Homeostasis: How Your Body Stays in Balance with its Environment
Summary
TLDRThe script explains the concept of homeostasis, a vital process where the body maintains a stable internal environment despite external changes. It details how organs like the liver, kidneys, and pancreas contribute to homeostasis through drug metabolism, water regulation, and blood glucose control. The script also delves into thermoregulation, describing how the hypothalamus acts as a thermostat, using mechanisms like vasoconstriction, piloerection, and sweating to maintain normal body temperature. These processes are part of negative feedback loops that ensure the body's equilibrium.
Takeaways
- 🌡️ Homeostasis is the body's process of maintaining a stable internal environment despite external changes.
- 💊 The liver plays a key role in homeostasis by metabolizing drugs and toxins.
- 🩸 Kidneys help maintain homeostasis by regulating water and solutes in the blood.
- 🍬 The pancreas contributes to homeostasis through the regulation of blood glucose levels.
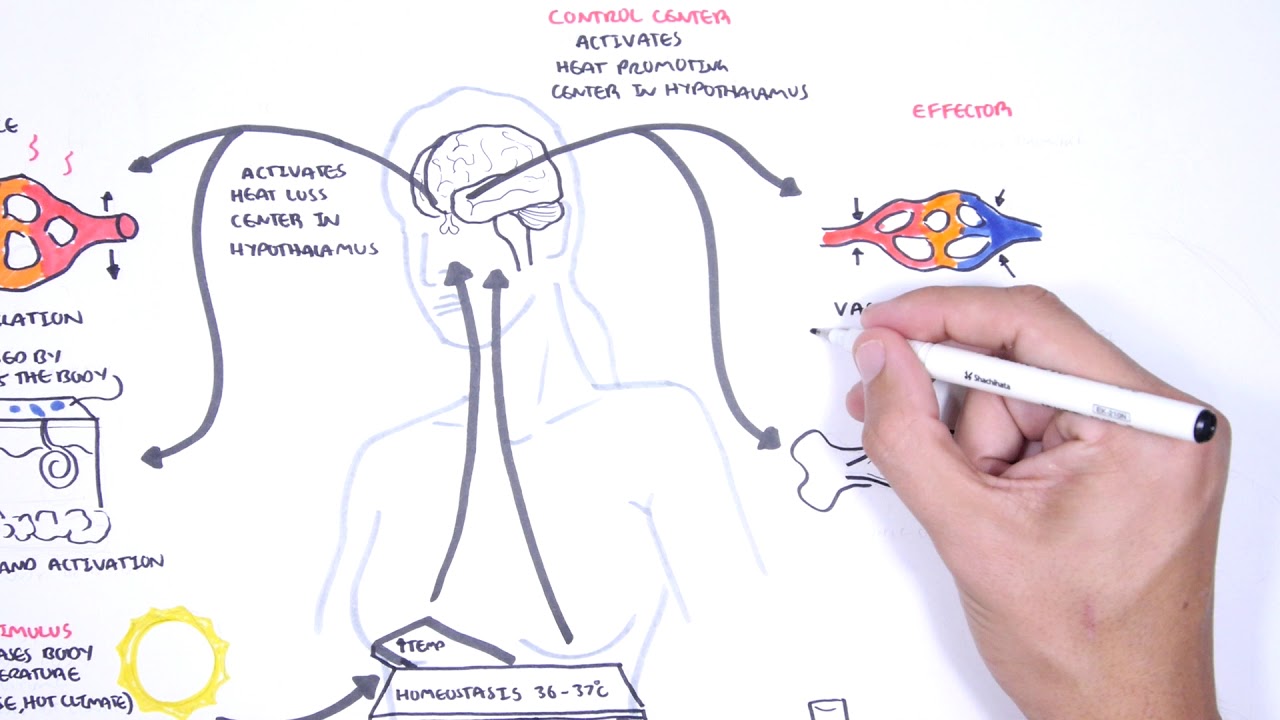
- 🧊 Thermoregulation is a critical homeostatic process that maintains normal body temperature.
- ❄️ In response to cold, the hypothalamus triggers vasoconstriction to conserve heat and piloerection to trap warm air.
- 🏋️♂️ Shivering reflex is activated to generate heat when body temperature drops.
- 🌞 When body temperature rises, the hypothalamus halts vasoconstriction, allowing heat to be dissipated through dilated blood vessels.
- 💧 Sweat glands produce sweat to cool the body down through evaporation when overheated.
- 🔄 Negative feedback loops are mechanisms by which the body counteracts stimuli to maintain homeostasis.
Q & A
What is homeostasis and why is it important for the body?
-Homeostasis is the process by which the body maintains its internal environment in response to the external environment, ensuring stability and balance. It is crucial as it allows the body to function optimally by keeping essential parameters like temperature, pH, and chemical concentrations within a narrow range.
How does the liver contribute to homeostasis?
-The liver contributes to homeostasis by metabolizing drugs and toxins, thereby preventing their accumulation and maintaining the body's internal environment.
What role do the kidneys play in maintaining homeostasis?
-The kidneys regulate water and solute levels in the blood, which is vital for maintaining the body's fluid balance and overall homeostasis.
How does the pancreas help in maintaining blood glucose levels?
-The pancreas regulates blood glucose levels by secreting insulin, which lowers blood sugar, and glucagon, which raises it, ensuring that the body has a stable source of energy.
What is thermoregulation and how does it relate to homeostasis?
-Thermoregulation is the maintenance of normal body temperature. It is a homeostatic process that involves various mechanisms to prevent the body's core temperature from deviating too far from the optimal range.
What happens when the body's skin or core temperature drops?
-When the body's skin or core temperature drops, thermal receptors in the skin or internal organs send signals to the hypothalamus, which then triggers responses like vasoconstriction, piloerection, and shivering to generate heat and maintain temperature.
What is the role of the hypothalamus in thermoregulation?
-The hypothalamus acts as the body's thermostat, receiving signals from thermal receptors and initiating appropriate responses through the nervous system to maintain body temperature.
How does vasoconstriction help in preventing heat loss?
-Vasoconstriction constricts blood vessels in the skin, diverting blood away from the skin and extremities to the warmer interior of the body, thus preventing further heat loss.
What is piloerection and how does it assist in thermoregulation?
-Piloerection is the contraction of erector pili muscles causing hair follicles to stand up, which can trap a layer of air close to the skin, providing insulation and helping to retain body heat.
How does the body respond to an increase in skin or core temperature?
-In response to an increase in skin or core temperature, the hypothalamus halts sympathetic stimulation of blood vessels, causing them to dilate and distribute heat through the skin. It also triggers relaxation of erector pili muscles and activates sweat glands to produce sweat, facilitating heat loss through evaporation.
What are negative feedback loops, and how do they contribute to homeostasis?
-Negative feedback loops are mechanisms that counteract stimuli to maintain stability. They allow the body to respond to changes by initiating processes that reverse the initial condition, thus maintaining homeostasis.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GCSE Biology - Homeostasis | Receptors, Coordination Centres, Effectors | Negative Feedback
Homeostasis - negative and positive feedback (thermoregulation and lactation)

GCSE Biology - Homeostasis #54

Homeostatic Loops

Homeostasis | BAMS 1st Year Physiology Modren Lecture | Kirya Sharir Modern 1st Paper | #IAD

Negative Feedback | Physiology | Biology | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)