Why don't oil and water mix? - John Pollard
Summary
TLDRThis script explores why salt dissolves in water while oil does not, delving into the principles of chemistry, energetics, and entropy. Water molecules engage in a constant 'dance' of hydrogen bonding, and salt ions, once separated, join this dance, increasing the possible arrangements. In contrast, oil molecules, larger and less compatible, disrupt the water's dance, leading to a preference for oil to separate and form its own group, illustrating the complex interplay of molecular forces and random motion.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Salt dissolves in water due to the balance between energetics (attractive forces) and entropy (random motion and arrangement of particles).
- 🌌 In a glass of water, there are more molecules than known stars in the universe, illustrating the scale at which molecular interactions occur.
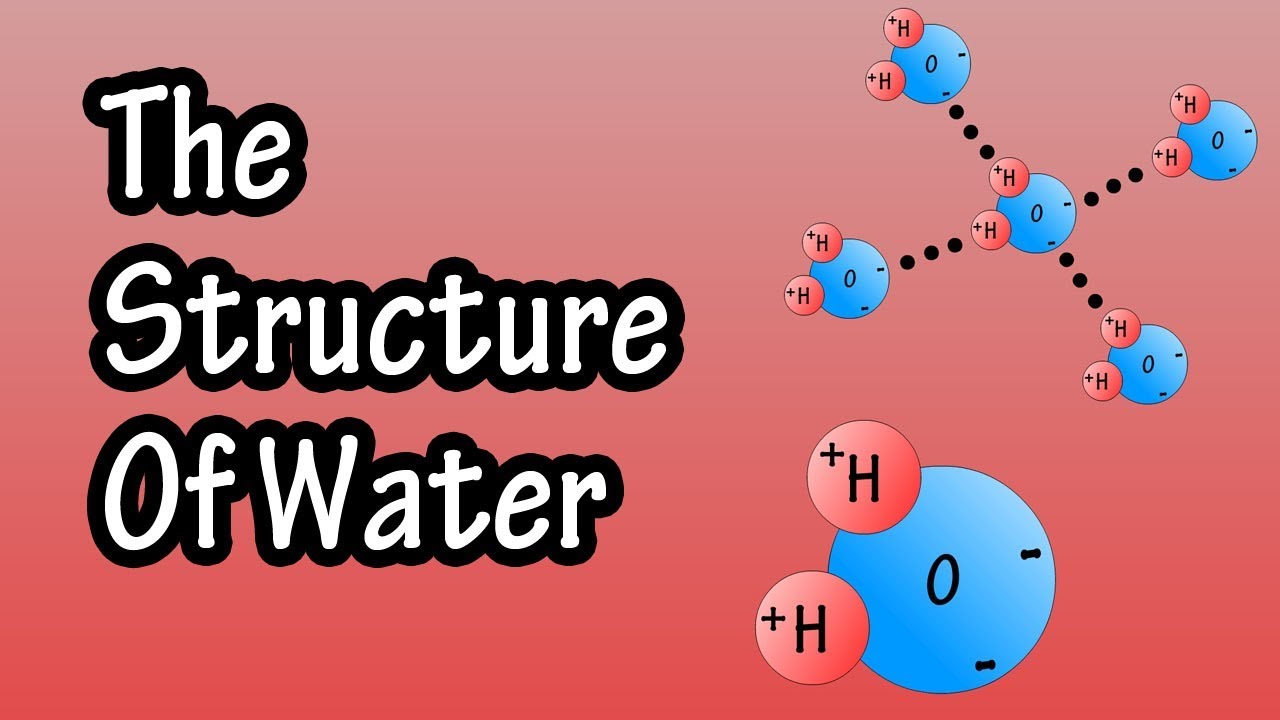
- 💧 Water molecules are in constant motion, vibrating, and rotating, held together by hydrogen bonding, which is a form of energetic interaction.
- 🕺 Entropy favors mixing, as there are more possible arrangements for mixed molecules compared to separated ones, like a square dance versus a line dance.
- 🧂 When salt is added to water, its ions (sodium and chlorine) are initially reluctant but eventually join the water's 'dance', increasing the possible arrangements and thus are favored to stay mixed.
- 🚫 Oil molecules, being larger and less compatible with water's hydrogen bonding network, disrupt the water's dance and are not favored to mix.
- 👗 The 'ballgowns' metaphor for oil molecules suggests their size and lack of compatibility with water, leading to their exclusion from the water's dance.
- 🤝 The interaction between water and substances is determined by how they can engage with water's hydrogen bonding and how they affect the water's self-interaction.
- 🔄 The constant random exchange of partners in water's 'dance' is a key factor in whether substances can dissolve or not.
- 🤷♂️ Oil molecules, when forced into the water's dance, take up too much space and disrupt the dance, leading to them being pushed out and forming a separate group.
- 💃 The final state of a mixture is dictated by the interplay between molecular interactions and the entropy-driven tendency for particles to arrange in the most possible ways.
Q & A
Why does salt dissolve in water?
-Salt dissolves in water because the energetics of the interaction between salt ions and water molecules favor the salt ions joining the water's hydrogen bonding network, enhancing the possible dance positions and thus increasing entropy.
What is the role of entropy in the dissolution of salt in water?
-Entropy favors the mixing of salt in water because it increases the number of possible arrangements or 'dance positions' for the water molecules, making it more likely for salt ions to stay mixed with water.
How does the size of oil molecules affect their interaction with water?
