Metabolism & Nutrition, Part 1: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #36
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the intricate processes of human metabolism, detailing how our bodies convert food into energy and raw materials for growth and repair. It explains how anabolic reactions build up structures using energy, while catabolic reactions break them down to release energy. The video highlights essential nutrients like water, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and their roles in sustaining life. By illustrating the continuous cycle of breaking down and rebuilding molecules, it provides a fascinating look into how metabolism sustains our bodies at a cellular level.
Takeaways
- 💧 64% of the body is water, and it plays a critical role in maintaining our form and function.
- 💪 After water, 16% of the body is made up of protein, which is crucial for muscles, enzymes, and various cellular functions.
- 🍔 Another 16% of the body is fat, which provides energy storage, insulation, and is essential for overall health.
- ⚖️ The body's metabolism consists of two types of reactions: anabolic reactions, which build up molecules, and catabolic reactions, which break them down.
- 🔥 Metabolism isn’t just about how fast you burn energy; it’s a complex system of all the biochemical reactions in the body.
- 🍞 Carbohydrates are primarily broken down into glucose, which is essential for energy, particularly for the brain and red blood cells.
- 🥩 Fats and proteins are not just energy sources; they play vital roles in cell structure, hormone production, and various biological functions.
- 🧠 Omega 3 and 6 fatty acids are essential because the body cannot produce them, and they play critical roles in brain function and inflammation.
- 🍗 Proteins from food are broken down into amino acids, which are then reassembled to form the proteins that make up your body.
- 🔄 The body is constantly rebuilding itself by breaking down nutrients and synthesizing new components, making metabolism a never-ending process.
Q & A
What percentage of the human body is made up of water?
-The human body is approximately 64% water, which plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
What are the primary components of the human body after water?
-After water, the human body is composed of 16% protein, 16% fat, 4% minerals, and 1% carbohydrates.
What is the role of protein in the body besides building muscle?
-Protein is not just for muscles. It is involved in various functions, including sodium-potassium pumps in neurons, hemoglobin in blood, and enzymes that drive chemical reactions in the body's cells.
Why does the body constantly require new chemicals and nutrients?
-The body requires new chemicals and nutrients because its components, like enzymes and cell membranes, wear out, break down, or become oxidized over time. Thus, these must be replenished to maintain proper function.
What is metabolism, and how does it relate to the body’s processes?
-Metabolism refers to all the biochemical reactions happening in the body. It includes anabolism (building up molecules) and catabolism (breaking down molecules), both of which are essential for energy production and repair.
How do anabolic and catabolic reactions differ?
-Anabolic reactions construct larger molecules from smaller ones and require energy, while catabolic reactions break down larger molecules into smaller ones and release energy.
What are the six major groups of nutrients essential for the body?
-The six major nutrients are water, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, lipids (fats), and proteins.
Why are carbohydrates important for the body’s energy needs?
-Carbohydrates, specifically glucose, are the primary source of energy for cells, especially neurons and red blood cells, which rely almost exclusively on glucose for energy.
What is the importance of lipids (fats) in the body?
-Lipids store energy, cushion organs, form cell membranes, and assist in storing fat-soluble vitamins. They also play a role in myelin formation for neurons and hormone production.
Why do proteins play such a crucial role in the body?
-Proteins form muscle and connective tissue, ion channels, pumps in neurons, and enzymes that drive every chemical reaction in the body, making them essential for overall function.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Can Exercise Actually "Boost" Your Metabolism? | Body Stuff with Dr. Jen Gunter | TED

Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Electron Transport [3D Animation]
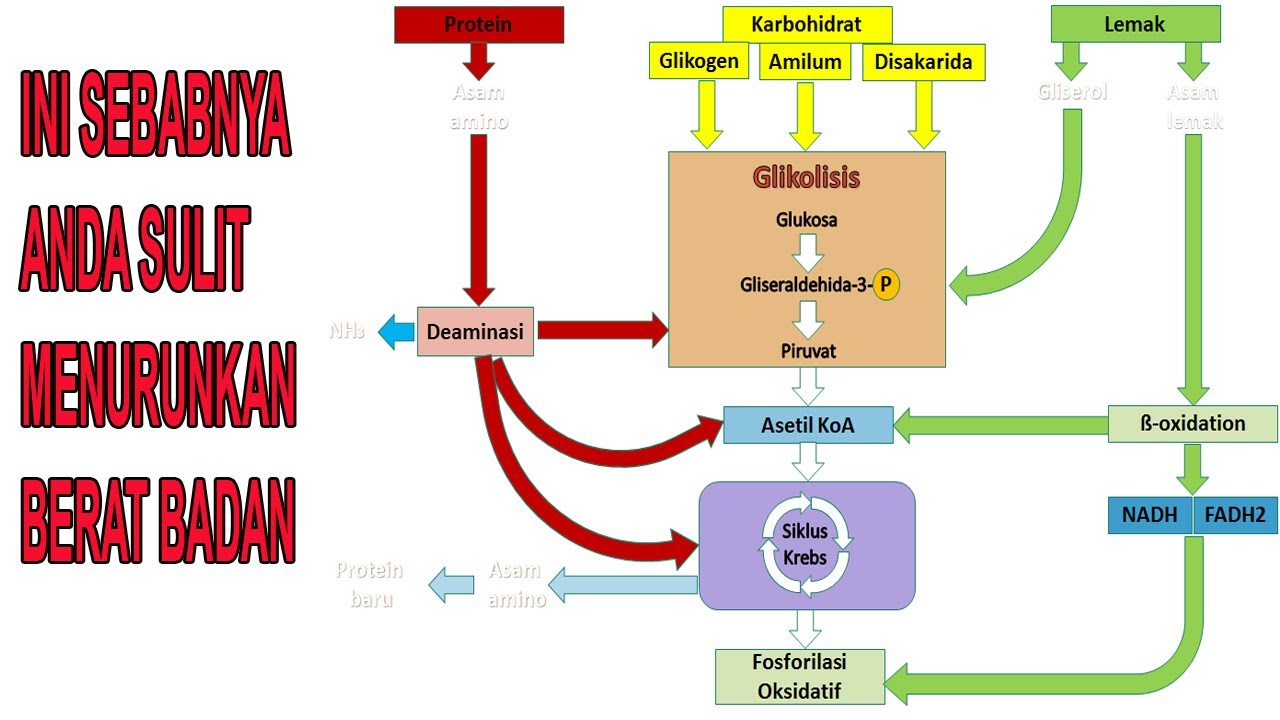
CARBOHYDRATE, FAT AND PROTEIN METABOLISM PATHWAYS

LESSON 5 - Human Nutrition: Metabolism Digestion Absorption and Utilisation of Nutrients.

thermodinamika

The Correlation between Thermodynamics and Food Science.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)