Introduction to the concept of Data and Database Management System Part 2
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into data validation within database management systems, emphasizing its importance for data accuracy and security. It discusses various validation techniques like alphabetic, numeric, range, and consistency checks to ensure data integrity. The lecture also touches on the evolution of database management software, their advantages like consistency, reduced redundancy, and enhanced security. Furthermore, it introduces database architecture, explaining one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships, crucial for efficient data management across businesses of all sizes.
Takeaways
- 📚 The session is a continuation of an introduction to data and database management systems, focusing on data validation.
- 🔍 Data validation is crucial to ensure that only data fitting the specifications of a field is entered, reducing errors and maintaining data integrity.
- 🛡️ Primary data validation is emphasized, as secondary data should have been validated at the initial collection stage.
- 🔤 Examples of data validation include ensuring that alphabetic characters are used for names and numeric checks for dates or phone numbers.
- 💾 Different database management software like Microsoft Access, MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server are mentioned, each with its own capabilities for data validation.
- 🔑 Data validation techniques such as range checks, consistency checks, and completeness checks are discussed to guide data quality.
- 💼 The importance of accurate data is highlighted, as wrong data can lead to poor decisions and significant consequences, like the collapse of investments.
- 💼 Database management systems (DBMS) provide advantages like consistency, reduced redundancy, improved data integrity and accuracy, and adaptability to changes.
- 🔐 DBMS also enhances security and privacy of data, ensuring that only authorized access and use of information are allowed.
- 🏛️ Database architecture is briefly touched upon, with examples of one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships in data organization.
- 🌐 The speaker emphasizes the universal need for database management, from small businesses to multinational corporations, to leverage the benefits of electronic DBMS.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the second part of the introduction to data and database management systems?
-The main focus is on data validation, including what it is, how to implement it, and why it is necessary for ensuring data quality and accuracy in database management systems.
Why is data validation important in the context of database management?
-Data validation is crucial because it ensures that only data fitting the specifications of a field is entered, which minimizes errors and maintains the integrity and accuracy of the data.
What are some examples of data validation techniques mentioned in the script?
-Examples include alphabetic checks, numeric checks, range checks, consistency checks, and completeness checks.
How does data validation contribute to the quality of data in a database?
-Data validation contributes to data quality by guiding the type, size, and nature of data entered into each field, thus ensuring that the data is reliable and useful for decision-making.
What are some of the database management software options mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions Microsoft Access, SQL, MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server as examples of database management software.
What are the advantages of using database management software for data management?
-Using database management software offers advantages such as data consistency, reduced redundancy, improved data integrity and accuracy, enhanced adaptability to changes, improved performance, and enhanced security and privacy of information.
What is the significance of database architecture in managing data?
-Database architecture is significant as it determines how data is organized and related within the database, affecting the efficiency and effectiveness of data retrieval and management.
Can you explain the one-to-one relationship in database architecture as described in the script?
-A one-to-one relationship in database architecture refers to a situation where one record in a table is related to only one record in another table, such as a table holding personal information relating to a table holding transaction information.
What is meant by a one-to-many relationship in the context of database architecture?
-A one-to-many relationship in database architecture occurs when one record in a table is related to multiple records in another table, such as a table with personal data relating to multiple tables with transaction, credit, and vendor information.
How is a many-to-many relationship different from one-to-one and one-to-many relationships in database architecture?
-A many-to-many relationship is different as it involves multiple records in one table relating to multiple records in another table, such as multiple projects each having multiple accounts, each with its own transactions and creditors.
What are the implications of different database relationships for business operations?
-Different database relationships impact business operations by affecting how data is accessed, managed, and utilized, which in turn influences business decisions, efficiency, and the ability to adapt to changes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is a Database?
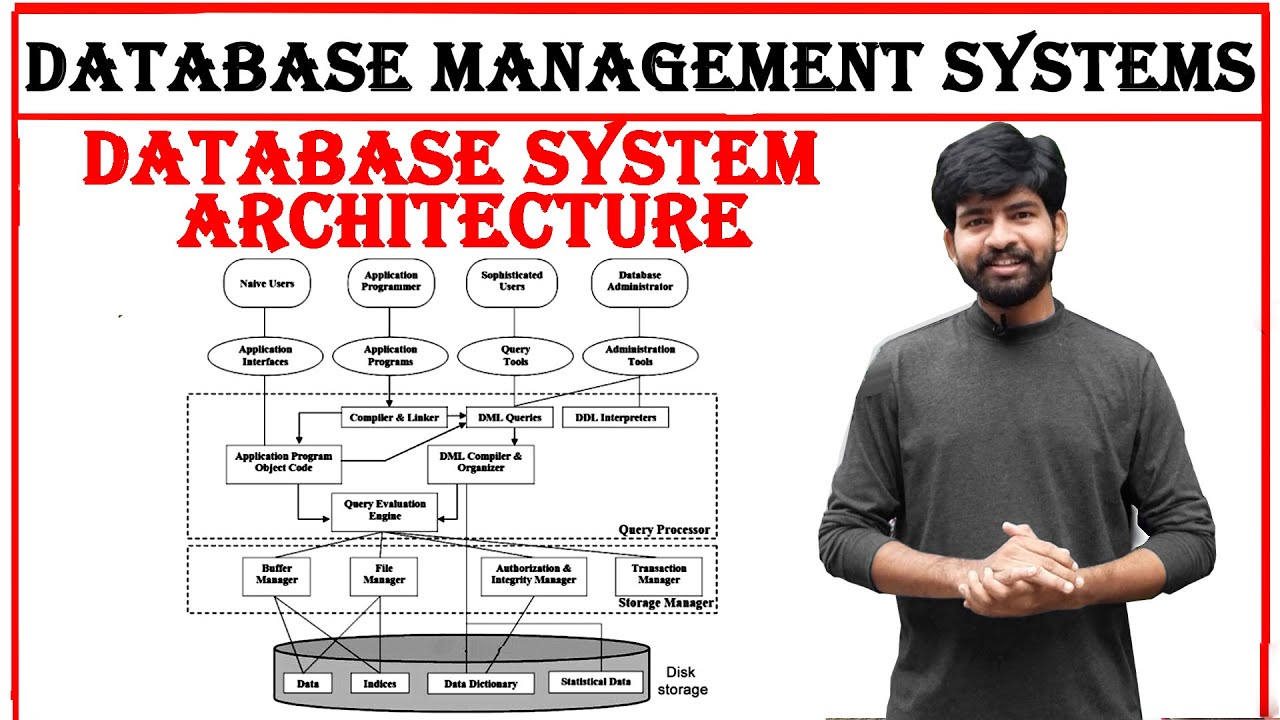
database system architecture in dbms | database management system | Architecture | DBMS | btech

Pemrograman Basis Data : Introduction

INPUT, PROSES, OUTPUT, STORAGE & KONTROL DALAM SISTEM INFORMASI MANAJEMEN (SIM) | ANSHAR AKIL

Manajemen Data dan Informasi

Introduction to the concept of Data and Database Management System
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)