How 3 Phase Power works: why 3 phases?
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the generation and distribution of AC power, highlighting the role of electrical generators in producing three-phase electricity. It explains how mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy, the significance of different voltages and frequencies used globally, and the impact on household outlets. The script delves into the physics behind the rotation of magnets and wire coils to generate sine waves, the concept of single-phase versus three-phase power, and the practical applications in powering homes and industries. It also touches on the importance of transformers in adjusting voltage levels for efficient power transmission and the calculation of root mean square voltage for measuring AC power.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Outlets provide 120 volts AC at 60 Hz, but other countries use different voltages and frequencies.
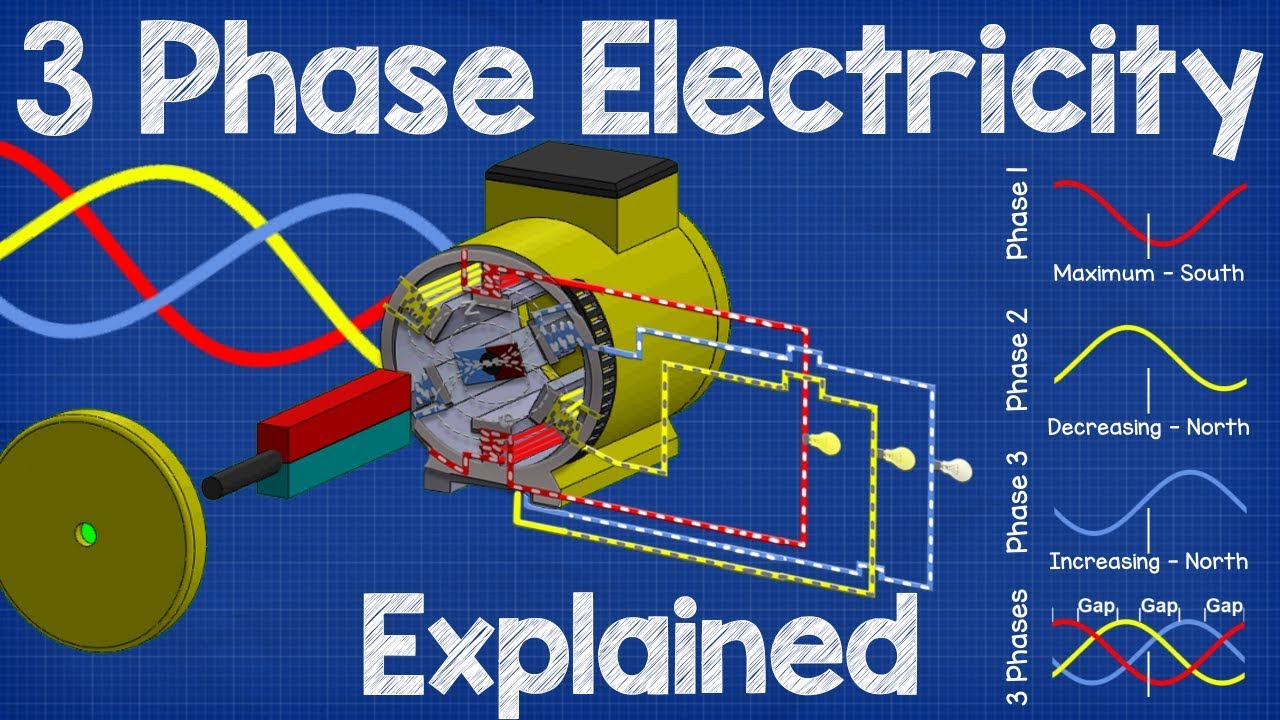
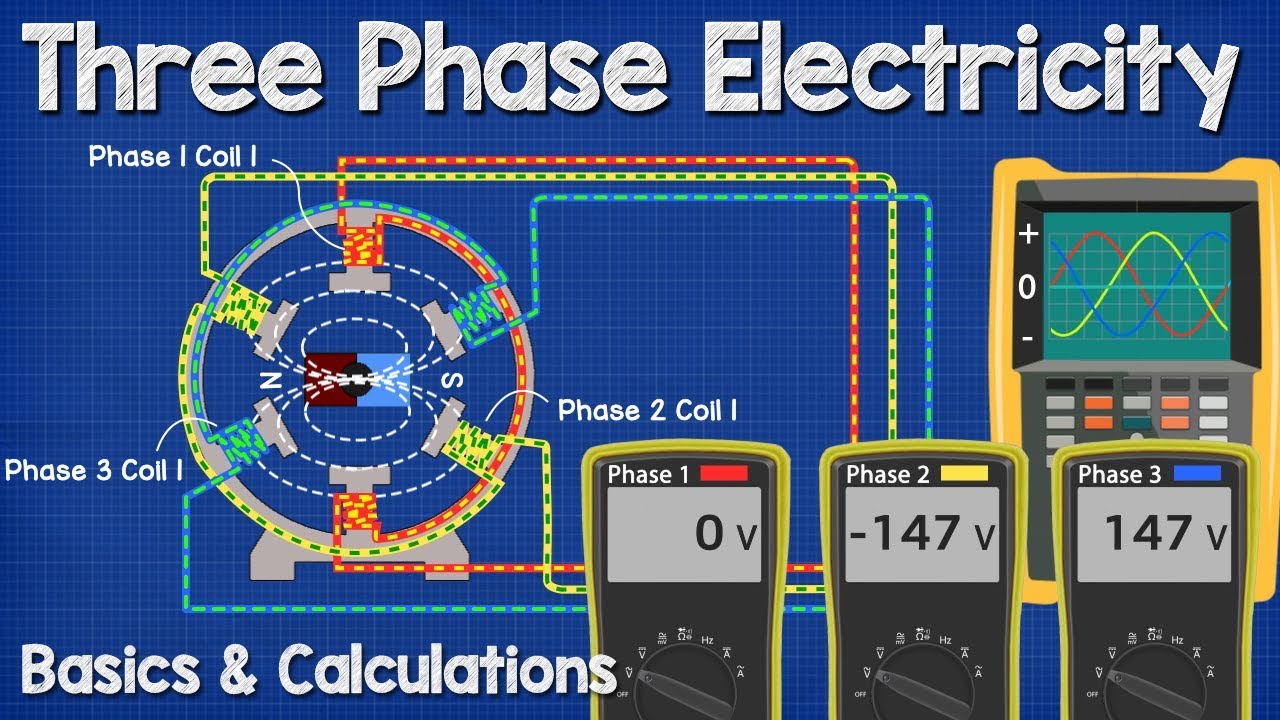
- ⚙️ Electrical generators at power stations produce three-phase AC electricity, which is more efficient than single-phase.
- 🧲 The generator's rotor shaft, with a magnet attached, rotates to produce a changing magnetic field that induces a sine wave in the stator's coils.
- 💡 LEDs can demonstrate the direction of current flow in AC, illuminating in sequence as the magnetic field changes.
- 🏡 Home outlets provide either 50 or 60 Hz, meaning the sine wave repeats 50 or 60 times per second.
- 🔄 By adjusting the coil and magnet configuration, the speed of the generator and thus the frequency of the AC can be controlled.
- 🔗 Three-phase systems provide a more constant output power compared to single-phase, which is beneficial for heavy industrial use.
- 🔵 The phase difference in three-phase systems is 120°, which allows for even spacing of the sine waves and efficient power distribution.
- 🌐 Different countries have different standards for voltage and frequency, leading to variations in how electricity is distributed and used.
- ⚡ The voltage provided by outlets is RMS (root mean square), which is a measure that represents the effective value of AC and is used by multimeters.
Q & A
What is the function of an electrical generator?
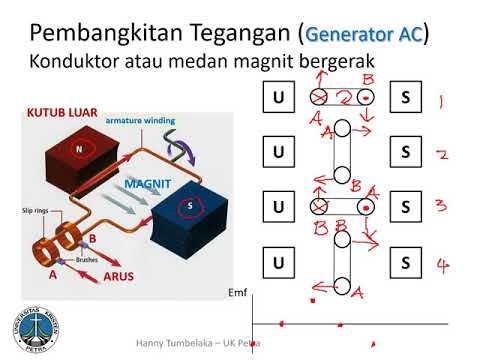
-An electrical generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, typically producing three-phase AC electricity.
What is a single-phase 60 Hz sine wave?
