Movimiento Rectilíneo Uniformemente Acelerado o Variado MRUA MRUV | Ejemplo 2
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed explanation of solving a physics problem involving motion with constant acceleration. The speaker demonstrates how to use kinematic equations to calculate time and distance, with a focus on the concept of an object coming to a stop. Key steps include handling negative values in equations, calculating time using initial velocity and acceleration, and determining the distance traveled during deceleration. The speaker encourages viewers to practice more advanced problems and engage with additional educational content for further learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 The teacher explains how to simplify equations by multiplying by -1, which changes the signs of all terms, making it easier to solve.
- 😀 The teacher clarifies the process of calculating time when an object is stopping, using the equation with initial velocity and acceleration.
- 😀 The time required for the object to stop is calculated as 7 seconds, which is based on the velocity and acceleration values provided.
- 😀 The teacher emphasizes the importance of understanding formulas like velocity, acceleration, and time in solving motion problems.
- 😀 The displacement (distance traveled) is calculated using the formula involving initial velocity, time, and acceleration.
- 😀 The final velocity is zero when the object stops, and this information is crucial in determining the displacement.
- 😀 The formula for displacement includes initial velocity, time, and acceleration, with the time squared term contributing significantly to the result.
- 😀 The final displacement is found to be 73.5 meters, calculated using the known values and the equation for motion.
- 😀 The teacher encourages students to practice more exercises to deepen their understanding of the concepts and to tackle more difficult problems.
- 😀 Viewers are encouraged to subscribe to the channel, share the video with others, and leave comments or likes to engage further with the content.
- 😀 The teacher provides a thorough breakdown of the problem-solving process, ensuring viewers understand the logic behind each step of the calculation.
Q & A
What does multiplying the equation by -1 accomplish in this context?
-Multiplying the equation by -1 changes all the signs, making the equation easier to work with, especially when solving for time or other variables.
How do you interpret the meaning of 'stopping' in this exercise?
-In this context, 'stopping' refers to the point where the final velocity becomes zero, meaning the object has come to a complete halt.
What formula is used to calculate the distance traveled?
-The formula used to calculate the distance is: Distance = Initial velocity * Time + (1/2) * Acceleration * Time^2.
Why is the final velocity set to 0 in the third question?
-The final velocity is set to 0 because the object is stopping, meaning it reaches a velocity of zero at the point of halt.
What is the significance of the time value of 7 seconds in the exercise?
-The time value of 7 seconds is the amount of time it takes for the object to stop, calculated from the earlier part of the problem.
How is acceleration handled in the distance formula?
-Acceleration is included in the formula as a negative value because it represents deceleration (slowing down), and it is multiplied by the square of the time to account for the change in velocity over time.
What does the result of 73.5 meters represent in the exercise?
-The result of 73.5 meters represents the total distance the object travels before coming to a stop.
How does the calculation of distance help solve the problem?
-By using the given initial velocity, acceleration, and time, the distance traveled before the object stops can be calculated, which is a key part of solving the problem.
Why is the time squared in the distance formula?
-The time is squared in the formula because acceleration acts on the velocity over time, and thus the time variable has a squared relationship with the distance traveled when acceleration is involved.
What kind of acceleration is being used in this problem?
-The acceleration in this problem is negative, indicating that it is decelerating or slowing down the object until it comes to a stop.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Rovnoměrně zrychlený pohyb - vzorce

