Class 6 CBSE Physics | Chapter 9: Electricity And Circuit - One Shot | Xylem Class 6 CBSE
Summary
TLDRThis transcript explains the basics of electric cells, circuits, and bulbs. It covers how electric cells produce electricity through chemical reactions, the importance of maintaining polarity between terminals, and the flow of electricity from positive to negative. It also describes the role of a filament in a lightbulb and how a break in the filament can cause the bulb to fuse. Additionally, it discusses the function of a switch in breaking or completing a circuit and touches on the concept of conductors, materials that allow electricity to flow.
Takeaways
- 🔋 Electric cells produce electricity from the chemicals stored inside them.
- ⚡ When the chemicals in electric cells are used up, the cells stop producing electricity.
- 🔄 The positive terminal must always be connected to the negative terminal for electricity to flow.
- 💡 A thin wire that gives off light in a bulb is called a filament, and it is fixed into two thicker wires.
- ⚙️ The filament connects to the metal case at the base of the bulb and another thick wire connects to the center of the base.
- 🔌 An electric circuit is formed when the two terminals of an electric cell are connected to the two terminals of a bulb.
- 🔁 The direction of electric current is always considered to flow from the positive to the negative terminal.
- ⚠️ A bulb may not glow if its filament is broken, meaning no current can pass through the filament.
- 🔘 A switch is a simple device that either breaks or completes an electric circuit.
- 🔗 Materials through which electric current flows are called conductors.
Q & A
What is the primary function of an electric cell?
-An electric cell produces electricity from the chemical energy stored inside it.
What happens when the chemicals in an electric cell are depleted?
-When the chemicals in an electric cell are used up, the cell stops producing electricity.
How should the terminals of an electric cell be connected to ensure proper functioning?
-The positive terminal of an electric cell must be connected to the negative terminal, and this polarity must be maintained.
What is the direction of electric current flow?
-Electric current is considered to flow from the positive to the negative terminal.
What is a filament and what is its role in an electric bulb?
-A filament is a thin wire that gives off light when electricity passes through it. It is fixed into the metal base of the bulb.
What is the purpose of the thicker wires connected to the metal base of the bulb?
-The thicker wires are connected to the metal base of the bulb to provide a complete path for the electricity to flow to the filament.
What is an electric circuit and how is it formed?
-An electric circuit is a complete path of electricity flow, which is formed when the two terminals of an electric cell are connected to the two terminals of a bulb.
Why might an electric bulb not glow even when connected to an electric cell?
-An electric bulb might not glow if there is a break in its filament, which means a break in the path of current between the terminals of the electric cell.
What is the role of a switch in an electric circuit?
-A switch is a device that can either break the circuit or complete it, allowing or stopping the flow of electricity.
What are conductors and why are they important in an electric circuit?
-Conductors are materials through which electric current can flow. They are important in an electric circuit because they allow the flow of electricity to power devices like bulbs.
What happens when an electric bulb fuses?
-When an electric bulb fuses, it means the filament has broken, preventing current from passing through it, and thus, the bulb does not light up.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
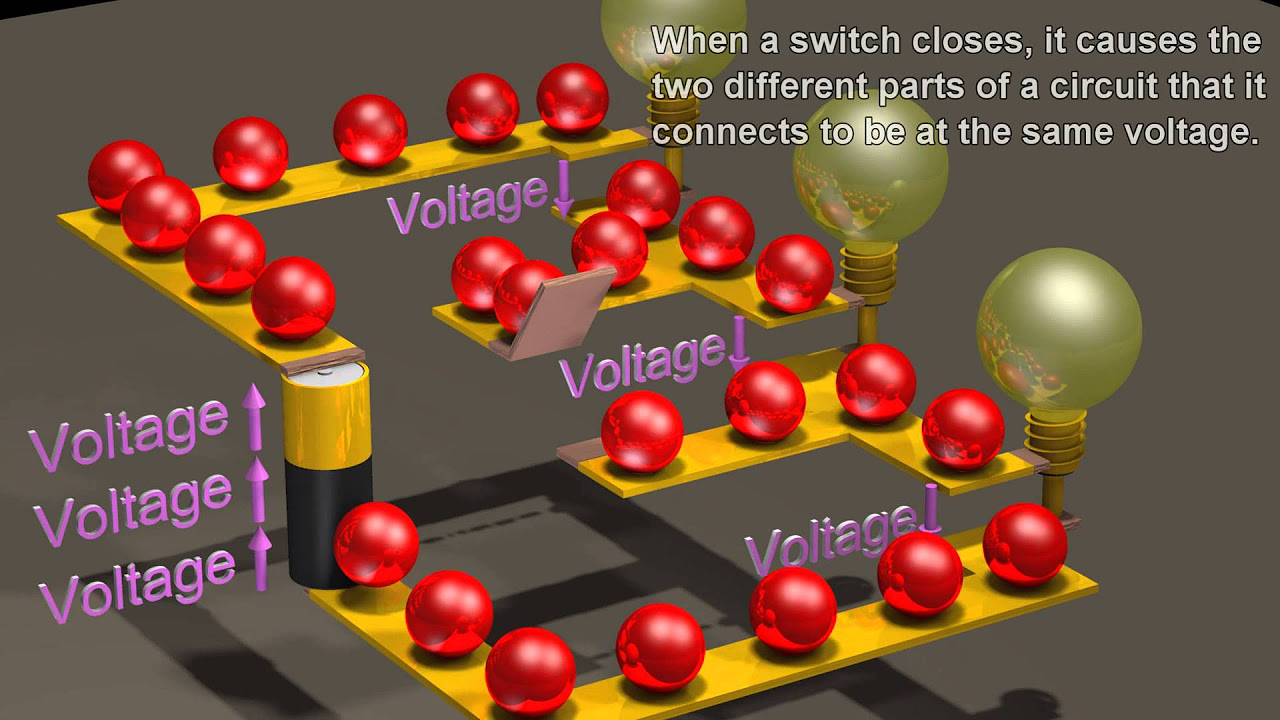
Electric Circuits: Basics of the voltage and current laws.

Aula 8 - Circuito em série e paralelo

GCSE Physics - Electricity 3 - Parallel and Series Circuits and Diagrams

Lecture5: Single Loop Circuits

Magnetic and Electrical Circuit Similarities & Dissimilarities

PRIMEIRA LEI DE OHM | ELETRODINÂMICA | AULA 5 - Professor Boaro
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)