Fermentation
Summary
TLDRThe video script explores the importance of oxygen in cellular respiration and how organisms adapt to its absence. It explains the process of ATP production, the misconception about plants needing oxygen, and the shift to fermentation in anaerobic conditions. Examples include alcoholic fermentation by yeast and lactic acid fermentation in muscle cells, emphasizing the limited ATP yield compared to aerobic respiration.
Takeaways
- 🏊 Swimming was the speaker's favorite childhood activity, and they had a childhood misconception about fish not needing oxygen.
- 🐟 Most fish use gills to extract oxygen from water, debunking the speaker's early belief that fish don't need oxygen.
- 🌿 Oxygen is essential for a variety of organisms, including humans, fish, and plants, which counteracts the common misconception about plants not needing oxygen.
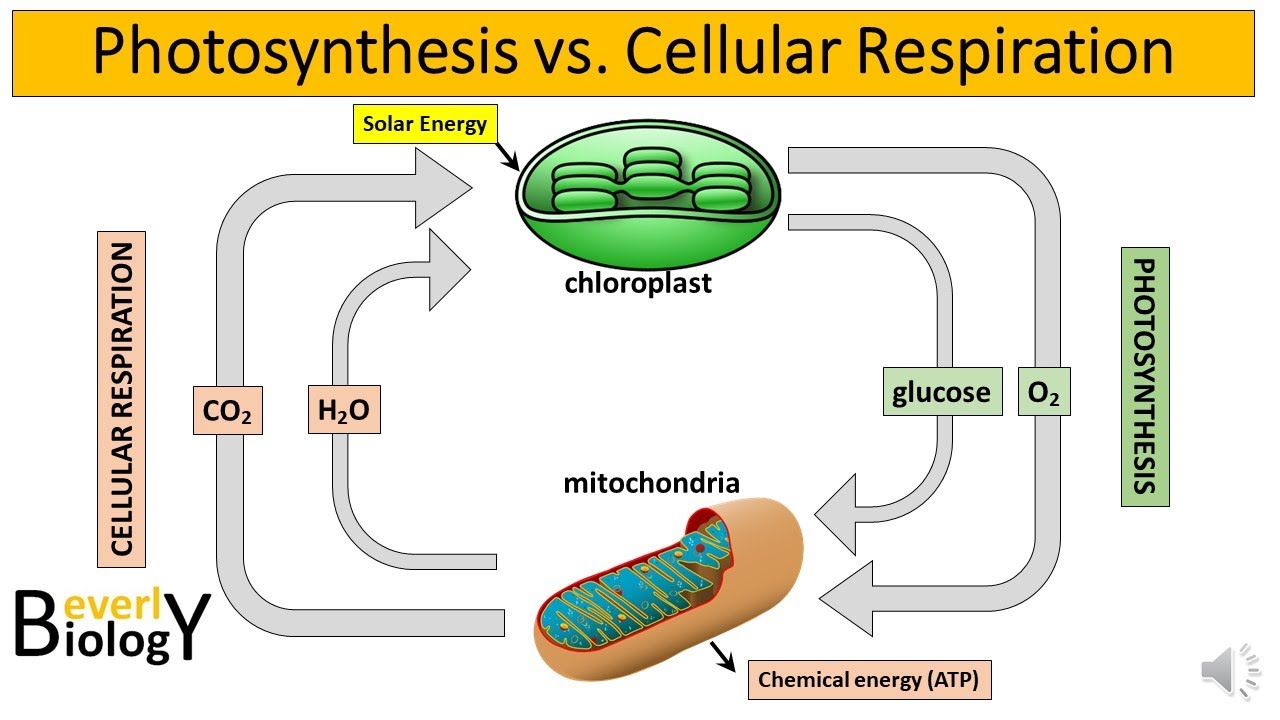
- 🔬 Cells require oxygen for cellular respiration, a process that uses oxygen to break down glucose and produce ATP, the energy currency of cells.
- 🔋 ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule with high energy potential, crucial for powering many cellular functions.
- ♻️ During cellular respiration, ATP can be converted to ADP and back again, with the help of enzymes, to sustain cellular energy needs.
- 🌀 When oxygen is absent, certain cells and organisms, like some bacteria, archaea, yeast, and muscle cells, can resort to anaerobic respiration or fermentation to produce ATP.
- 🍺 Fermentation is an anaerobic process that allows glycolysis to continue by regenerating NAD+, with different products like ethanol in alcoholic fermentation and lactate in lactic acid fermentation.
- 🍞 Yeast performs alcoholic fermentation to make bread rise, utilizing the carbon dioxide produced and generating a small amount of alcohol that evaporates during baking.
- 🏋️♀️ Lactic acid fermentation occurs in muscle cells under oxygen debt, such as during intense exercise, and may not be the direct cause of post-exercise muscle soreness as previously thought.
Q & A
What was the speaker's childhood fascination with swimming?
-The speaker loved swimming and was on the swim team starting at the age of four. They dreamed of being like a fish and even had a misconception that fish didn't need oxygen.
How do most fish obtain the oxygen they need?
-Most fish have gills that allow them to extract the oxygen they need from the water.
What is the role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
-Oxygen is a reactant in cellular respiration, needed to break down glucose to form ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which powers many cellular processes.
Why do plants, which produce oxygen through photosynthesis, still need oxygen?
-Although plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis, they also need oxygen for cellular respiration, as they perform respiration and thus require oxygen for their own cells.
What happens to ATP after it loses a phosphate?
-When ATP loses a phosphate, it becomes ADP (adenosine diphosphate), which has two phosphates.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration?
-Aerobic cellular respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen, and organisms like some bacteria and archaea can perform it using alternative electron acceptors.
How do muscle cells handle a lack of oxygen during intense exercise?
-Muscle cells can shift to lactic acid fermentation when oxygen is scarce, such as during intense exercise, allowing them to continue producing ATP through glycolysis.
What is fermentation and why is it important for organisms in low oxygen conditions?
-Fermentation is a process that allows glycolysis to continue and produce ATP in the absence of oxygen. It is important for organisms as it provides a way to generate energy when oxygen is limited.
How does alcoholic fermentation differ from lactic acid fermentation?
-In alcoholic fermentation, pyruvate is converted into acetaldehyde, which then produces carbon dioxide and ethanol. In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is converted directly into lactate, which can contribute to muscle soreness.
What is the role of NAD+ and NADH in glycolysis and fermentation?
-NAD+ is an oxidizing agent that is reduced to NADH when it gains electrons during glycolysis. In fermentation, NADH gives its electrons to an electron acceptor to be oxidized back into NAD+, which is necessary for glycolysis to continue.
How does the process of fermentation relate to the production of bread and yogurt?
-Fermentation is used by yeast in bread making to produce carbon dioxide, which helps the bread rise, and by bacteria in yogurt production, where lactic acid contributes to its sour taste.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)