Convection
Summary
TLDRThis video explores convection, the heat transfer mechanism caused by the bulk movement of fluids. It explains how water in a pot boils due to warm water rising and cool water sinking, a process driven by density differences from temperature changes. The video also discusses atmospheric convection, exemplified by Hadley cells, and oceanic convection, both influenced by the Earth's tilt and solar heat distribution. Additionally, it touches on the hypothesis of mantle convection as a driving force behind plate tectonics, featuring the creation of rifts, subduction zones, and volcanoes.
Takeaways
- 🔥 Convection is the process of heat transfer due to the bulk movement of fluids, such as water in a pot or air in the atmosphere.
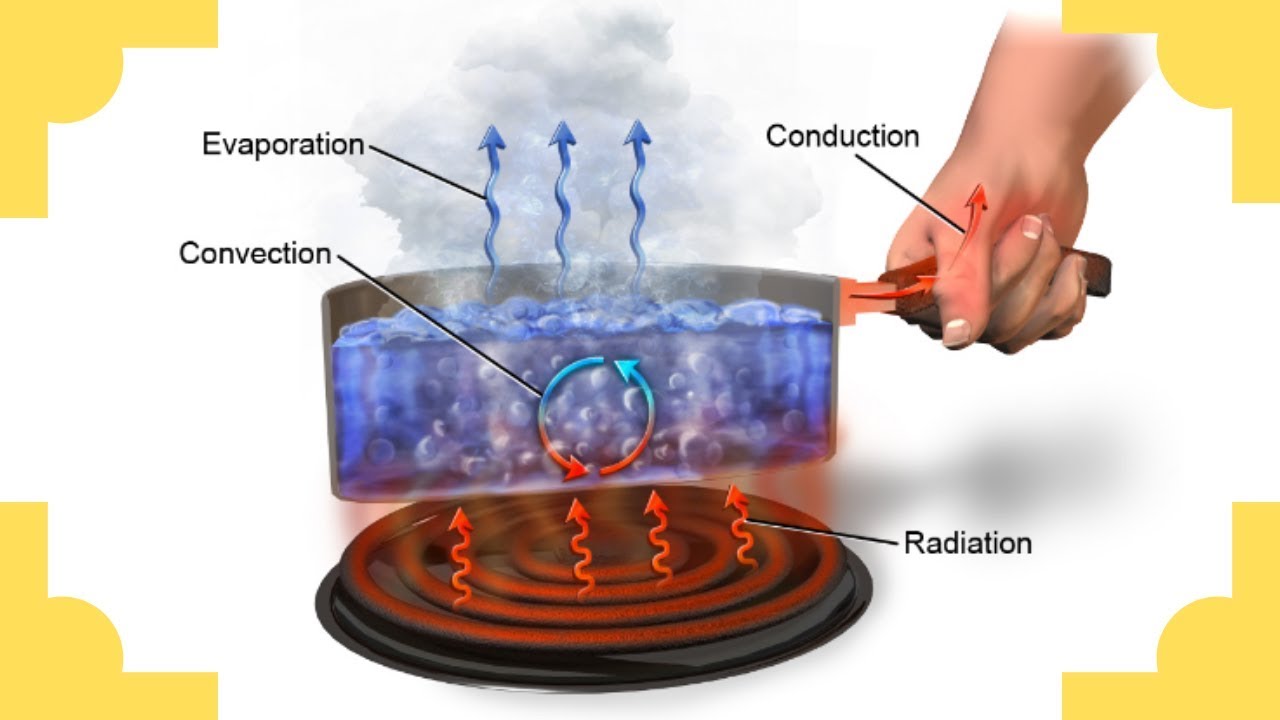
- 💧 In a pot of boiling water, bubbles form due to the convection process where heated water rises and cooler water sinks.
- 🌀 Convection is driven by differences in density caused by temperature changes, with warmer, less dense materials rising and cooler, denser materials sinking.
- 🌍 Hadley cells are large convection cells in the Earth's atmosphere, influenced by the tilt and position of the Earth relative to the Sun.
- ☀️ The equator receives consistent heat from the Sun, causing warm air to rise and create convection currents that move toward the poles.
- 🌐 At 30-degree latitudes, warm air rises, cools at the poles, and then sinks back to the Earth's surface, contributing to atmospheric convection.
- 🌊 Oceans also experience convection, with warm water at the equator moving toward the cooler poles, where it cools and sinks.
- 🌋 Mantle convection is hypothesized to drive plate tectonics, with magma moving towards the Earth's surface, cooling, and sinking back towards the center.
- 🏔️ Mantle convection can lead to the formation of spreading rifts, hot spots, subduction zones, mountains, and volcanoes.
- 👨🏫 This educational video from 'Teacher's Pet' aims to inform viewers about the concept of convection and its various manifestations on Earth.
Q & A
What is convection?
-Convection is the heat transfer due to the bulk movement of fluids, such as water, air, or molten rock, in response to temperature differences. It involves the rising of warmer, less dense material and the sinking of cooler, denser material under the influence of gravity.
How does convection occur in a pot of boiling water?
-In a pot of boiling water, convection occurs as the water near the heat source warms up, becomes less dense, and rises to the top. Once it reaches the surface, it cools, becomes denser, and sinks back to the bottom.
What causes the turbulent motion observed in boiling water?
-The turbulent motion in boiling water is caused by the convection currents. The heated water at the bottom rises, creating wiggly paths and turbulent movement as it interacts with the cooler water above.
What are Hadley cells, and how are they related to convection?
