Gravitational Force | Physics
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the concept of gravitational force and Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation. It explains why objects fall towards Earth due to gravitational pull and clarifies that the origin of this force remains unexplained. The script highlights Sir Isaac Newton's pivotal role in formulating the law, which quantifies the gravitational force between two masses. It uses the formula F_G = G * M * m / R^2, where G is the gravitational constant, to demonstrate calculations. The video also touches on the inverse square law, illustrating how gravitational force diminishes with distance. It concludes with a practical example of calculating the gravitational force between two people, emphasizing the minuscule force in everyday life.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Gravitational force is the reason why objects fall towards the Earth when released above its surface.
- 🤔 The origin of gravitational force remains unexplained by scientists, despite various hypotheses and laws.
- 📚 Sir Isaac Newton is a prominent scientist who explained gravitational force through his law of universal gravitation.
- 🔍 Newton's law of universal gravitation allows us to calculate the gravitational force between any two masses, regardless of whether they are living or non-living.
- ⚖️ The gravitational force (FG) is directly proportional to the product of the masses (M and m) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (R) between their centers.
- 🔢 The gravitational constant (G) is approximately 6.672 × 10^-11 N(m/kg)^2, which is used in the formula to calculate gravitational force.
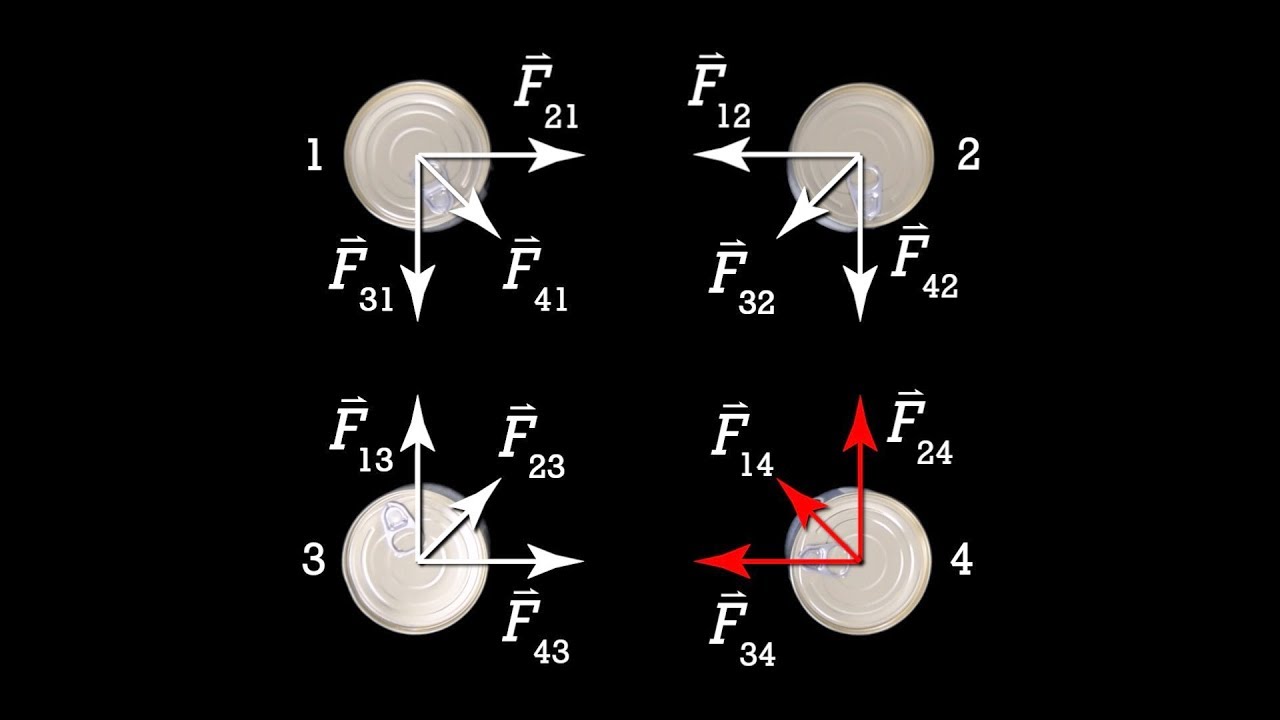
- 📐 According to Newton's third law of motion, every action has an equal and opposite reaction, meaning that gravitational forces between two masses are mutual.
- 👫 An example calculation in the script demonstrates how to find the gravitational force between a boy and a girl, showing it to be an extremely small force.
- 📉 The gravitational force follows an inverse square law, meaning if the distance between two masses doubles, the force decreases by a factor of four.
- 🎓 The script encourages viewers to like and subscribe for more physics and math lectures, indicating the channel's focus on educational content.
Q & A
What causes objects to fall towards the Earth?
-Objects fall towards the Earth due to gravitational force, which is the attraction exerted by the Earth on objects in its vicinity.
Why can't scientists explain the origin of gravitational force?
-The origin of gravitational force, like other fundamental forces such as magnetic or electric force, is not fully understood by scientists, although there are various hypotheses and laws in physics to calculate and understand its effects.
Who is credited with explaining the gravitational force in physics?
-Sir Isaac Newton is credited with explaining the gravitational force through his law of universal gravitation, which allows us to calculate the gravitational force between any two masses.
What is the universal law of gravitation?
-The universal law of gravitation states that there is a gravitational force between any two masses, which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
What is the formula for calculating the gravitational force according to Newton's law?
-The formula for calculating gravitational force (FG) is FG = G * (M * m) / R^2, where G is the gravitational constant, M and m are the masses of the two objects, and R is the distance between the centers of the two masses.
What is the value of the gravitational constant (G)?
-The value of the gravitational constant (G) is approximately 6.672 × 10^-11 N(m/kg)^2.
How does Newton's third law of motion relate to gravitational force?
-According to Newton's third law of motion, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Therefore, if one mass exerts a gravitational force on another, the second mass exerts an equal and opposite gravitational force on the first.
Why don't we feel the gravitational force between people?
-The gravitational force between humans is extremely small due to the relatively small masses and short distances involved, making it imperceptible to our senses.
How does the distance between two objects affect the gravitational force between them?
-The gravitational force follows the inverse square law, meaning that if the distance between two objects is doubled, the gravitational force decreases by a factor of four, and if the distance is tripled, the force decreases by a factor of nine.
What is an example of how to calculate the gravitational force between two people?
-To calculate the gravitational force between two people, one would use the formula FG = G * (M * m) / R^2, where M and m are the masses of the individuals, and R is the distance between them. For example, if a boy weighing 40 kg and a girl weighing 45 kg are standing 0.5 meters apart, the gravitational force between them would be calculated using their masses and the distance.
What is the significance of the inverse square law in understanding gravitational force?
-The inverse square law is significant because it explains how the gravitational force diminishes with increasing distance between objects, which is crucial for understanding the behavior of celestial bodies and the structure of the universe.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)