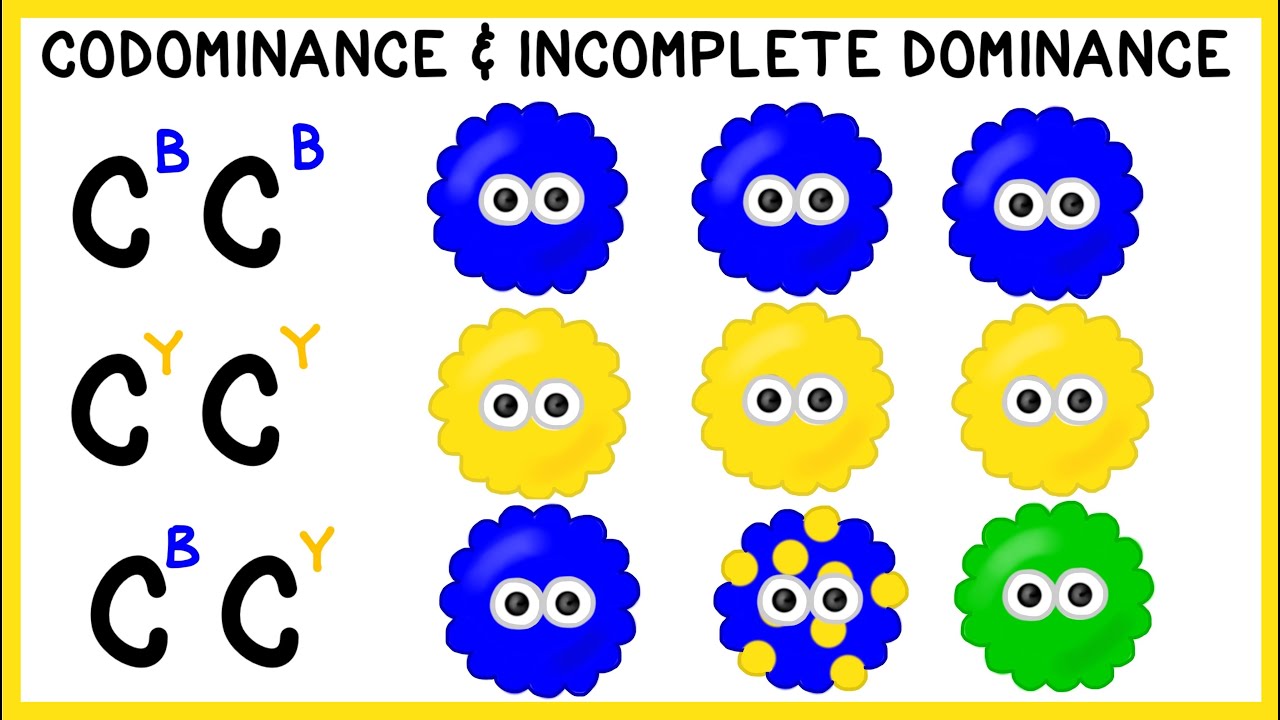
- 🎨 Incomplete dominance occurs when offspring display a phenotype that is a blend of the two parent phenotypes.
- 🖼️ An example of incomplete dominance is the snapdragon flower, which can display a pink color when crossed between white and red parents.
- 🐾 Another example of incomplete dominance is a pin that shows a mix of grey and blue when black and white parents are crossed.
- 🤝 Codominance is a genetic phenomenon where both alleles are expressed in the phenotype.
- 🐄 A common example of codominance is the spotted cow, which displays both white and brown patches from its parents.
- 🐔 A speckled chicken is another example of codominance, where both black and white feathers appear together.
- 🌸 The 4 o'clock plant is an example where both alleles are expressed, showing both parent traits in the offspring.
- 📈 The video aims to educate viewers on the differences between incomplete dominance (blending of traits) and codominance (cooperation of traits).
Q & A
Who is considered the father of genetics?
-Gregor Mendel is considered the father of genetics.
What did Gregor Mendel study in his experiments?
-Gregor Mendel studied pea plants and their offspring's traits.
What is the difference between complete dominance and incomplete dominance?
-In complete dominance, one trait masks the other, while in incomplete dominance, a blending of traits occurs, resulting in a third phenotype that is in between the two parental traits.
What is an example of incomplete dominance mentioned in the script?
-An example of incomplete dominance is the color of a snapdragon flower, which can be a mix between a white and red flower, resulting in a pink color.
What is codominance in genetics?
-Codominance is a genetic phenomenon where both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, and both traits appear together in the offspring.
How does the coloration of a speckled chicken illustrate codominance?
-A speckled chicken is an example of codominance because both the black and white alleles are expressed, resulting in a pattern where both colors appear together.
What is the significance of the term 'co' in codominance?
-The term 'co' in codominance signifies 'together', as in both traits work together and are expressed simultaneously in the phenotype.
What is another example of codominance provided in the script?
-Another example of codominance is the 4 o'clock plant, where both alleles are expressed, and both traits appear together.
How does the blending of traits in incomplete dominance relate to mixing colors?
-The blending of traits in incomplete dominance is likened to mixing colors, where combining two colors results in an intermediate color, such as mixing red and white paint to get pink.
What is the outcome when a white and black parent pin is crossed, according to the script?
-When a white and black parent pin is crossed, the offspring exhibits an in-between color, which is a mix of grey and blue.
What is the recommendation for viewers at the end of the script?
-The script encourages viewers to subscribe to moomoomath and share their videos, as they upload a new math and science video every day.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Dominância incompleta e Co-Dominância - Aula 05 - Módulo 2: Genética

Ethiopian Grade 11 Biology 4#8 Non Mendelian Inheritance

110 Extensions to Mendel

Types of dominance - Genetics and Inheritance

Intro to Genetics: Why Your Cat Looks Like That: Crash Course Biology #31
Codominance and Incomplete Dominance: Non-Mendelian Genetics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)