Spermatogenesis
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script explores spermatogenesis, the process of sperm production in males. It details the journey from spermatogonia to spermatozoa, occurring in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. The script explains the cellular transformations through mitosis and two meiotic divisions, resulting in haploid sperm cells. It also touches on the role of Sertoli cells in providing nutrients. The process culminates in the formation of four mature sperm cells capable of fertilization, highlighting the complexity of male gamete development.
Takeaways
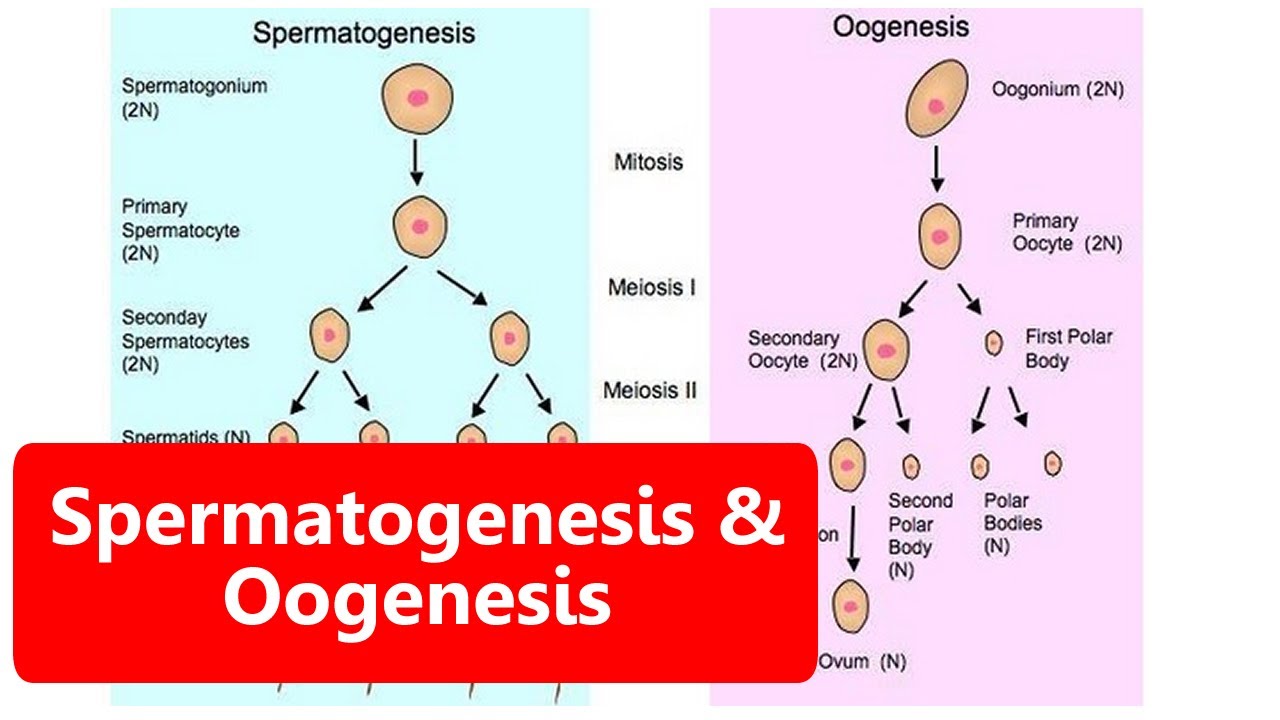
- 😎 Spermatogenesis is the process of male gamete production, specifically the creation of sperm, also known as spermatozoa.
- 🔬 This process occurs in the testis, with the seminiferous tubules being the site of spermatogenesis.
- 🌟 After production, sperm is stored in the epididymis, from where it is transported through the sperm duct during ejaculation.
- 📍 The spermatogenesis process takes place in the walls of the seminiferous tubules, where sperm cells begin as primordial germ cells.
- 📈 The primordial germ cell undergoes mitosis to produce spermatogonia, which are diploid cells containing 2n chromosomes.
- 🔄 The spermatogonium develops into a primary spermatocyte without changing the chromosome number, still at 2n.
- 🧬 Meiosis I reduces the chromosome number from 2n to n, producing secondary spermatocytes with a haploid number of chromosomes.
- 🔄 Meiosis II further divides the secondary spermatocytes into spermatids, maintaining the haploid chromosome count.
- 🌱 Spermatids are immature sperm cells that undergo spermiogenesis, a differentiation process to develop into mature spermatozoa.
- 🏋️♂️ The Sertoli cell plays a crucial role by providing nutrients necessary for the spermatogenesis process.
Q & A
What is the process of sperm production in males called?
-The process of sperm production in males is called spermatogenesis.
Where does spermatogenesis take place in the male body?
-Spermatogenesis takes place in the seminiferous tubules within the testis.
What is the role of the epididymis in the sperm production process?
-The epididymis is where sperm is stored after it has been produced.
How does sperm leave the testis during ejaculation?
-Sperm leaves the testis through a duct known as the sperm duct, vas deferens, or ductus deferens, which connects to the urethra.
What is the initial cell type that undergoes mitosis to produce spermatogonia?
-The initial cell type that undergoes mitosis to produce spermatogonia is the primordial germ cell.
What is the significance of the number of chromosomes in a spermatogonium?
-A spermatogonium has a diploid number of chromosomes (2n), meaning it contains both sets of chromosomes from homologous pairs.
What is the first meiotic division called and what does it produce?
-The first meiotic division is called Meiosis I, and it produces secondary spermatocytes with a haploid number of chromosomes (n).
How many spermatids are produced from one spermatogonium after the second meiotic division?
-One spermatogonium produces four spermatids after the second meiotic division.
What is the process that spermatids undergo to develop into mature sperm cells called?
-The process that spermatids undergo to develop into mature sperm cells is called spermiogenesis.
What is the role of Sertoli cells in spermatogenesis?
-Sertoli cells provide nutrients and support during spermatogenesis, aiding in the development of sperm cells.
What are the five processes involved in the sperm production as described in the script?
-The five processes involved in sperm production are mitosis to produce spermatogonia, growth into primary spermatocytes, Meiosis I, Meiosis II, and differentiation into spermatids.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
SPERMATOGENESIS DAN OOGENESIS - Sistem Reproduksi Pada Manusia | Belajar IPA Kelas 9 SMP/ MTS

GAMETOGENESIS #videopembelajaranipa @nova_scienceart9251

Gamet Structure part 1

Spermatogenesis || Proses Pembentukan Sperma

Lesson 3: The Role of Hormones in Male and Female Reproductive Systems

spermatogenesis (pembentukan sel sperma) biologi sma bab.sistem reproduksi kelas 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)