Introductory Uniformly Angularly Accelerated Motion Problem - A CD Player
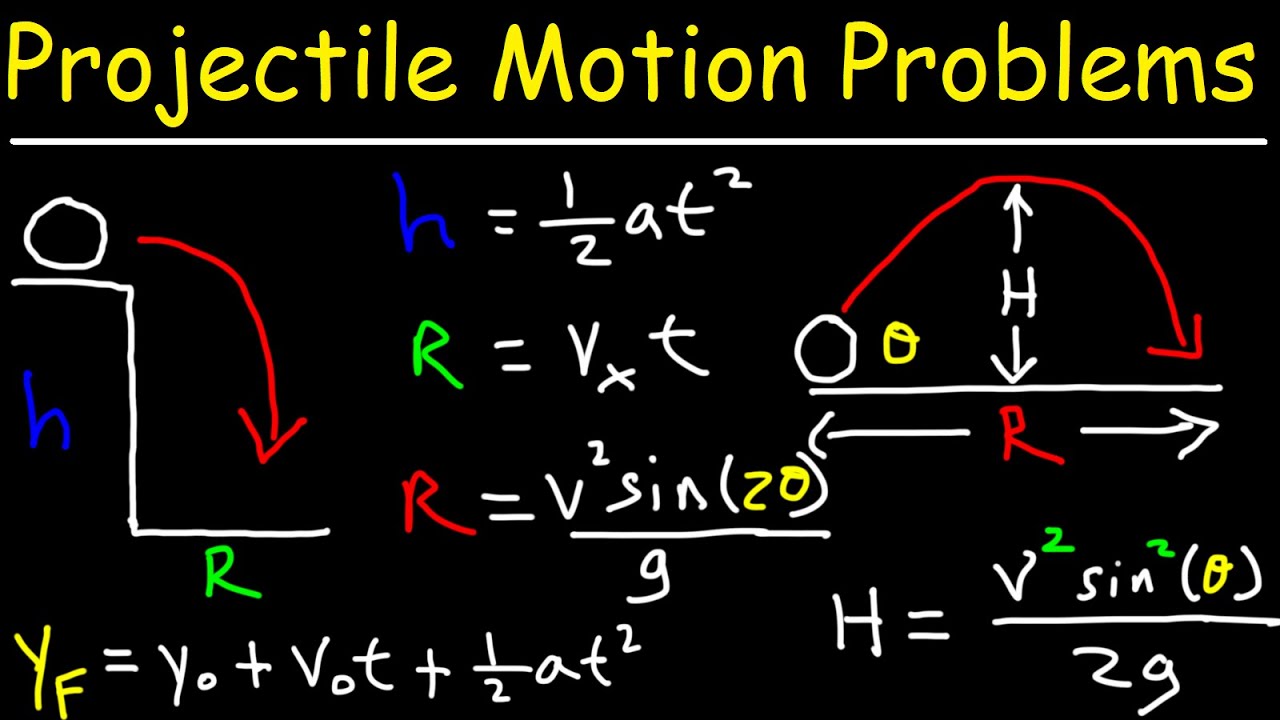
How To Solve Projectile Motion Problems In Physics

Fisika SMA - Hukum Newton (6) - Penerapan Hukum Newton Pada Katrol (I)

Dualisme Gelombang Partikel • Part 1: Radiasi Benda Hitam, Pergeseran Wien, dan Teori Kuantum Planck
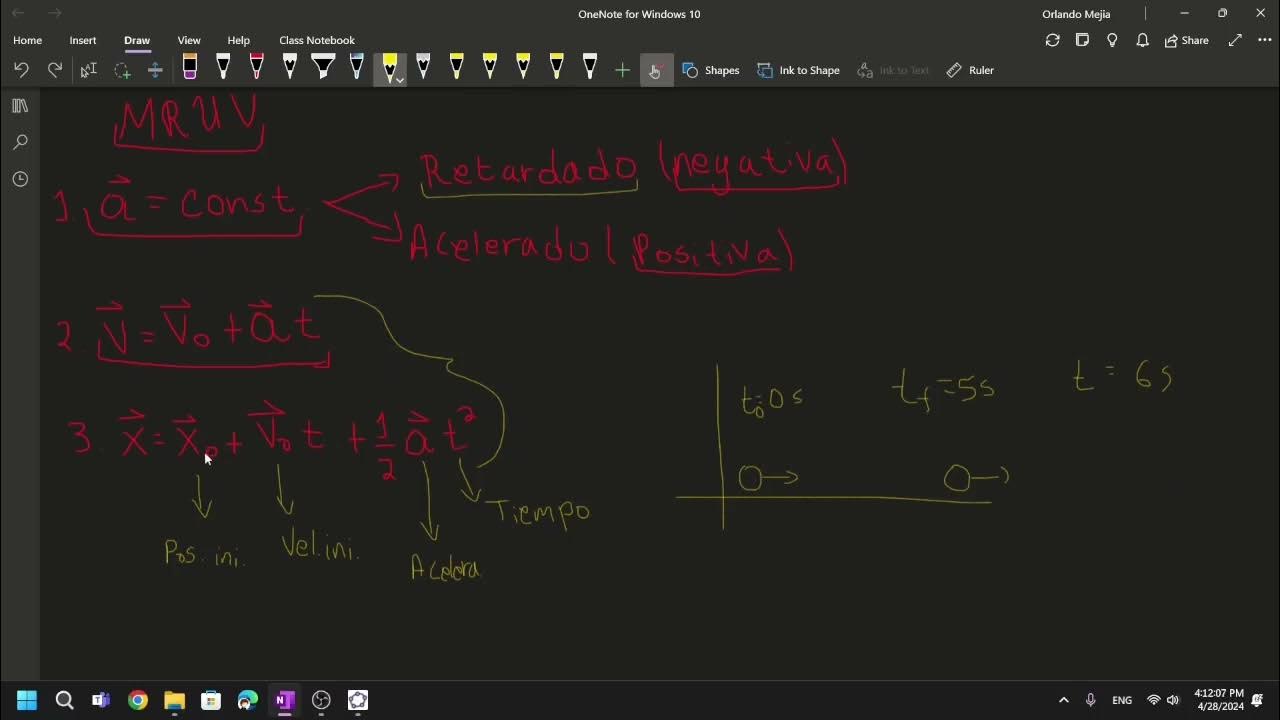
Continuación: Movimiento Rectílineo Uniformemente Variado.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)