Circle Theorems IGCSE Maths
Summary
TLDRThis educational session delves into the properties of a circle, defining it as a set of points equidistant from a central point. Key concepts covered include the radius, circumference, diameter, and the relationships between them. The session also explores tangents, secants, and chords, emphasizing the perpendicularity of the radius to the tangent and the bisector property of chords. It discusses angles in a semicircle being 90° and the relationship between angles at the center and on the circumference. The video concludes with insights on cyclic quadrilaterals, where opposite angles are supplementary, and the sum of all angles equals 360°.
Takeaways
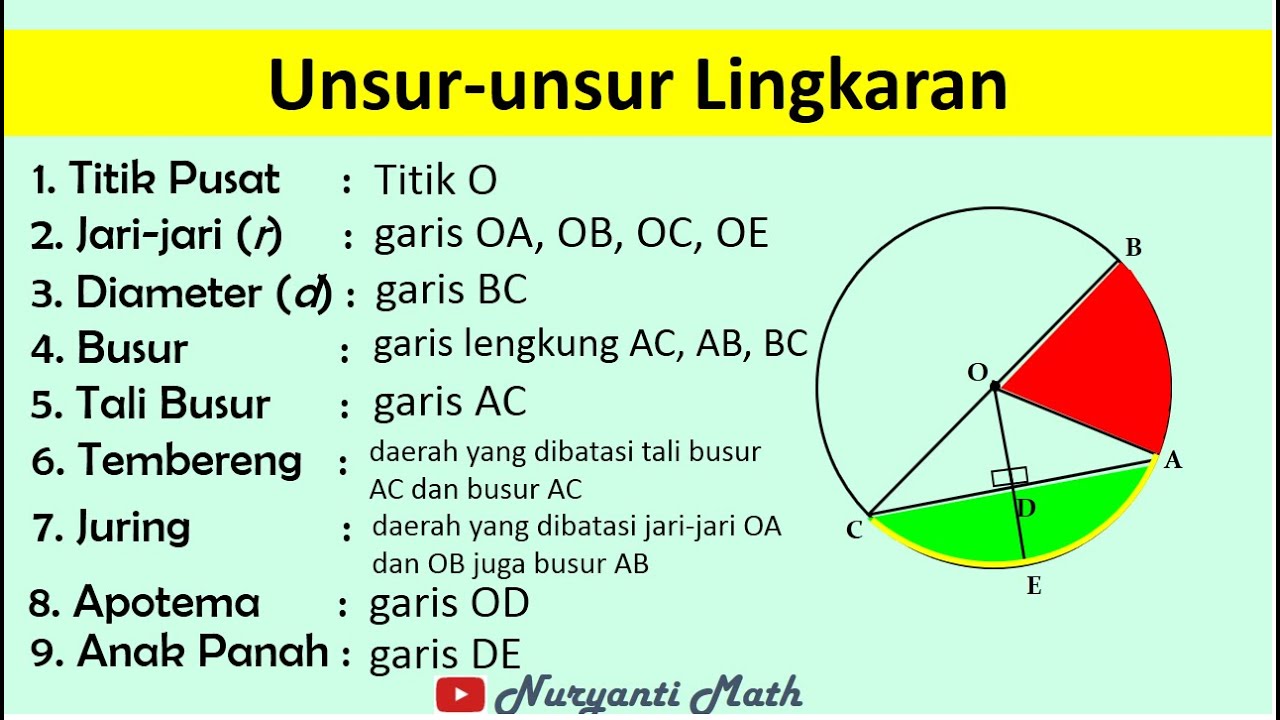
- 🔵 A circle is defined as a set of points equidistant from a fixed point known as the center.
- 📏 The radius of a circle is the distance from the center to any point on the circumference.
- 🌀 The circumference of a circle is calculated as \( 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- 📏 The diameter of a circle is the longest chord that divides the circle into two equal parts, and it is equal to twice the radius (\( D = 2R \)).
- 📐 A tangent to a circle is a line that touches the circle at exactly one point.
- 📐 A secant is a line that intersects a circle at two points, extending beyond the circle.
- ✂️ The property of equal chords in a circle states that if two chords are equal, their distances to the center are also equal.
- 🔼 The angle in a semicircle is always 90 degrees, reflecting the right angle property of a semicircle.
- 🔼 The angle between a tangent and a radius is always 90 degrees, indicating the perpendicular relationship.
- 🔄 The angle at the center of a circle subtended by an arc is twice the size of the angle on the circumference subtended by the same arc.
Q & A
What is the definition of a circle?
-A circle is the set of all points that are equidistant from a fixed point, known as the center.
What is the term for the distance from the center of a circle to any point on its circumference?
-The distance from the center of a circle to any point on its circumference is called the radius.
How is the circumference of a circle calculated?
-The circumference of a circle is calculated using the formula C = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
What is the term for a line that divides a circle into two equal parts?
-A line that divides a circle into two equal parts is called the diameter, which is also the longest chord in a circle.
What is the relationship between the diameter and the radius of a circle?
-The diameter of a circle is twice the length of its radius, expressed as D = 2R.
What is a tangent in the context of a circle?
-A tangent is a line that touches the circle at exactly one point.
What is a secant in relation to a circle?
-A secant is a line that intersects the circle at two points, extending beyond the circle.
What property ensures that a line drawn from the center of a circle to the midpoint of a chord is perpendicular to the chord?
-The property that ensures a line from the center to the midpoint of a chord is perpendicular is known as the perpendicular bisector theorem.
How are the angles in a semicircle related?
-Any angle inscribed in a semicircle is always a right angle, meaning it measures 90 degrees.
What is the relationship between the angle at the center of a circle and the angle on the circumference subtended by the same arc?
-The angle at the center of a circle subtended by an arc is twice the size of the angle on the circumference subtended by the same arc.
What is a cyclic quadrilateral, and what is one of its properties?
-A cyclic quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a circle. One of its properties is that the sum of the opposite angles is supplementary, meaning they add up to 180 degrees.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CIRCLES || PRE-CALCULUS

Unsur-unsur Lingkaran | Matematika Kelas XI

Pre-Calculus - Parabola : If the Vertex is (0,0) find the Focus, Directrix, Axis of Symmetry, Latus

Standard Equation of Circle | Conic Sections | Don't Memorise
Unsur-unsur Lingkaran

Every Theorem on Circle with Proofs.| Theorem on Circles.| Class 9 |NCERT.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)