Saltwater Intrusion
Summary
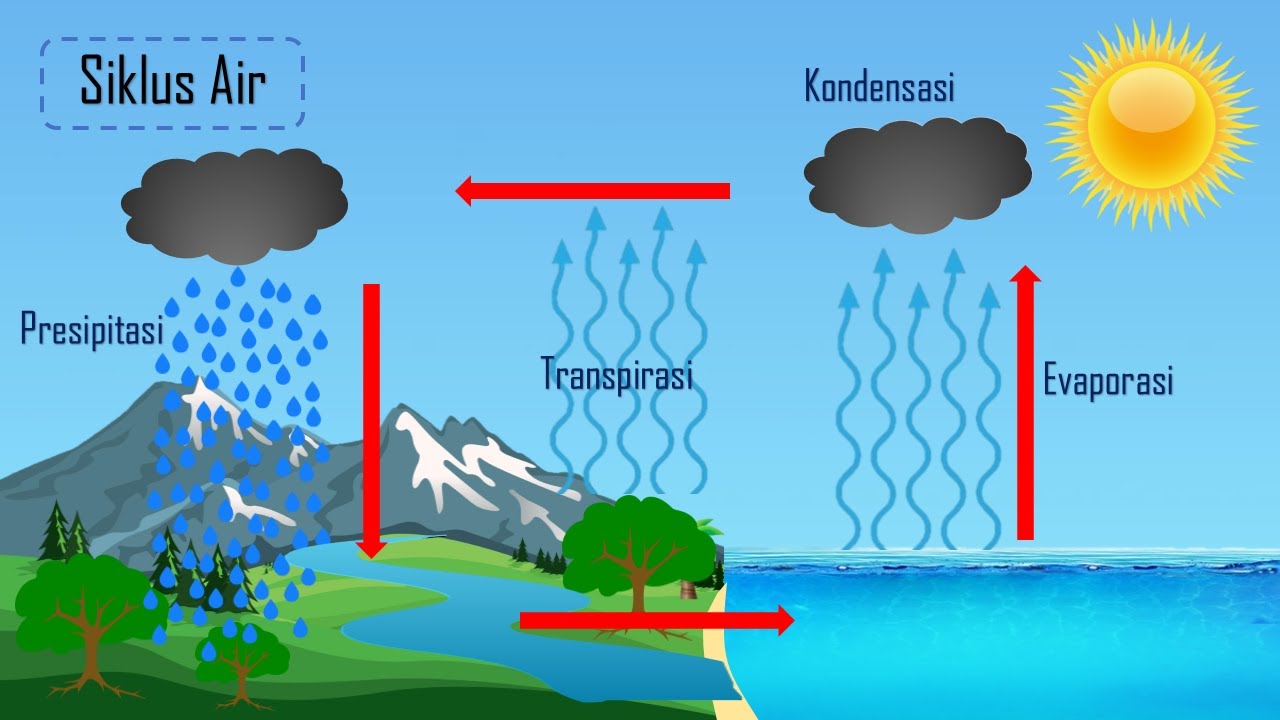
TLDRThe US Geological Survey defines saltwater intrusion as the encroachment of saltwater into freshwater aquifers due to excessive water pumping. This over-pumping depletes the underground water table faster than natural recharge rates, allowing seawater to infiltrate and mix with freshwater, creating a border of dispersion. Once contaminated, the aquifer suffers irreversible damage.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Saltwater intrusion is a phenomenon where saltwater encroaches on freshwater aquifers.
- 🔍 According to the US Geological Survey, this occurs due to excessive water pumping.
- 💧 Over-pumping leads to a decrease in the underground water table, causing freshwater levels to drop.
- 🌊 When freshwater is depleted faster than it can be naturally replenished, seawater intrusion occurs.
- 📉 The invading seawater mixes with the remaining freshwater, creating a zone of dispersion.
- 🚫 Once saltwater contaminates an aquifer, the damage is irreversible.
- ⚠️ The process of saltwater intrusion begins with the depletion of freshwater resources.
- 🌐 This issue is particularly relevant in coastal areas where the risk of seawater intrusion is higher.
- 💡 The script emphasizes the importance of managing water resources to prevent such contamination.
- 🔬 Understanding the dynamics of saltwater intrusion is crucial for water resource management and protection.
Q & A
What is saltwater intrusion?
-Saltwater intrusion occurs when saltwater encroaches on a freshwater aquifer, contaminating it.
What is the main cause of saltwater intrusion?
-The main cause of saltwater intrusion is excessive water pumping, which depletes freshwater levels faster than they can be replenished.
What happens when over-pumping reduces the underground water table?
-When over-pumping reduces the underground water table, the freshwater levels drop below the recharge rate, allowing saltwater to invade the aquifer.
What is the 'zone of dispersion' mentioned in the script?
-The 'zone of dispersion' is the area where freshwater and saltwater mix, forming a border between the two.
Can the damage caused by saltwater intrusion be reversed?
-No, once saltwater contaminates the freshwater aquifer, the damage is considered irreversible.
Why does saltwater intrusion become a problem when freshwater levels drop?
-Saltwater intrusion becomes a problem when freshwater levels drop because the pressure balance between saltwater and freshwater is disrupted, allowing saltwater to move inland.
How does over-pumping contribute to saltwater intrusion?
-Over-pumping drains freshwater from the aquifer faster than it can be naturally recharged, lowering the water table and creating an opportunity for saltwater to intrude.
What is an aquifer, as mentioned in the script?
-An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing rock or sediment that stores freshwater, which can be accessed through wells or natural springs.
Why is it important to maintain a balance between freshwater extraction and recharge rates?
-Maintaining a balance between freshwater extraction and recharge rates is crucial to prevent the depletion of the water table and avoid saltwater intrusion.
What long-term impact does saltwater intrusion have on freshwater resources?
-Saltwater intrusion irreversibly contaminates freshwater resources, making the water unusable for drinking and irrigation, and harming the ecosystem.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)