-Hadley cells are large convection cells in the Earth's atmosphere. They are driven by convection due to the angle of Earth's tilt and its position relative to the Sun, causing warm air to rise at the equator and move toward the poles, where it cools and sinks back to the Earth's surface.
How does convection affect the Earth's climate?
-Convection affects the Earth's climate by distributing heat from the equator to the poles. This process helps in maintaining a relatively stable temperature distribution across the planet, despite the varying amounts of solar radiation received at different latitudes.
What is the role of convection in the oceans?
-Convection in the oceans helps in the distribution of heat and nutrients. Warm water at the equator rises and moves toward the poles, while cooler water sinks and is returned to the equator, creating a continuous circulation pattern known as thermohaline circulation.
What is the relationship between mantle convection and plate tectonics?
-Mantle convection is the proposed driving force behind plate tectonics. The movement of magma within the Earth's mantle due to convection can create spreading rifts, subduction zones, and volcanic activity, all of which contribute to the movement and interaction of the Earth's tectonic plates.
How does the Earth's interior heat contribute to mantle convection?
-The Earth's interior is very hot, and this heat causes the mantle material to become less dense when it is heated. This less dense material rises towards the Earth's surface, cools, and then sinks back towards the center, creating a convection current.
What are the signs of mantle convection on the Earth's surface?
-Signs of mantle convection on the Earth's surface include the formation of spreading rifts, hot spots, subduction zones, and volcanic activity. These features are evidence of the movement of magma and tectonic plates driven by the convection currents in the mantle.
How does convection differ in liquids compared to gases?
-Convection in liquids and gases involves the same principle of rising warm, less dense material and sinking cool, denser material. However, gases are less dense and more easily compressible than liquids, which can result in more rapid and turbulent convection currents in gases compared to liquids.
What are some practical applications of understanding convection?
-Understanding convection is important in various fields such as meteorology, oceanography, and geology. It helps in predicting weather patterns, understanding climate change, managing energy resources, and studying the geological processes that shape the Earth's surface.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Conduction -Convection- Radiation-Heat Transfer

CONVECÇÃO TÉRMICA (Física - 2o ANO)

Heat Transfer - Conduction, Convection, and Radiation

MANTLE CONVECTION (Grade 10 Science Lesson)

GCSE Physics - Conduction, Convection and Radiation #5

Física Térmica, Experimento 05: Propagação de Calor por Convecção - 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)