Order of Draw and Additives | Blood Collection
Summary
TLDRThis ICU Advantage video lesson, presented by Eddie Watson, delves into the critical procedure of blood sampling, emphasizing the proper order of draw to avoid contamination and ensure accurate test results. The video educates on various blood collection tubes, their purposes, and additives, concluding with a mnemonic 'Stoplight Red Stay Green, Power Light Go' to memorize the correct sequence. It highlights the importance of this process for patient care and accurate diagnosis.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The proper order of draw in blood sampling is crucial to prevent inaccurate results and potential misdiagnosis.
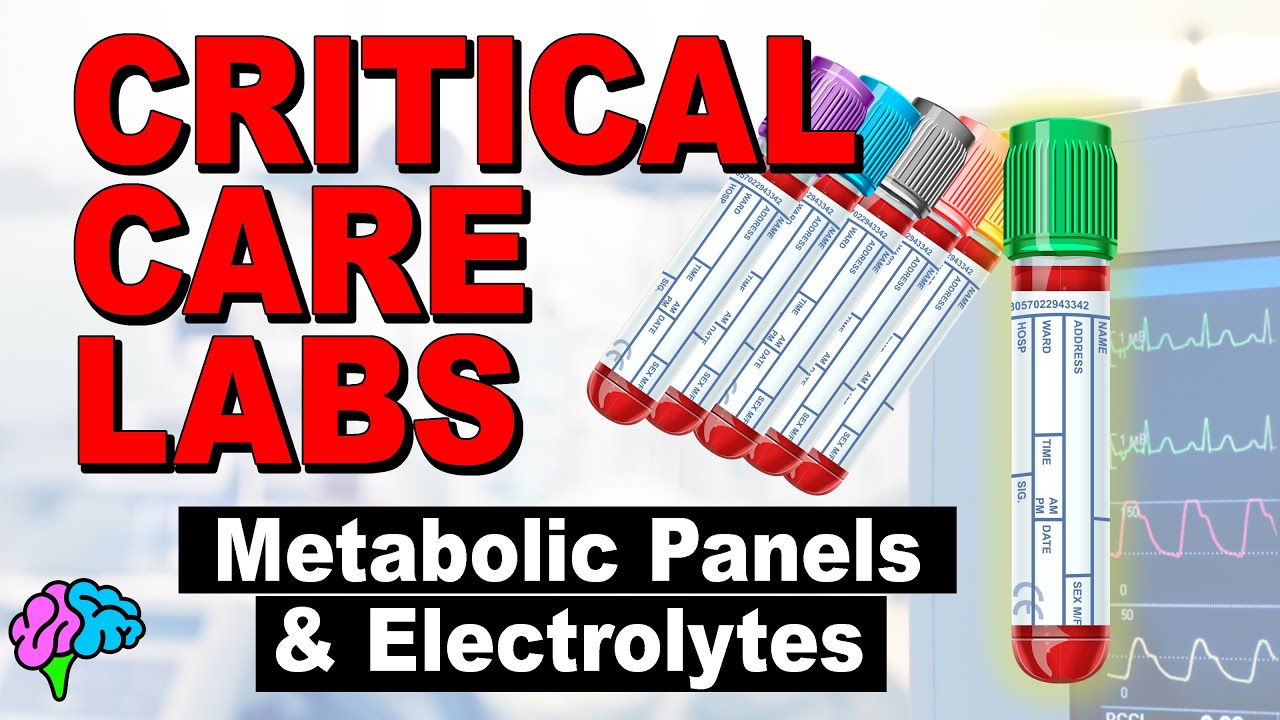
- 💉 Blood culture tubes should be filled first to minimize the risk of contamination.
- 🔵 The light blue tube is used for coagulation studies and contains sodium citrate to prevent clotting.
- 🔴 The red top tube is used for certain chemistry panels and serum tests, and may contain a silica clot activator.
- 🟠 The gold or SST tube is used for chemistry tests and has a gel separator to divide cells from serum.
- 🟢 The green top tube is commonly used for a wide range of chemistry tests and contains heparin as an anticoagulant.
- 🟣 The purple top tube is used for hematology studies and contains EDTA to preserve cell morphology and inhibit clotting.
- 💖 The pink top tube, identical to the purple top, is specifically used for blood type sampling.
- ⚪ The gray top tube is used for select tests like lactate level, ethanol level, and fasting glucose, containing sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate.
- 🔁 It's important to invert tubes with additives gently to ensure proper mixing without shaking.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video lesson?
-The main topic of the video lesson is the proper order of draw for blood sampling or phlebotomy, focusing on the sequence in which blood tubes should be filled to ensure accurate test results.
Why is the order of draw important in blood sampling?
-The order of draw is important to prevent additives in blood tubes from contaminating each other, which can cause inaccurate results, misdiagnosis, and incorrect treatment for patients.
What should be the first blood sample collected and why?
-Blood cultures should be the first samples collected to reduce the risk of contamination, as they require a sterile collection process to properly identify and grow bacteria.
What are the two types of blood culture bottles mentioned in the script, and how do they differ?
-The two types of blood culture bottles mentioned are aerobic and anaerobic. They differ in the environment they provide for bacterial growth, with aerobic supporting the growth of bacteria in the presence of air, and anaerobic supporting the growth of bacteria without air.
What additive is found in light blue blood collection tubes, and what is its purpose?
-Light blue tubes contain sodium citrate, which binds with calcium to prevent clot formation. This is crucial for coagulation tests as it maintains the blood in a liquid state for accurate testing.
What is the purpose of the red top tube in blood collection?
-The red top tube is used for tests that require serum, such as chemistry panels, and sometimes includes a silica clot activator to help form a clot and separate the serum from the blood cells.
What does SST stand for, and what is its purpose in blood collection?
-SST stands for Serum Separator Tube. Its purpose is to separate the serum from the blood cells using a gel, which is useful for certain chemistry tests that require serum.
Why should green top tubes be kept on ice immediately after drawing a blood sample?
-Green top tubes should be kept on ice to preserve the integrity of certain tests, such as cardiac markers like troponin, ammonia levels, and ionized calcium, ensuring the accuracy of the results.
What is the chemical inside purple top tubes that preserves cell morphology and inhibits clotting?
-The chemical inside purple top tubes is EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid), which preserves cell morphology and inhibits clotting by binding calcium, preventing it from participating in the clotting cascade.
What is the significance of the high potassium content in EDTA, and how can it affect test results?
-The high potassium content in EDTA can affect test results by skewing the potassium levels in blood samples if the additive from an EDTA-containing tube, like the purple or pink top tube, contaminates another tube that tests for potassium.
What is the recommended mnemonic to remember the proper order of draw for blood tubes?
-The recommended mnemonic to remember the order is 'Stoplight Red Stay Green, Power Light Go', which corresponds to the colors and types of tubes in the order of draw: sterile (blood culture), light blue (coagulation), red (chemistry), SST/gold top, green (chemistry), purple (hematologic), pink (blood type), and gray (special tests).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)