mitosis 3d animation | Phases of mitosis | cell cycle and cell division | mitosis and meiosis
Summary
TLDRThis educational module delves into mitosis, a critical process for cell division and regeneration. It's broken down into four key phases: prophase, where chromatin condenses into chromosomes; metaphase, with chromosomes aligning at the cell's equator; anaphase, where sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles; and telophase, which sees the reformation of nuclei. Post-mitosis, cytokinesis partitions the cytoplasm, creating two identical daughter cells. The script offers a detailed look at the cellular mechanics behind growth and repair.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Mitosis is a cell division process that enables the regeneration of body parts.
- 🔬 The process involves the separation of nuclear chromosomes into two identical daughter nuclei.
- 📅 Mitosis is divided into four key phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- 🌱 An additional phase, cytokinesis, occurs after nuclear division and involves the partitioning of the cytoplasm.
- 🌱 Before mitosis, cells undergo interphase, a period of growth and rest where genetic material increases.
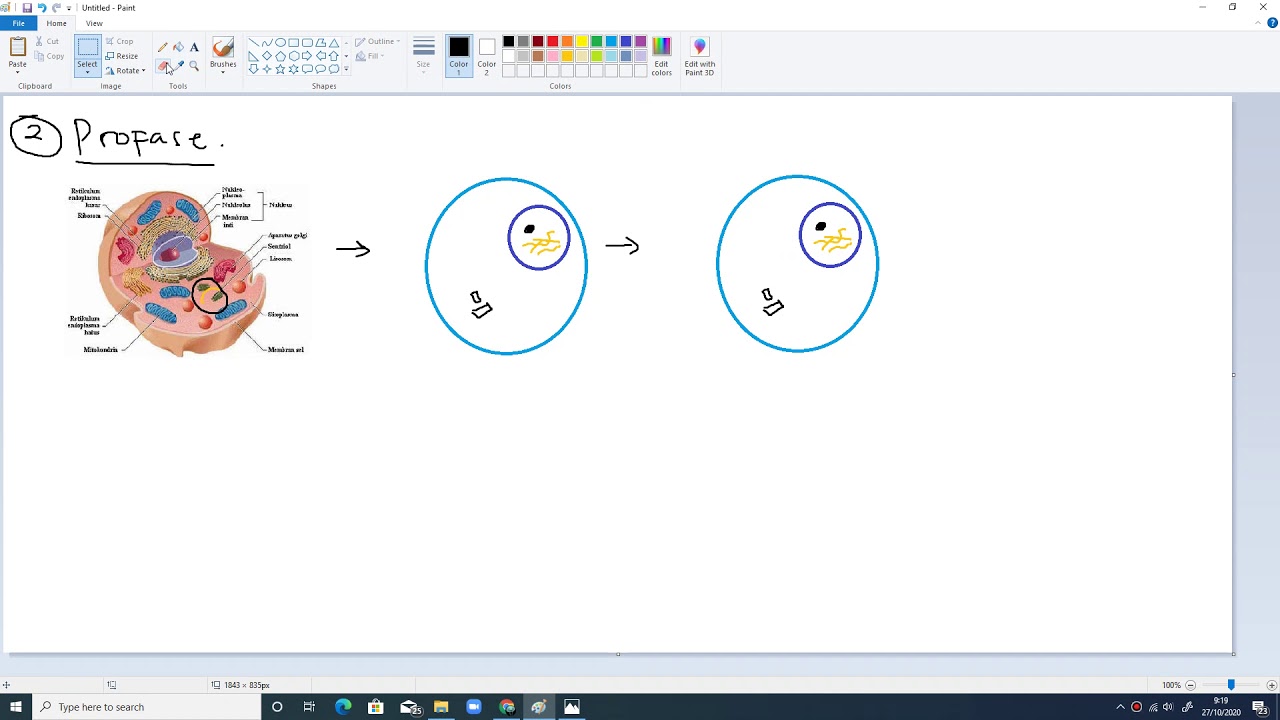
- 🧬 During prophase, chromatin condenses to form chromosomes, the nucleolus disappears, and the nuclear membrane breaks down.
- 🔭 In metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equator due to interactions with spindle microtubules.
- 🧲 Anaphase is characterized by the separation of sister chromatids and their movement towards opposite poles.
- 🔄 Telophase involves the arrival of daughter chromosomes at the poles, decondensation of chromatin, and reformation of the nuclear membrane.
- 🌿 In cytokinesis, animal cells form a cleavage furrow, while plant cells form a cell plate that leads to the creation of new cell walls.
Q & A
What is mitosis?
-Mitosis is a process of cell division that allows for the regeneration of body parts and results in two identical daughter nuclei.
What are the four key phases of mitosis?
-The four key phases of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What occurs during interphase before mitosis?
-During interphase, the cell undergoes a period of growth and rest, and the genetic material of the cell increases.
What happens to the chromatin during prophase?
-During prophase, the chromatin condenses and becomes short and thick to form chromosomes, each with two sister chromatids joined at the centromere.
What is the role of the centrosomes during mitosis?
-The centrosomes, each with a pair of centrioles, move apart to the opposite poles during prophase, forming a spindle between them.
How do microtubules interact with chromosomes during metaphase?
-During metaphase, microtubules of the spindle interact with chromosomes, causing them to align along the middle of the cell at the equatorial plate.
What is the function of the kinetochore during anaphase?
-During anaphase, the sister chromatids separate at the kinetochore, and the daughter chromosomes move towards the opposite poles as the microtubules shorten.
What changes occur during telophase?
-During telophase, the daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles, the chromatin starts to decondense, and the nuclei reform along with the nucleoli, leading to the reformation of the nuclear membrane.
How does cytokinesis differ in animals and plants?
-In animals, cytokinesis involves the formation of a cleavage furrow that divides the cytoplasm into two daughter cells, while in plants, a cell plate forms and grows outwards to create two daughter cells.
What is the significance of the separation of sister chromatids during mitosis?
-The separation of sister chromatids ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes, maintaining genetic integrity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)