First Aid for a Child Choking
Summary
TLDRThis educational video from Nicklaus Children's Health System, led by Linda, instructs viewers on how to respond to a child choking. It differentiates between mild and severe choking, emphasizing the importance of quick action. Techniques demonstrated include the Heimlich maneuver for conscious children and CPR for unresponsive ones. The video also covers chest thrusts for larger children and provides a step-by-step guide for performing CPR with compressions, checking the airway, and rescue breaths, all crucial for saving a choking child's life.
Takeaways
- 🆘 Choking is a serious condition where an object blocks the airway, preventing air from reaching the lungs.
- 🔍 Mild choking allows the child to cough and make sounds, while severe choking completely blocks the airway, preventing breathing, coughing, or speaking.
- 🚨 In case of severe choking, immediate action is crucial as it can be life-threatening.
- 🤔 If you suspect a child is choking, ask them directly to confirm and reassure them that you will help.
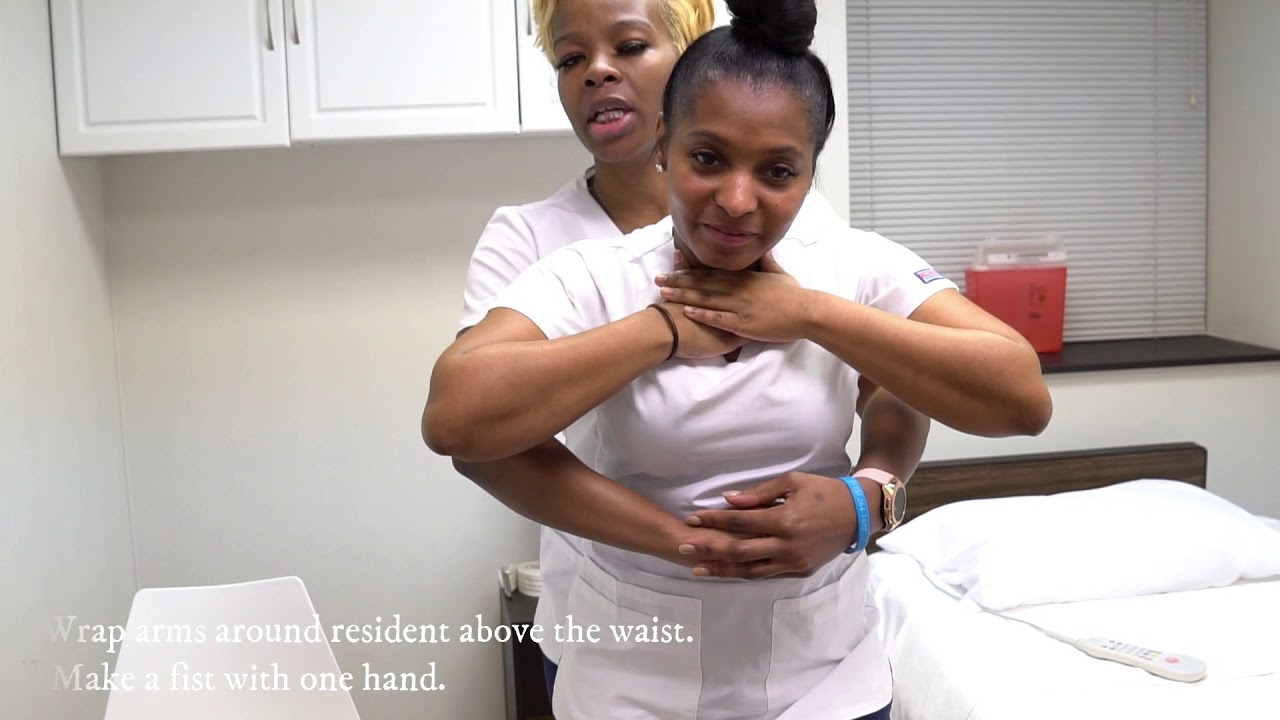
- 🤲 The Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrusts) is a first-aid technique used to dislodge an object causing choking by applying upward force under the ribcage.
- 👶 For larger children, chest thrusts may be used instead of abdominal thrusts, applying force to the lower half of the breastbone.
- 🆘 If the child becomes unresponsive, lay them on a hard surface and shout for help, then begin CPR.
- 📞 In an emergency, call 911 and use the speakerphone so you can be guided through CPR by emergency staff.
- 👌 CPR for children involves 30 chest compressions on the lower half of the breastbone, followed by checking the airway and attempting rescue breaths.
- 🔁 Repeat the cycle of compressions, airway checks, and rescue breaths until the child responds or emergency help arrives.
- 🙌 The video emphasizes the importance of quick response and correct technique in saving a choking child's life.
Q & A
What is the definition of choking as described in the video?
-Choking is defined as something such as food or an object getting stuck in the airway, preventing air from getting into the child's lungs.
How can you tell if a child is mildly choking?
-Mild choking is indicated when the child can cough and make sounds.
What should you do if you are worried about a child's breathing?
-If you are worried about a child's breathing, do not hesitate to call 9-1-1.
What are the signs of severe choking in a child?
-Severe choking signs include the child holding his neck with one or both hands and being unable to breathe, cough, or speak.
What is the first step to take if you suspect a child is choking?
-The first step is to ask the child, 'Are you choking?' and if they nod, assure them that you are going to help.
How do you perform the abdominal thrusts to help a choking child?
-Stand behind the child, reach your arms under their arms, place one fist just above the belly button, and grasp that fist with your other hand, then give quick upward thrusts.
What is the alternative method for a very large choking child?
-For a very large choking child, chest thrusts may be used instead of abdominal thrusts, placing hands on the lower half of the child's breastbone and pulling straight back.
What should you do if the choking child becomes unresponsive?
-Lay the child down on a hard surface, yell for help, and start CPR with five cycles before calling 911.
How many compressions are recommended in one cycle of CPR for a child?
-One cycle of CPR for a child involves 30 compressions.
What is the correct hand position for chest compressions during CPR on a child?
-The correct hand position is placing the heel of one hand on the lower half of the child's breastbone.
How do you check for a clear airway in an unresponsive child?
-After performing chest compressions, use the head-tilt chin-lift method to check for objects, pinch the child's nose, and attempt to breathe into their mouth.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How to perform first aid and CPR on a choking infant / baby?

Caring for a Responsive Choking Child or Infant

Saving Lives With Gus: Heimlich Maneuver

Kinder und Jugendliche - als Gestalter/innen ihrer Lebenswelten – Prof. Dr. Ulrich Deinet
Nurse Aid Skill: Abdominal Thrust on Conscious Resident

Conscious Adult Choking
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)