The Water Cycle | The Dr. Binocs Show | Learn Videos For Kids
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the fascinating process of the water cycle, starting with evaporation where the sun's heat turns water into vapor. It then condenses to form clouds, which eventually precipitate as rain, snow, or hail. The script also touches on transpiration from plants and sublimation in cold climates, illustrating the continuous nature of the water cycle and its relevance to our everyday life.
Takeaways
- 🌞 The water cycle begins with evaporation, where the sun heats up bodies of water causing water to turn into vapor.
- 🌬️ Evaporation can be observed at home by heating water and watching the vapor rise.
- 🌧️ When water vapor cools and condenses in the sky, it forms tiny water droplets that combine with particles to create clouds.
- 💧 Demonstrating condensation can be done by holding a cold lid over a heated vessel to see water droplets form.
- 🌦️ Clouds release water when they become too heavy, resulting in precipitation in the form of rain, hail, or snow.
- 🌊 Precipitation leads to water being collected in oceans, lakes, rivers, and also seeping into the ground as groundwater.
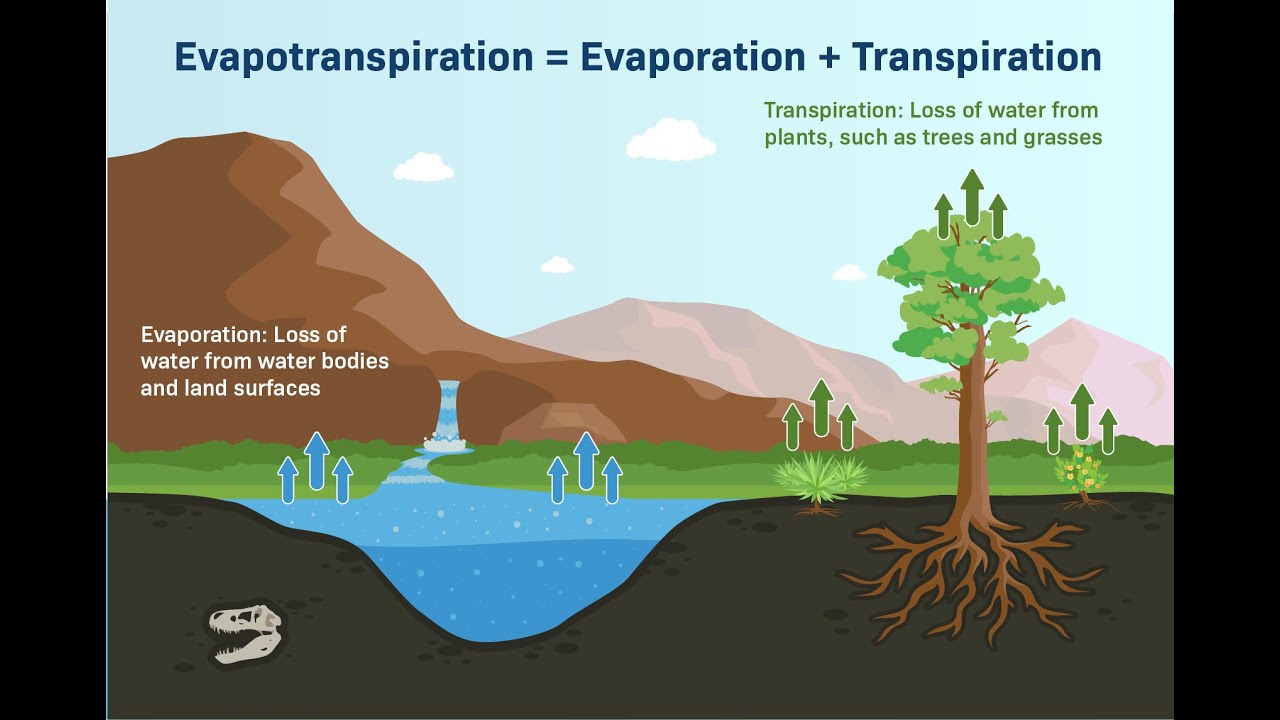
- 🌿 Plants contribute to the water cycle through transpiration, which is why areas with more vegetation, like forests, tend to have more rainfall.
- ❄️ In cold regions, snow can sublimate, turning directly into water vapor without becoming liquid first.
- 🌳 The presence of trees enhances local precipitation, as seen in hill stations and forests with high vegetation.
- 🔁 The water cycle is a continuous process involving evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
- 📚 Understanding the water cycle is crucial for appreciating the natural processes that sustain life on Earth.
