How Do Organisms Reproduce? Class 10 Full Chapter (Animation) | Class 10 Science Chapter 8 | NCERT
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the different modes of reproduction in organisms, including asexual and sexual reproduction. It covers asexual methods like binary fission, multiple fission, fragmentation, regeneration, budding, vegetative propagation, and spore formation with examples. It then describes sexual reproduction in flowering plants, including the structure and functions of reproductive organs, pollination, fertilization, and seed formation. The video also details the human male and female reproductive systems, the process of fertilization, puberty changes, reproductive health, and contraception methods, emphasizing the importance of understanding sexual maturity and health consequences.
Takeaways
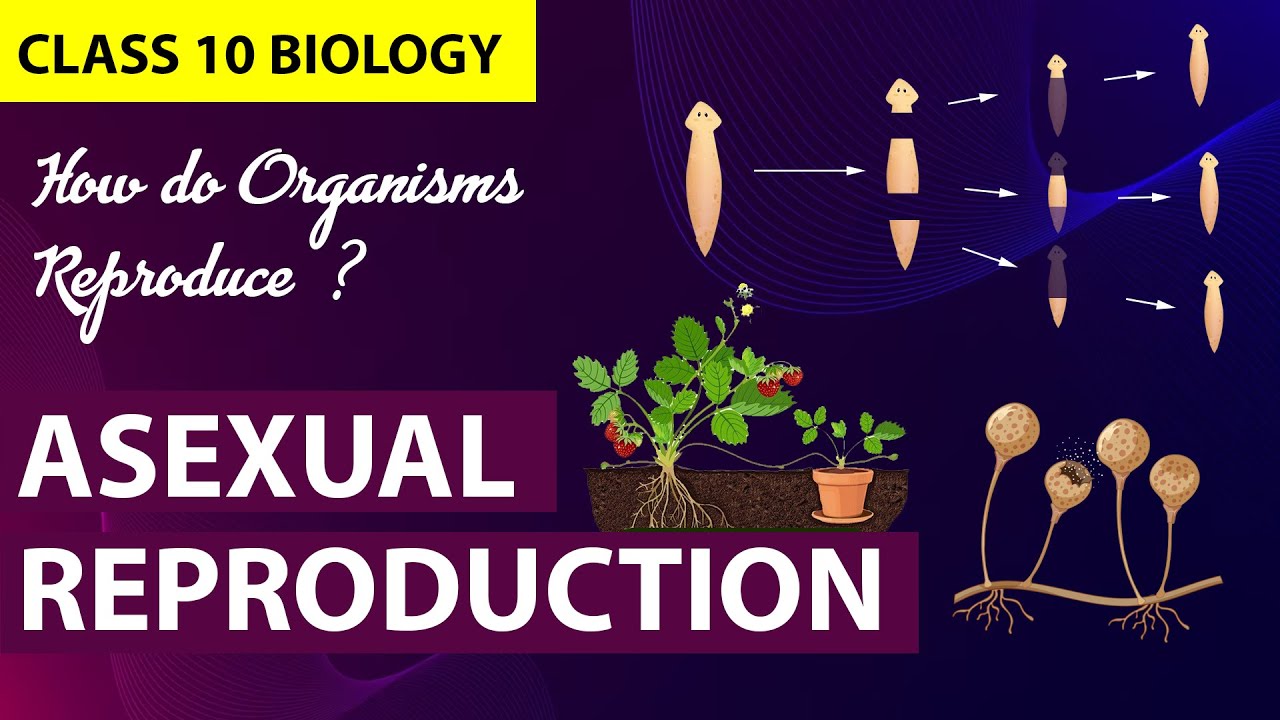
- 🔬 Asexual reproduction involves a single organism reproducing without pairing, with examples like binary fission, multiple fission, and budding.
- 🔄 Binary fission occurs when a single-celled organism like Amoeba splits into two; organisms like Leishmania split in a specific direction.
- 🧩 Fragmentation is when organisms like Spirogyra break into fragments, and each fragment grows into a new organism.
- 🌱 Vegetative propagation in plants occurs when parts like stem or root cuttings from plants such as roses or carrots can grow into new plants.
- 🌸 Sexual reproduction in plants involves male (stamen) and female (pistil) reproductive parts, with pollination helping transfer pollen between them.
- 🌾 Self-pollination happens within the same plant, while cross-pollination occurs between different plants, aiding fertilization and seed formation.
- ⚙️ The male human reproductive system includes the testes, scrotum, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and penis, with testosterone being a key hormone.
- 👶 The female reproductive system includes ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, and vagina, where fertilization and embryo development occur.
- 🔒 Contraceptive methods like condoms, oral pills, and devices like copper-T help prevent pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
- ⚖️ Medical termination of pregnancy (abortion) is legal only under specific circumstances and is prohibited if done by personal choice or sex selection.
Q & A
What is asexual reproduction, and how does it differ from sexual reproduction?
-Asexual reproduction is a process where a single organism reproduces without the involvement of another organism. This contrasts with sexual reproduction, which requires two organisms, typically one male and one female, to combine their genetic material.
What is binary fission, and can you provide an example?
-Binary fission is a mode of asexual reproduction where an organism splits into two. An example is amoeba, a single-celled organism that reproduces by splitting in any direction due to its lack of a specific shape.
What is multiple fission, and which organism uses this mode of reproduction?
-Multiple fission is when an organism splits into many parts. Plasmodium, a single-celled organism, reproduces through this process.
How does fragmentation work in asexual reproduction, and which organism uses it?
-Fragmentation is when an organism breaks into fragments, and each fragment grows into a new organism. Spirogyra, an alga, reproduces through this method.
What is budding, and how does Hydra reproduce using this method?
-Budding is a process where new individuals form as buds on the body of an organism. In Hydra, buds grow on the organism's body, separate, and develop into new individuals.
What is vegetative propagation in plants, and can you give examples?
-Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction in plants where new plants grow from parts like stems or roots. Examples include rose stems, sugarcane, and carrot roots.
How does pollination occur in flowering plants, and what are the two types?
-Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the stamen (male part) to the pistil (female part). Self-pollination happens within the same flower or plant, while cross-pollination occurs between different plants.
What is the role of the placenta during pregnancy?
-The placenta is a special tissue that provides the growing embryo with nutrients like glucose and oxygen from the mother's blood. It also helps remove waste generated by the embryo.
What are some changes that occur during puberty in both boys and girls?
-During puberty, both boys and girls experience hair growth in new areas (armpits, genital area), oily skin, and pimples. Boys may grow facial hair, experience voice cracking, and penile enlargement, while girls develop breasts and begin menstruating.
What are some contraceptive methods to prevent pregnancy?
-Contraceptive methods include mechanical barriers like condoms, chemical contraceptives like oral pills, contraceptive devices like copper IUDs, and surgical methods like vasectomy and tubectomy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Reprodução dos Seres vivos – Ciências – 8º ano – Ensino Fundamental

ELS- LESSON 2- REPRODUCTION
Class 10 reproduction | Asexual reproduction CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 | NCERT

Types of Reproduction: Sexual and Asexual | Grade 7 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 2 Module 5
EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE - Perpetuation of Life of the Representative Animals

Lecture - 5 Modes of Reproduction Crop Plants
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)