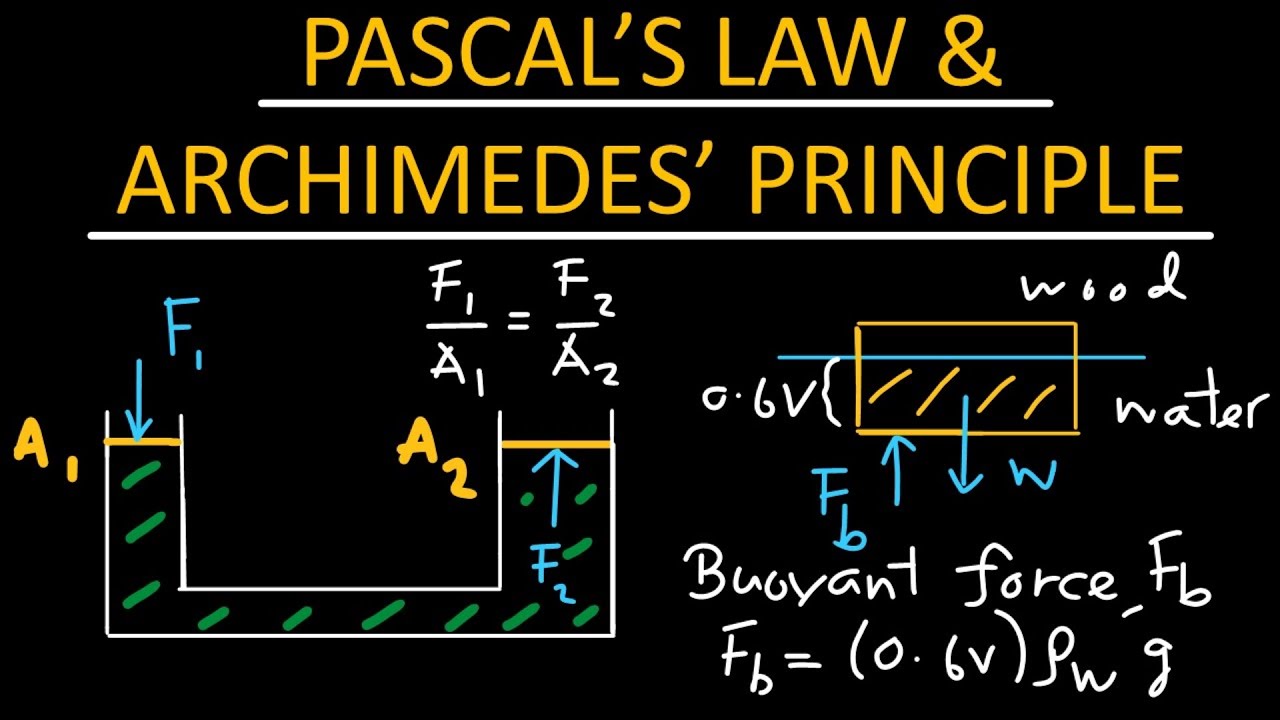
La poussée d'Archimède | cours + exercice corrigé | physique-chimie spé de lycée
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the principle of Archimedes' buoyancy force, providing a clear example of its application in real-world scenarios. It explains how the pressure exerted by a fluid on an object submerged in it varies depending on the depth and volume of the fluid above the object. The script emphasizes the importance of calculating both the buoyant force and the weight of an object to determine its behavior in a fluid, such as whether it will float or sink. Using the formula for buoyant force, which involves the density of the fluid, the volume of the object, and the acceleration due to gravity, the video demonstrates how to calculate the force exerted by air on a balloon. It also calculates the balloon's weight to compare with the buoyant force and concludes that if the buoyant force is greater than the weight, the balloon will rise. The video concludes by encouraging viewers to apply these principles to understand why a weather balloon ascends and by offering further educational resources.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding Archimedes' principle: The script explains the concept of buoyancy and Archimedes' principle, which states that an object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces.
