The Electrical Grid and Electricity Supply | A Simple Explanation
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how power grids work, detailing the main components involved in transferring electricity from power stations to homes. It covers the three key stages: generation, transmission, and distribution, and explains the importance of transformers in reducing power losses by increasing voltage and decreasing current. Viewers will learn how transformers, substations, and transmission towers function to efficiently deliver electricity over long distances, and how different voltages are used for various consumers. By the end, you'll understand the workings of power grids and how everyday electrical infrastructure operates.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Power grids consist of three main sections: generation, transmission, and distribution, with consumers at the end of the grid.
- 🔧 Power generation doesn't create power but converts energy from other sources (e.g., coal, hydro, wind) into electrical power.
- 🌡️ Power loss occurs due to the resistance in conductors, generating heat, and is mitigated by increasing voltage, which reduces current.
- 🔋 Transformers are critical to increase or decrease voltage, helping reduce power losses and allowing efficient long-distance power transmission.
- 🔄 Transformers operate through electromagnetic induction, transferring power between coils without direct contact and only work with alternating current.
- 🏗️ Transmission towers carry high-voltage lines and are designed to keep conductors far from the ground and other objects to prevent electrical arcing.
- ⚙️ Substations manage voltage changes, protect the grid, and allow sections of the grid to be isolated during faults or surges.
- 🏠 Step-down transformers reduce voltage as electricity gets closer to consumers, ensuring appropriate voltage levels for different types of users (industrial, commercial, residential).
- 🛠️ Substations and transformers help maintain grid stability, protecting equipment and ensuring reliable power delivery across large distances.
- 📡 Power grids are complex systems that depend on multiple components working together to ensure safe and efficient delivery of electricity to homes and businesses.
Q & A
What are the main components of a power grid?
-The main components of a power grid are generation, transmission, and distribution. Additionally, end consumers are sometimes considered a separate component.
Why is it incorrect to say that power stations 'generate' electrical power?
-It is incorrect to say that power stations 'generate' electrical power because, according to the law of conservation of energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed. Power stations convert other forms of energy, such as chemical, kinetic, or potential energy, into electrical power.
What is the purpose of step-up transformers in the power grid?
-Step-up transformers are used to increase the voltage of electrical power after it is generated. This is done to reduce the current, which helps minimize power losses and allows for the use of thinner conductors during long-distance transmission.
How do transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction?
-Transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which states that a conductor with current flowing through it creates a magnetic field. When this magnetic field changes, it induces voltage in a nearby secondary coil, allowing current to be transferred without direct contact between the coils.
Why are high voltage levels used in power transmission?
-High voltage levels are used in power transmission to reduce the current, which in turn reduces power losses due to the heating effect in conductors. This allows for the use of smaller, more cost-effective conductors and minimizes energy loss over long distances.
What role do substations play in the power grid?
-Substations play a critical role in regulating voltage levels, protecting the grid, and managing the flow of electrical power. They house equipment like transformers, circuit breakers, and surge arresters to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the power grid.
Why is air used as an insulator for transmission lines?
-Air is used as an insulator for transmission lines because it provides sufficient insulation to prevent electrical arcing between the conductors and the ground. The high placement of transmission lines ensures a large air gap, enhancing the insulation effect and preventing short circuits.
What are the differences between step-up and step-down transformers?
-Step-up transformers increase the voltage and reduce the current, which is ideal for long-distance transmission. Step-down transformers, on the other hand, decrease the voltage and increase the current, making it suitable for safe delivery of electricity to consumers at usable voltage levels.
Why are transformers so crucial to daily life and power distribution?
-Transformers are crucial because they manage voltage levels throughout the power grid, ensuring efficient transmission and safe distribution of electricity. Without them, it would be impossible to deliver electrical power efficiently over long distances or safely to end consumers.
What would happen if we tried to deliver power directly from a power station to consumers without using transformers?
-If power were delivered directly from a power station to consumers without using transformers, the high current required would cause significant energy loss due to heating, potentially melting conductors. This would make it impractical and unsafe to distribute electricity efficiently.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How do coal-fired power stations work?
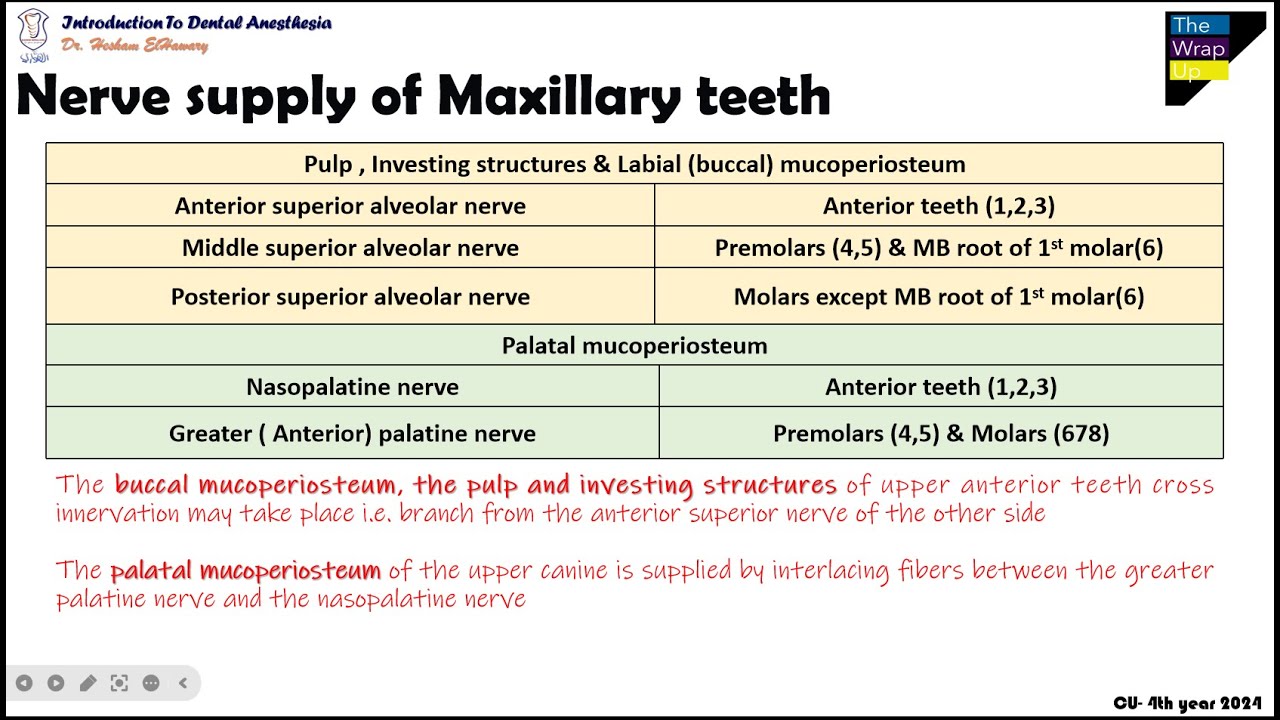
09 Summary Of Innervation Of Maxillary Teeth

PEMBANGKIT LISTRIK TENAGA AIR (PLTA) || SEJARAH, KOMPONEN DAN CARA KERJA

Guru Listrik Online : Sistem Pembangkitan, Transmisi dan Distribusi Listrik

Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya ( PLTS ) || Komponen dan Cara Kerjanya

How a Power Supply *ACTUALLY* works.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)