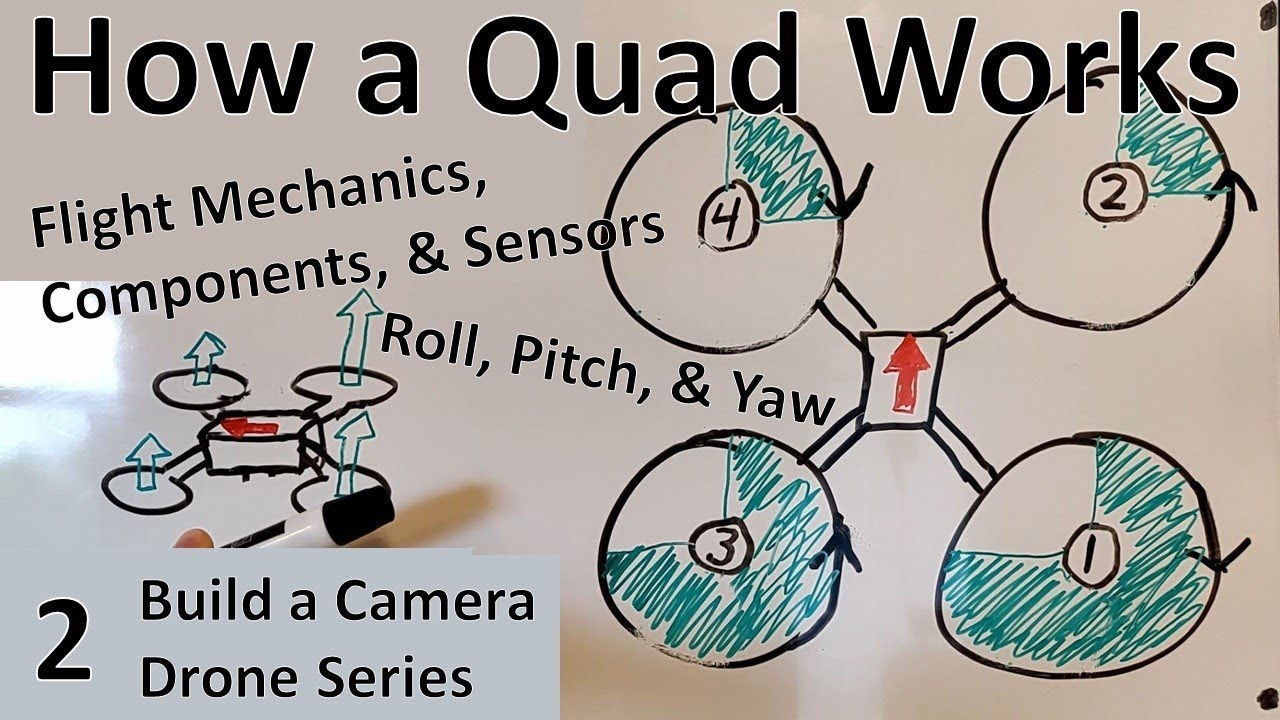
Building a sub 250g Autonomous Drone with Ardupilot and ExpressLRS AirPort Telemetry
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the creator introduces their DIY autonomous drone project, showcasing a lightweight quadcopter weighing under 250g. The video highlights the build process, including choosing cost-effective parts like the Speb F405 mini stack and Darvin FPV motors, and crafting a custom frame. It also covers installation of ArduPilot software, configuration of components like GPS and ExpressLRS, and various flight modes. The drone won first place at a major Polish competition, and viewers are shown how to build their own entry-level ArduPilot drone step by step.
Takeaways
- ?Üdd The video showcases a DIY autonomous drone project that won first place in a major drone competition in Poland.
- ?Üd2 The drone is lightweight, weighing less than 250g, and utilizes Ardupilot software for autonomous flight.
- ?Üd5 The project features a custom frame made from carbon fiber for stiffness and durability, sponsored by PCBWay.
- 💵 The drone is equipped with advanced telemetry over Express LRS, enhancing its autonomous capabilities.
- 💲 The frame design process involved multiple iterations to achieve the right balance of lightness and strength.
- 💵 The build includes affordable components like Darvin FPV motors and is designed to be an accessible entry-level project.
- 💵 The video provides a step-by-step guide on assembling the drone, including motor installation and wiring.
- 💲 The flight controller is programmed with ArduPilot, and the video demonstrates how to flash the firmware correctly.
- 💵 The drone's maiden flight tests various modes like Stabilize, Alt Hold, and Loiter, showing good initial performance.
- 💲 The video introduces an innovative use of Express LRS for bidirectional telemetry, overcoming the limitations of traditional radio control.
- 💵 Additional features like geofencing, RTL, and autonomous mission planning are demonstrated to highlight the drone's capabilities.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the DIY drone project mentioned in the video?
-The DIY drone project aims to build an autonomous drone that weighs less than 250g, runs on Ardupilot software, and uses ExpressLRS for telemetry, making it an affordable and lightweight quadcopter for beginners.
What are some of the key hardware components used in the drone build?
-The key hardware components include the SpeedyBee F405 Mini Stack, Darvin FPV motors, a GPS unit, ExpressLRS receivers, and a custom carbon fiber frame.
Why did the creator use carbon fiber for the drone frame, and how was it manufactured?
-Carbon fiber was chosen for its superior strength and stiffness compared to plastic. The creator used a company called PCBWay to manufacture the frame through CNC machining, resulting in a flawless, lightweight, and durable part.
What was the issue with the screws that came with the Darvin FPV motors, and how was it resolved?
-The screws that came with the Darvin FPV motors were too short and thin for the custom carbon fiber frame. The creator solved this by pre-drilling the mounting holes and threading them for M2 screws.
How does the creator configure and install the Ardupilot software on the drone?
-The creator configures and installs Ardupilot by flashing the firmware onto the flight controller using the STM32 Cube Programmer. Before doing this, the creator ensures the motors spin correctly using BLHeli software.
What is ExpressLRS, and how does it enhance the drone’s performance?
-ExpressLRS is a low-latency radio control system that provides telemetry over a long range. In this project, it enables wireless USB-like connection to Mission Planner, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments during flight.
What is the significance of the drone weighing less than 250 grams?
-Weighing under 250 grams is important because it allows the drone to comply with regulations in many countries, enabling the user to fly it in most locations without requiring special permits or licenses.
How did the creator integrate a geofence into the drone's mission, and what happens if the drone crosses it?
-The creator set up a geofence to restrict the drone's movement within a designated area. If the drone crosses the geofence in Loiter mode, it will stop; in AltHold mode, it will trigger an automatic Return to Launch (RTL) function.
What is the ‘throw mode,’ and how was it used during the flight test?
-Throw mode allows the drone to be launched by physically throwing it into the air, after which it automatically transitions into its pre-programmed flight mode. The creator demonstrated this by throwing the drone to start its mission.
What are some of the flight modes demonstrated in the video, and how do they function?
-The flight modes demonstrated include Stabilize, AltHold (maintains altitude), Loiter (hovers in place using GPS), Circle (orbits around a point), and Guided (autonomously flies to a point selected on a map). These modes showcase the drone's versatility.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)