Grade 8 Science Q1 Ep5: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Teacher MJ from Deb Ed TV explores the concepts of potential and kinetic energy. The episode begins with a review of Newton's laws of motion and progresses to an interactive lesson where viewers are challenged to answer questions about energy transformation. The script explains the factors affecting both types of energy, using real-life examples like a falling object and a thrown ball to illustrate the principles. The video also covers the relationship between work, energy, and force, and includes a practical problem-solving segment to reinforce learning. The engaging format aims to make physics accessible and enjoyable for viewers.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is an educational episode focused on exploring scientific concepts, specifically potential and kinetic energy.
- 🔍 The host, Teacher MJ, reviews Newton's three laws of motion, emphasizing the law of inertia, acceleration, and interaction.
- 🧠 The lesson's goal is to identify and explain the factors affecting potential and kinetic energy, which are key to understanding motion and forces.
- 📉 The script presents a quiz to engage viewers, asking questions about the transformation of potential and kinetic energy as an object falls.
- 🎾 An example of a ball thrown vertically is used to illustrate the concept that potential energy is greater than kinetic energy at the highest point.
- 🚗 The script clarifies that velocity is the primary factor influencing a car's kinetic energy while traveling, not mass, size, or weight.
- 🔄 The factors affecting kinetic energy are mass and velocity, as opposed to force and distance or mass and height.
- ⬆️ The illustration in the script helps to explain which points in a motion scenario have increasing kinetic energy and the greatest potential energy.
- ⚖️ Potential energy is dependent on an object's mass and its position relative to the ground, not on its velocity or the strength of gravity.
- 🎸 The script uses examples to show that potential energy is not applicable to actions without the transfer of energy, such as a person playing a guitar.
- 🔢 The kinetic energy of an object increases four times if its velocity is doubled, demonstrating the direct relationship between velocity and kinetic energy.
Q & A
What are the three laws of motion discussed in the previous episode?
-The three laws of motion discussed in the previous episode are Newton's Law of Inertia, Law of Acceleration, and Law of Interaction.
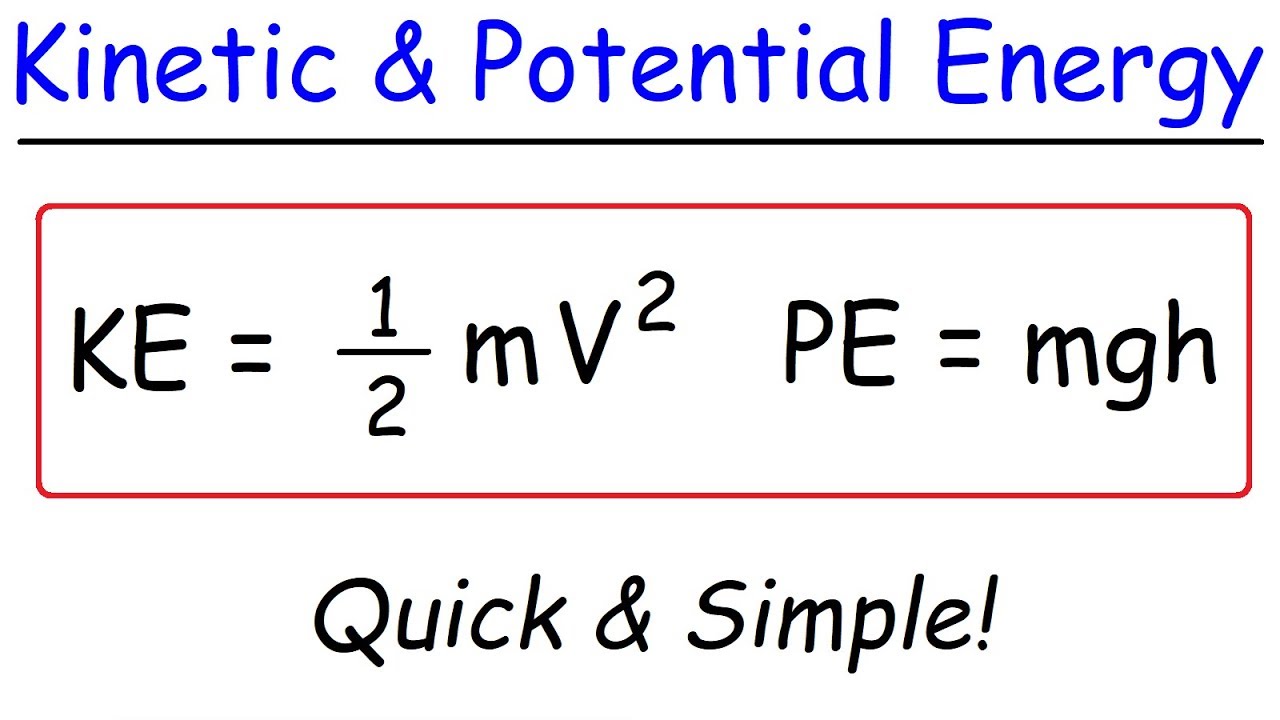
What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy?
-Potential energy is the stored energy an object possesses due to its position or state, while kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion.
What happens to an object's potential and kinetic energy as it falls freely from a height?
-As an object falls freely from a height, it loses potential energy and gains kinetic energy.
Compare the potential energy of a ball at its highest point when thrown vertically upward to its kinetic energy at that point.
-At the highest point of its vertical throw, a ball's potential energy is greater than its kinetic energy.
Which factor has the greatest influence on the amount of kinetic energy a car has while traveling on a highway?
-The velocity of the car has the greatest influence on its kinetic energy.
What are the factors that affect kinetic energy according to the script?
-The factors that affect kinetic energy are mass and velocity.
Which point in the illustration has the greatest potential energy?
-Point b in the illustration has the greatest potential energy.
What is true about potential energy in relation to an object's mass and location?
-Potential energy is affected by the mass of the object and its location with respect to the ground.
What does not affect the amount of potential energy an object possesses?
-Velocity does not affect the amount of potential energy an object possesses.
How does the kinetic energy of an object change if its velocity is doubled?
-If an object's velocity is doubled, its kinetic energy increases four times.
What is the concept of work in physics, and how is it related to energy?
-In physics, work is an abstract idea related to energy, where energy is needed for an object to do work. Work is done when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)