- 📊 Pressure distribution in fluids: It describes how pressure in a fluid is not uniformly distributed, with greater pressure at greater depths. This knowledge is crucial for understanding buoyant forces in different scenarios.
- ⚖️ Comparison of forces: The script emphasizes the comparison between the weight of an object and the buoyant force exerted by the fluid. This comparison determines whether the object sinks, floats, or rises.
- 🎈 Application to real-world scenarios: It discusses practical applications of Archimedes' principle, such as in weather balloons, to measure atmospheric conditions.
- 🧪 Formulas for calculation: Various formulas are introduced for calculating buoyant force and weight, highlighting the importance of understanding and applying these equations correctly.
- 📝 Importance of data accuracy: The script emphasizes the significance of using accurate data, such as fluid density and volume, in calculations to obtain reliable results.
- 🔍 Data interpretation: It provides guidance on interpreting data from problem statements and extracting relevant information for calculations.
- 🚀 Factors influencing buoyancy: Factors such as fluid density, object volume, and gravitational intensity are discussed as key determinants of buoyant force.
- 📚 Need for conceptual clarity: Conceptual understanding of buoyancy and related principles is crucial for solving problems accurately, as demonstrated in the script's examples.
- 💡 Educational resources: The script encourages using educational platforms for additional learning and support in scientific subjects like physics, chemistry, and mathematics.
Q & A
What is the principle of Archimedes' buoyancy?
-The principle of Archimedes' buoyancy states that an object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward force called buoyancy, which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
How is the pressure exerted by a fluid on an object distributed?
-The pressure exerted by a fluid on an object is not distributed uniformly. It increases with depth, meaning that the pressure is greater at the bottom of the object than at the top due to the increased column of fluid above it.
Why do objects submerged in a fluid experience a force directed upwards?
-Objects submerged in a fluid experience an upward force due to the greater pressure exerted on the bottom surface of the object compared to the top, resulting in a net upward force known as buoyancy.
What is the formula for calculating the buoyant force exerted by a fluid on an object?
-The formula for calculating the buoyant force is: Buoyant Force = (Mass density of the fluid) x (Volume of the object) x (Acceleration due to gravity).
Why is it important to consider the mass density of the fluid outside the object when calculating buoyant force?
-The mass density of the fluid outside the object is used because the buoyant force is a result of the pressure exerted by the fluid on the object's surface, which is determined by the fluid surrounding the object.
How does the weight of an object compare to the buoyant force when determining if the object will float or sink?
-If the buoyant force is greater than the weight of the object, the object will float. If the weight is greater, the object will sink. The object will remain neutrally buoyant if the buoyant force equals the weight.
What is the formula for calculating the weight of an object?
-The formula for calculating the weight of an object is: Weight = Mass x Acceleration due to gravity.
Why is it crucial to maintain the correct number of significant figures in physics and chemistry calculations?
-Maintaining the correct number of significant figures ensures the precision and accuracy of the calculation, reflecting the level of certainty in the measured or calculated values.
What is the role of buoyant force in the operation of weather balloons?
-The buoyant force allows weather balloons to rise in the atmosphere. If the buoyant force is greater than the weight of the balloon, it will ascend and be used for various meteorological measurements.
How does the depth of an object in a fluid affect the pressure it experiences?
-The deeper an object is submerged in a fluid, the greater the pressure it experiences due to the increased column of fluid above it, which results in a greater buoyant force.
Why is the buoyant force often negligible in the case of a car compared to its weight?
-For common objects like cars, the weight of the object is usually much greater than the buoyant force it experiences in air or water, making the buoyant force negligible in most practical scenarios.
What should one do when faced with a calculation involving both the buoyant force and the weight of an object?
-One should calculate the value of both forces using the appropriate formulas and then compare them to determine the net force acting on the object and predict its behavior (whether it will float, sink, or remain neutrally buoyant).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)