MATH 7 Solving simple interest week 5 #matatag #matatagcurriculum #simpleinterest #solvinginterest
Summary
TLDRThis video is a Tagalog tutorial on solving money problems involving simple interest. The instructor explains key concepts such as interest, interest rate, principal, and time. Various formulas for calculating simple interest are introduced, including the main formula: Interest = Principal × Rate × Time. The video provides step-by-step examples demonstrating how to calculate the interest, principal, rate, and time for different scenarios. The instructor also discusses how to convert percentages to decimals and offers tips for remembering the formulas using a pyramid structure.
Takeaways
- 📊 This video is a Tagalog tutorial about solving money problems involving simple interest.
- 💰 The presenter explains the basic terms needed to understand simple interest: interest, interest rate, principal, and time.
- 📈 Simple interest is the amount earned from investing or borrowing money and is calculated using the formula: Interest = Principal × Rate × Time (I = PRT).
- 📝 Interest is defined as the profit made when investing money in a bank or the cost of borrowing money.
- 💹 The interest rate is the percentage of the principal charged as interest, typically expressed as a percentage per annum.
- 💵 Principal refers to the total amount of money invested or borrowed.
- ⏳ Time is the duration for which the money is invested or borrowed, usually measured in years.
- 🔢 The presenter illustrates how to calculate interest using various examples, showing how changes in principal, rate, or time affect the total interest.
- 📊 The tutorial also covers how to rearrange the formula to find unknown values such as principal, rate, or time using derived formulas from I = PRT.
- 📚 The video provides practical examples of calculating simple interest for different scenarios and explains the step-by-step process clearly.
Q & A
What is simple interest according to the script?
-Simple interest is the amount earned from investing or borrowing money. It is calculated using the formula: Interest = Principal x Rate x Time.
What are the key terms needed to solve simple interest problems?
-The key terms are Interest, Principal, Rate, and Time. Interest is the money earned or paid, Principal is the amount invested or borrowed, Rate is the percentage of interest, and Time is the length the money was invested or borrowed.
How do you convert a percentage to a decimal?
-To convert a percentage to a decimal, divide the percentage by 100. For example, 10% becomes 0.10.
What is the formula to calculate interest if the Principal, Rate, and Time are known?
-The formula is Interest = Principal x Rate x Time.
How do you calculate the Principal if the Interest, Rate, and Time are given?
-The formula to calculate Principal is Principal = Interest / (Rate x Time).
In the example where Makoy borrows Php30,000 at 10% annual interest for 3 years, what is the interest?
-The interest is Php9,000. This is calculated using the formula: Interest = 30,000 x 0.10 x 3.
What is the formula to calculate the Rate if the Interest, Principal, and Time are known?
-The formula is Rate = Interest / (Principal x Time).
In the example where Mike borrows Php10,000 and repays Php11,400 after 2 years, what is the interest rate?
-The interest rate is 6%. This is calculated by dividing the interest (Php1,400) by the product of Principal (Php10,000) and Time (2 years).
How do you calculate the Time if the Interest, Principal, and Rate are known?
-The formula to calculate Time is Time = Interest / (Principal x Rate).
In the example where Php6,000 interest is earned on a Php40,000 investment at 15% annually, how long was the money invested?
-The money was invested for 3 years, calculated using the formula Time = Interest / (Principal x Rate).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

X - ALL - MATEMATIKA - Bunga Tunggal Dan Majemuk

Bunga majemuk dan anuitas kelas XI | Matematika

PART#01: BAHASAN SOAL TRYOUT-3 TKA NUMERASI (MATEMATIKA) SMP 2026

Derivada del Seno | Ejemplo 2

Tredence Analytics Online Test Questions | Aptitude Questions for Tredence | Pseudocode Questions
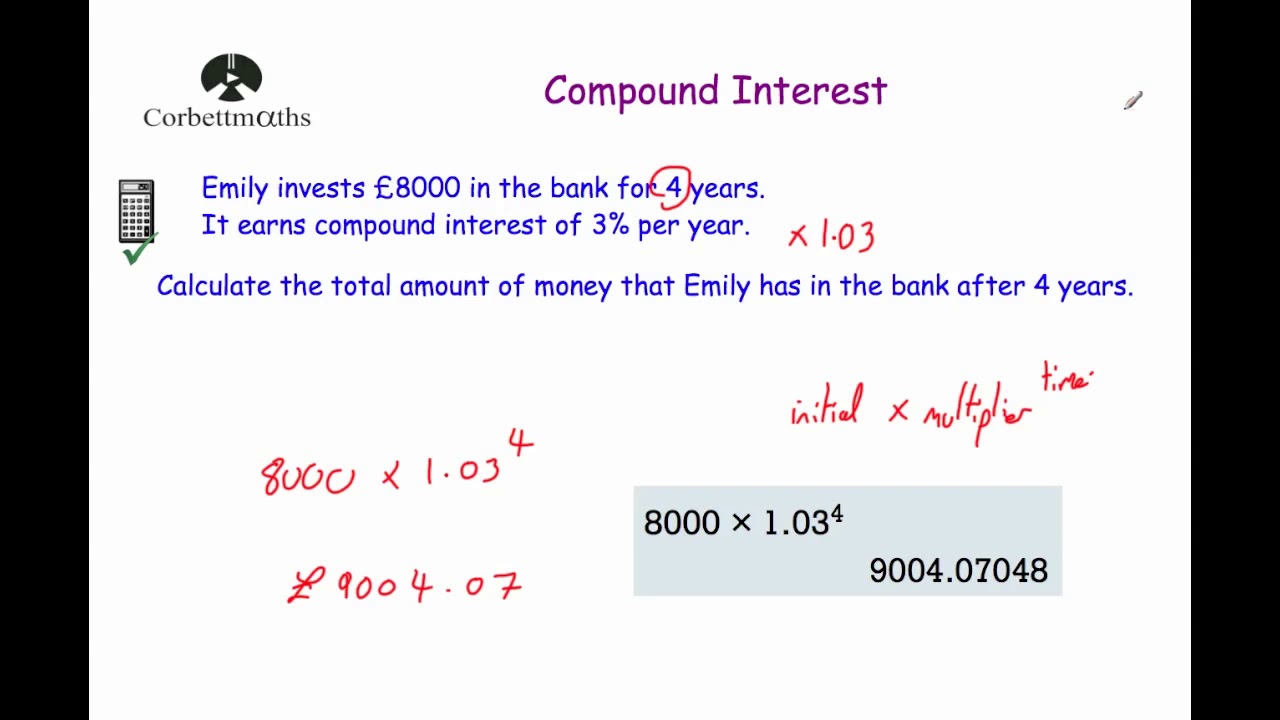
Compound Interest - Corbettmaths
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)