-A single-phase 60 Hz sine wave is a type of alternating current (AC) where the voltage varies in a smooth, continuous cycle 60 times per second.
How does the rotation of a magnet in a generator produce electricity?
-The rotation of a magnet in a generator produces electricity by creating a changing magnetic field that induces a current in the surrounding coils of wire.
What is meant by 'three-phase AC electricity'?
-Three-phase AC electricity refers to an electrical system where three separate sine waves occur at slightly different times on three different wires, providing a more constant output power.
Why are LEDs used in the demonstration of alternating current direction?
-LEDs are used in the demonstration of alternating current direction because they only allow current to flow in one direction, which helps to show the forward and backward flow of current in a sine wave.
How does the frequency of an AC power source affect the magnet's rotation speed?
-The frequency of an AC power source determines how many times the sine wave repeats per second, which in turn affects how many times the magnet must rotate per minute to achieve that frequency.
What is the significance of the 120° spacing between the coils in a three-phase generator?
-The 120° spacing between the coils in a three-phase generator ensures that the sine waves produced by each coil are evenly spaced, providing a balanced and more constant output power.
Why do most homes receive single-phase connections instead of three-phase?
-Most homes receive single-phase connections because they generally require less power and have fewer appliances to power, making single-phase connections sufficient and more cost-effective.
What is the difference between a Y connection and a Delta connection in a three-phase system?
-In a Y connection, the loads connect to a neutral point, providing a lower voltage across each phase and allowing for a neutral wire. In a Delta connection, the loads connect across two phases directly, which can deliver more power but is typically used for balanced loads only.
How is the root mean square (RMS) voltage calculated, and why is it important?
-The RMS voltage is calculated by squaring the instantaneous voltage values to make them all positive, summing them, taking the mean, and then taking the square root. It is important because it represents the effective voltage that produces the same amount of heat in a resistor as a DC voltage of the same value, allowing for accurate power calculations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)