Isolating Plasmid DNA
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers a detailed guide on manipulating plasmids, circular DNA segments used in genetic engineering. It explains the process of introducing synthetic plasmids into bacteria, using them as vectors for gene replication and expression. The script outlines the steps for plasmid DNA extraction from bacteria, including transformation, isolation using a mini prep kit, and purification through centrifugation and silica matrix binding. The final product is purified plasmid DNA, ready for use in various biological applications.
Takeaways
- 🧬 A plasmid is a circular, non-chromosomal DNA segment found in some bacteria and is used as a vector for genetic engineering.
- 🔬 Biologists can manipulate plasmids in vitro and introduce them into bacteria, often using selectable markers like antibiotic resistance genes.
- 🔄 Plasmids typically include an origin of replication, a multiple cloning site, and the gene or DNA sequence of interest.
- 🌱 Transformation is the process used to introduce plasmids into bacteria, which is not always 100% efficient but can be made efficient through antibiotic selection.
- 📈 Bacterial cells can replicate plasmid DNA, allowing for the production of large amounts of specific DNA sequences.
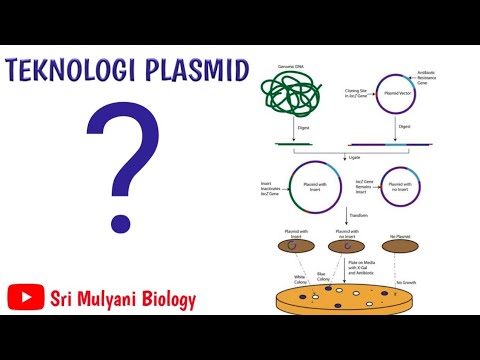
- 🧪 Plasmid isolation kits, or minir prep kits, are used to extract plasmid DNA from bacteria through a series of steps involving buffers and a purification column.
- 🧫 The process begins with an overnight culture of transformed bacteria, followed by centrifugation to separate bacterial cells from the growth medium.
- 🌡️ Resuspension and lysis buffers are used to break open the cells and release plasmids, with care taken to avoid shearing genomic DNA.
- 🌀 Neutralization buffer is added to precipitate cellular debris and leave plasmid DNA in solution, followed by centrifugation to separate the components.
- 🧴 The supernatant containing plasmid DNA is passed through a spin column with a silica matrix that binds to the DNA, allowing for purification.
- 💧 Finally, elution buffer is used to release the purified plasmid DNA from the silica matrix, yielding the desired DNA for further use.
Q & A
What is a plasmid?
-A plasmid is a circular, non-chromosomal segment of DNA that exists in some bacteria and can be manipulated by biologists for various genetic engineering purposes.
How are plasmids used in genetic engineering?
-Plasmids are used as vectors to replicate or express particular genes or DNA sequences of interest that have been inserted into them.
What is a selectable marker on a plasmid?
-A selectable marker, such as an antibiotic resistance gene, is a feature on a plasmid that allows for the selection of cells that have successfully taken up the plasmid.
What is the purpose of an origin of replication on a plasmid?
-The origin of replication is a specific DNA sequence that allows the plasmid to be replicated within a host cell.
What is a multiple cloning site or polylinker?
-A multiple cloning site or polylinker is an area on a plasmid with many known restriction enzyme sites where a gene or DNA sequence of interest can be inserted.
How are plasmids introduced into bacteria?
-Plasmids are introduced into bacteria through a process called transformation, which is not 100% efficient but can be made more successful with antibiotic selection.
Why is antibiotic selection used after introducing plasmids into bacteria?
-Antibiotic selection is used to efficiently select for cells carrying the plasmid of interest because bacteria with the plasmid will be resistant to the antibiotic.
How can bacterial cells serve as factories for making large amounts of plasmid DNA?
-Bacterial cells can serve as factories because they replicate plasmid DNA before each cell division, and some plasmids are present in multiple copies per cell, allowing for rapid production of plasmid DNA.
What is a plasmid isolation kit or mini-prep kit?
-A plasmid isolation kit, sometimes called a mini-prep kit, contains various buffers and a column that binds to plasmid DNA to purify it from bacterial cells.
What are the steps involved in extracting plasmid DNA from bacteria using a mini-prep kit?
-The steps include labeling tubes, harvesting bacterial cells by centrifugation, resuspending cells in resuspension buffer, lysing cells with L buffer, neutralizing with neutralization buffer, centrifuging to precipitate debris, passing the supernatant through a spin column, washing the column, and eluting the purified plasmid DNA with elution buffer.
Why is it important to balance the centrifuge when spinning bacterial cultures?
-Balancing the centrifuge ensures even distribution of weight and prevents uneven spinning, which could affect the pellet formation and the quality of the plasmid DNA isolation.
How does the addition of neutralization buffer affect the DNA during the plasmid DNA extraction process?
-The neutralization buffer returns the pH to neutral, allowing DNA strands to renature. Chromosomal DNA forms an insoluble precipitate with cellular debris, while plasmid DNA remains in solution.
What is the role of the silica matrix in the spin column during plasmid DNA purification?
-The silica matrix in the spin column binds to the plasmid DNA, allowing it to be separated from other cellular components like RNA, proteins, and salts that pass through the membrane.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cloning Vectors | Plasmid | Insertional Inactivation |Cosmid|Artificial Chromosome|Class 11 Biology

What is a Plasmid? - Plasmids 101
TEKNOLOGI PLASMID (KLONING GEN/DNA REKOMBINAN)

GMOs | Genetics | Biology | FuseSchool

Plasmids | Genetics | Biology

Genetic Modification Explained || Insulin-Producing Bacteria
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)