Macromolecules
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the world of biomolecules, essential for life and often referred to as macromolecules. It introduces four main types: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, each playing a critical role in our bodies and diets. The script explains that each biomolecule is composed of smaller units like monosaccharides, glycerol and fatty acids, amino acids, and nucleotides. It also touches on the functions of these molecules, such as energy storage, structural components, and genetic information transmission, providing a foundational understanding of biology.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Biomolecules, also known as macromolecules, are large molecules essential for life and can have multiple names.
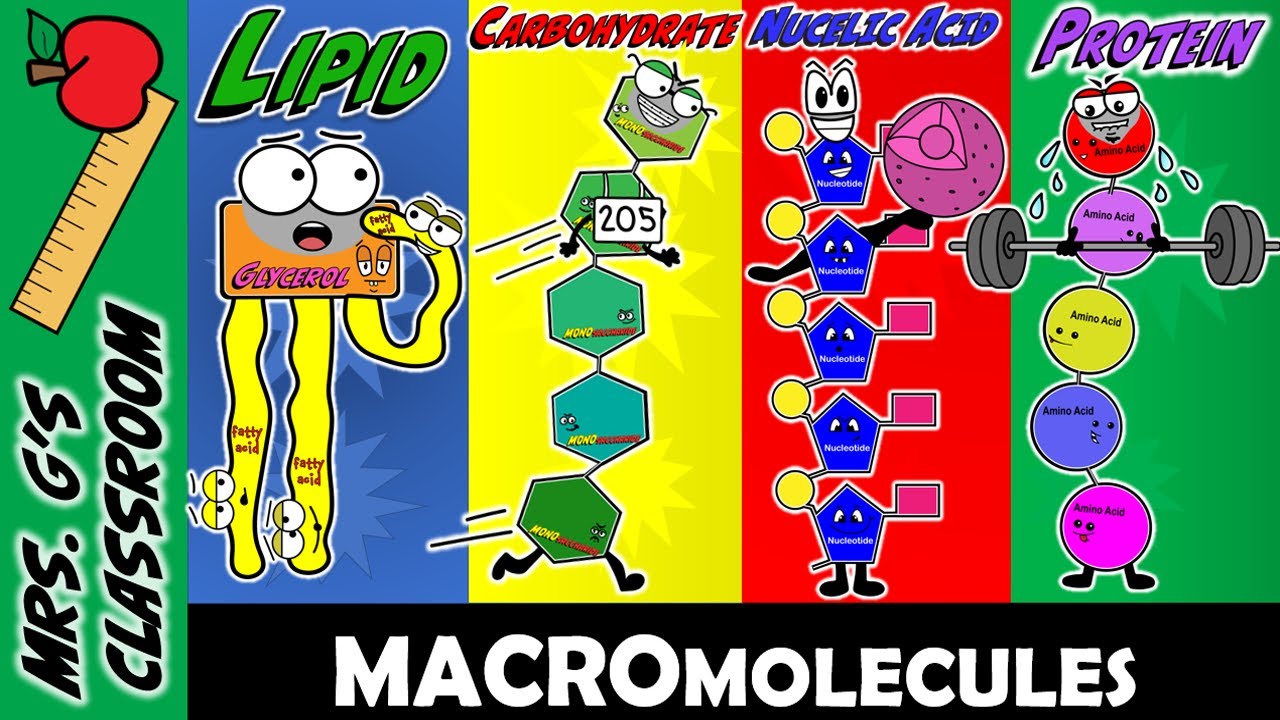
- 🍚 The four main types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are also found in food.
- 🔑 Monosaccharides are the monomers that make up carbohydrates, glycerol and fatty acids make up lipids, amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and nucleotides form nucleic acids.
- 🏃♂️ Carbohydrates serve as a quick energy source and are also part of the structural component in plants, like cellulose, and as storage in the form of starch and glycogen.
- 💧 Lipids are hydrophobic and diverse, including fats and oils, and play roles in cell membrane structure, long-term energy storage, insulation, and hormone production.
- 🧬 Nucleic acids, with nucleotides as their monomers, are the genetic blueprint of all living things, including DNA and RNA, which store and transmit genetic information.
- 🥚 Proteins, made up of amino acids, are crucial for the body's structure, catalyzing chemical reactions, transport and communication, and defense mechanisms.
- 🔋 Proteins have multiple functions, including being a structural component, aiding in chemical reactions, and providing immunity through antibodies.
- 🌿 The elements that make up biomolecules are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O), with proteins also containing nitrogen (N) and nucleic acids containing phosphorus (P).
- 🔑 The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins, which dictates the protein's function.
Q & A
What are biomolecules and why are they important for life?
-Biomolecules are large molecules, also known as macromolecules, that are essential for life. They are crucial because they are the building blocks of living organisms, performing various functions necessary for growth, maintenance, and reproduction.
What are the four main types of biomolecules?
-The four main types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each plays a distinct role in the structure, function, and regulation of living organisms.
How are lipids related to fats and how do they function in the body?
-Lipids, often referred to as fats, are hydrophobic biomolecules that are diverse and include fats, oils, triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. In the body, they serve as structural components of cell membranes, provide long-term energy storage, offer insulation, and are involved in hormone production and chemical messaging.
What is the monomer of carbohydrates and what is its role?
-The monomer of carbohydrates is monosaccharides, which are simple sugars like glucose. They serve as a quick energy source for the body, are part of the structural component in plants, and can be stored as starch in plants and glycogen in animals.
What is the significance of nucleic acids in living organisms?
-Nucleic acids, with their monomer being nucleotides, are the genetic blueprint of living organisms. They are found in all living things and include DNA and RNA, which store and transmit genetic information and instruct cells on what to do.
How do nucleic acids contribute to the formation of proteins?
-Nucleic acids, particularly the sequence of nucleotides in DNA, contain the instructions for making proteins. The arrangement of nucleotides determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins, which in turn dictates the type and function of the protein.
What are the basic elements that make up biomolecules?
-The basic elements that make up biomolecules include carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). Proteins also contain nitrogen (N), and nucleic acids include phosphorus (P) in addition to the other elements.
What is the role of proteins in the body and what are their monomers?
-Proteins are essential for the body as they have multiple functions including structural support, catalyzing chemical reactions, transporting and communicating information, and providing defense through antibodies. Their monomers are amino acids.
How does the term 'macros' relate to both diet and biomolecules?
-The term 'macros' is used in both dietary contexts and to describe biomolecules. In diet, 'macros' refers to macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that are needed in large amounts. In the context of biomolecules, 'macromolecules' refers to large molecules like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the significance of the term 'monomer' in the context of biomolecules?
-A monomer is the basic building block or subunit of a polymer. In the context of biomolecules, each type of biomolecule is made up of specific monomers: carbohydrates from monosaccharides, lipids from glycerol and fatty acids, proteins from amino acids, and nucleic acids from nucleotides.
Why is it important to understand the different names for biomolecules?
-Understanding the different names for biomolecules is important because it helps in recognizing the versatility and interconnectedness of scientific concepts. It also aids in communication across different scientific disciplines and in everyday contexts, such as understanding dietary recommendations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Overview of Organic Compounds

Proteins II Biomolecules II Std.11Th & 12Th II Biology II Dr.Shalini Rao II Digital Biology Shastra

MORFOFISIOLOGIA HUMANA 1 CLASE 3

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES

Proteínas - BIOQUÍMICA: Estructuras proteicas y aminoácidos.
What Are the 4 Major Macromolecules and How Are They Made?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)