-The size of oil molecules is disruptive to the water's hydrogen bonding network, as they are much larger than water molecules and take up more space, hindering the random exchange of partners in the water's 'dance'.
Why do oil and water not mix?
-Oil and water do not mix because the interactions between oil molecules and water molecules are weak, and the configurations available to them when moving randomly favor the oil molecules sticking together rather than mixing with water.
What is the 'square dance' metaphor referring to in the context of water molecules?
-The 'square dance' metaphor refers to the constant and random hydrogen bonding network among water molecules, where they engage in a dynamic and random exchange of partners.
How does the energetics of water molecules influence their interaction with other substances?
-The energetics of water molecules, which involves the strength of their interactions, plays a crucial role in determining whether other substances can mix well with water or not.
What is the significance of the hydrogen bonding network in water?
-The hydrogen bonding network in water is significant because it is the primary force that holds water molecules together and influences their interactions with other substances, including their ability to dissolve salts.
Why are salt ions eager to join the water's 'dance'?
-Salt ions are eager to join the water's 'dance' because once they are part of the hydrogen bonding network, they can engage in more possible interactions, which is entropically favorable.
How does the concept of energetics relate to the interaction between oil and water?
-In the interaction between oil and water, energetics relates to the lack of strong attractive forces between the two, which means that the oil molecules are not drawn to the water's hydrogen bonding network and thus do not mix.
What is the role of molecular motion in the mixing of substances in water?
-Molecular motion is crucial in the mixing of substances in water as it allows for the random interactions and exchanges that can lead to dissolution or the formation of separate phases.
How does the balance between energetics and entropy determine the solubility of substances in water?
-The balance between energetics and entropy determines solubility in water by considering both the attractive forces between molecules and the possible arrangements of molecules, which together influence whether a substance will mix or separate.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
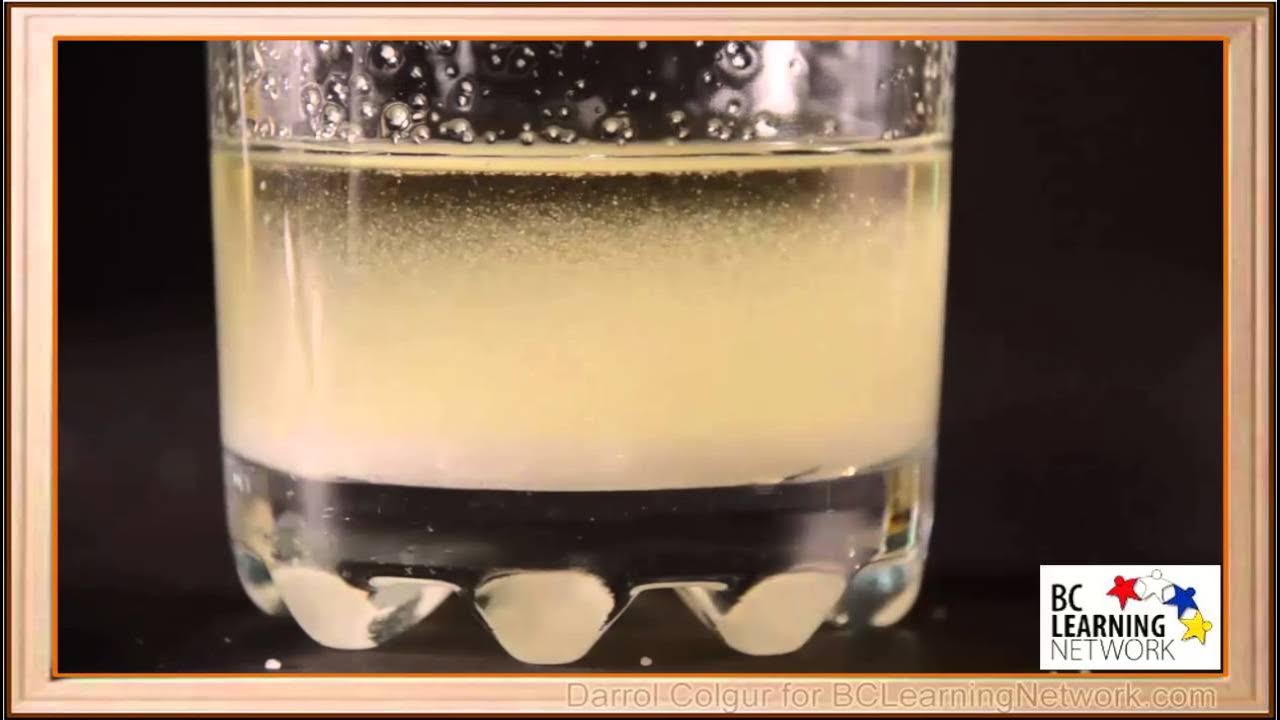

WCLN - Solubility - What dissolves in what?

The chemistry of cold packs - John Pollard

Strong, Weak, and Non-Electrolytes

Pop Up Science: Oil and Water

Compare solubility of salt, sugar and chalk | Solutions | Chemistry
Structure Of Water Molecule - Chemistry Of Water - Properties Of Water - Composition Of Water
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)