Gerak Parabola Fisika Kelas 10 - materi fisika SMA - Gerak parabola
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the parabolic motion of objects, exemplified by a softball game where the ball's trajectory forms a parabola. It explains the characteristics of parabolic motion, including the constant horizontal velocity and accelerating vertical velocity due to gravity. The script also covers the mathematical representation of this motion, including initial velocity components, the effect of gravity, and formulas for calculating maximum height, range, and time of flight. It highlights Galileo's contribution to understanding projectile motion and emphasizes the importance of considering the initial position and angle of projection.
Takeaways
- 🏋️♂️ The trajectory of an object in motion, such as a ball in sports, often follows a parabolic path due to the influence of gravity.
- 📚 Galileo first described the parabolic motion, analyzing the horizontal and vertical components of the motion.
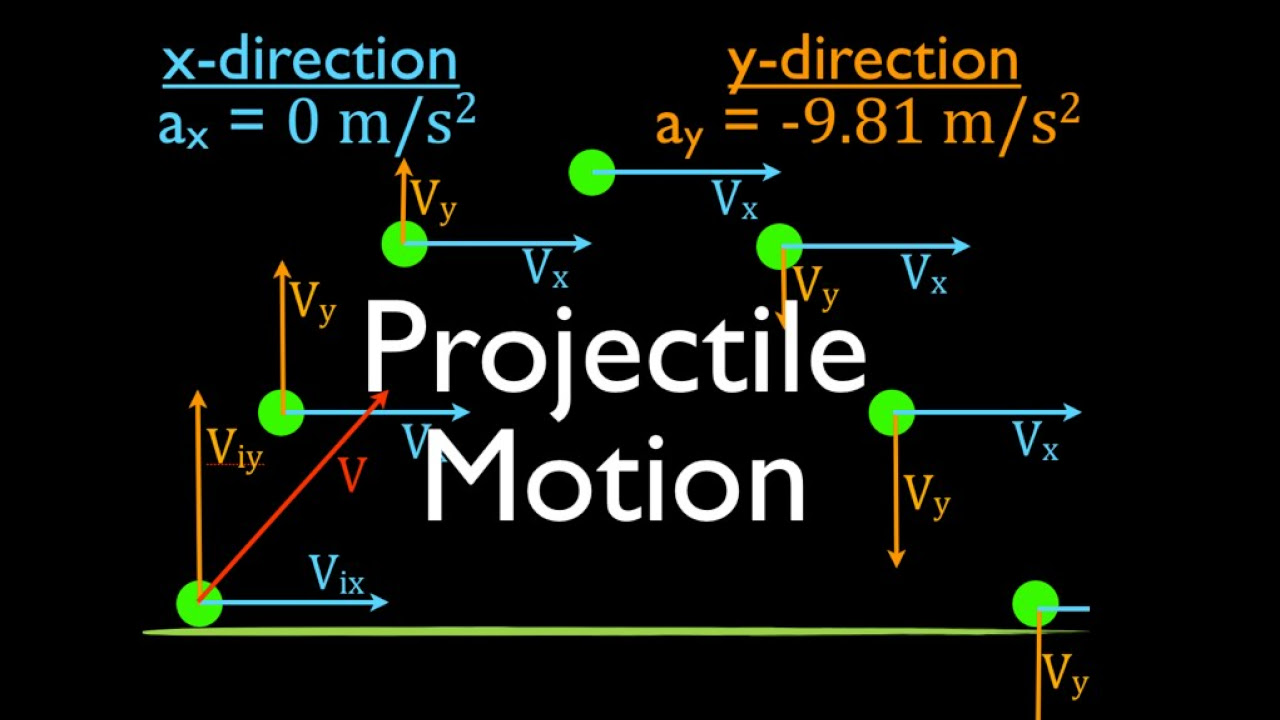
- 🔄 In parabolic motion, an object moves in two dimensions, with constant velocity in the horizontal direction (x-axis) and accelerating velocity in the vertical direction (y-axis) due to gravity.
- 🎾 The characteristics of parabolic motion are observed in various sports, including football, volleyball, and badminton, where the trajectory of the ball is curved.
- 📉 The vertical component of the velocity changes due to the acceleration caused by gravity, which is represented as g in the equations.
- 🔢 The initial velocity of the object can be broken down into horizontal (v_{0x}) and vertical (v_{0y}) components using trigonometric functions of the launch angle (α).
- 🔄 The horizontal velocity remains constant throughout the motion, while the vertical velocity changes due to the acceleration of gravity.
- 📈 The maximum height reached by the object in parabolic motion can be calculated using the initial vertical velocity and the acceleration due to gravity.
- 📏 The range or the farthest point reached by the object can be determined using the initial velocity and the launch angle.
- 🕒 The time taken to reach the highest point or the time of flight can be calculated using the initial vertical velocity and the acceleration due to gravity.
Q & A
What is the shape of the trajectory followed by a softball when it is hit?
-The trajectory followed by a softball when it is hit is parabolic.
What is the characteristic shape of a parabolic motion?
-The characteristic shape of parabolic motion is a curved path, similar to the trajectory of a football when it is kicked.
Which sport activities can exhibit parabolic motion besides football?
-Parabolic motion can also be observed in sports like volleyball, badminton, and long jump.
Why can air resistance be ignored in the case of parabolic motion?
-Air resistance can be ignored in parabolic motion because the focus is on the initial velocity and gravitational forces, which are the primary determinants of the trajectory.
Who first described the parabolic motion or projectile motion?
-Galileo first described parabolic motion, analyzing the horizontal and vertical components of the motion.
What are the two dimensions in which an object in parabolic motion moves?
-An object in parabolic motion moves in two dimensions, specifically along the x-axis and y-axis.
What is the initial velocity component along the x-axis represented by?
-The initial velocity component along the x-axis is represented by v_0 cos(α), where v_0 is the initial velocity and α is the angle of projection.
What is the relationship between the initial velocity component along the y-axis and the angle of projection?
-The initial velocity component along the y-axis is represented by v_0 sin(α), indicating that it is directly proportional to the sine of the angle of projection.
What is the acceleration experienced by an object in parabolic motion along the x-axis?
-The acceleration experienced by an object in parabolic motion along the x-axis is zero because there is no change in horizontal velocity.
How is the acceleration experienced by an object in parabolic motion along the y-axis described?
-The acceleration experienced by an object in parabolic motion along the y-axis is the acceleration due to gravity, which is represented as g and is directed downward.
What is the significance of the angle α in the context of parabolic motion?
-The angle α in parabolic motion is significant as it determines the initial velocity components in both the x and y directions, affecting the trajectory of the object.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Isto é Matemática T02E01 A Parábola da Parábola - Parte 1

Gerak Parabola | Fisika Kelas 10 - KHATULISTIWA MENGAJAR

Der waagerechte Wurf - tolles Experiment

Gerak Parabola - Fisika Kelas 10 (Quipper Video)
Two Dimensional Motion (1 of 4) An Explanation
12-88 | Engineering Dynamics Hibbeler 14th Edition | Engineers Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)