Q & A
What is the water cycle?
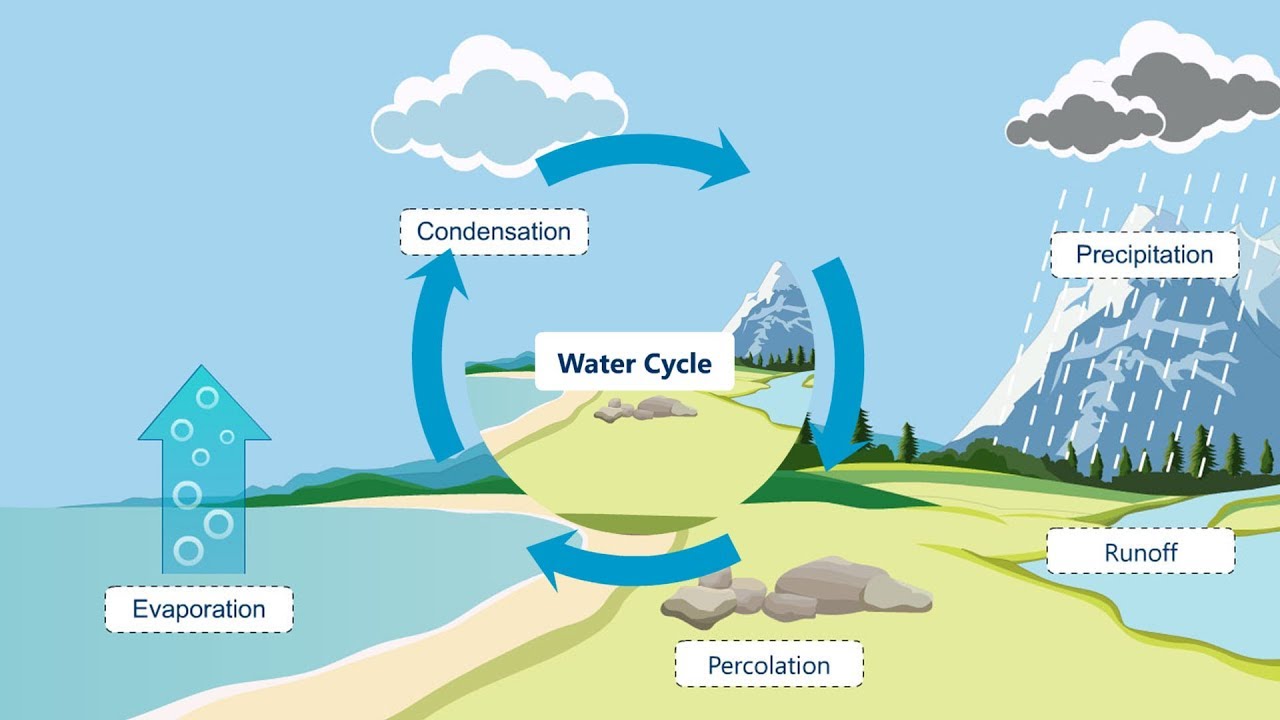
-The water cycle is a continuous process that involves the movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. It includes the processes of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
How does evaporation occur?
-Evaporation occurs when the sun heats up bodies of water like rivers and oceans, causing water to turn into water vapor and rise into the air.
What is the role of water vapor in the formation of clouds?
-Water vapor rises into the sky and, when it cools, turns into tiny water droplets. These droplets, along with various gases and dust particles, come together to form clouds.
Can you explain the process of condensation?
-Condensation is the process where water vapor in the air cools and changes into tiny water droplets, which then combine to form clouds.
How can you observe condensation at home?
-You can observe condensation at home by heating water in a vessel and then holding a cold lid over it. After some time, you will see water droplets forming on the lid.
What causes precipitation?
-Precipitation occurs when clouds become too heavy with water and can no longer hold it, leading to rain, hail, or snow.
How does the water cycle replenish water sources like oceans, lakes, and rivers?
-As it rains, water is collected in oceans, lakes, and rivers, and also seeps through the soil to become groundwater, thus continuously replenishing these water sources.
What is transpiration and how does it relate to rain?
-Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere through small pores in their leaves. It contributes to the water cycle and can lead to more rain in areas with more trees, like hill stations and forests.
What is sublimation and how does it occur?
-Sublimation is the process where snow or ice turns directly into water vapor without melting into liquid water first. This typically happens in cold countries.
Why does it rain more in places with more trees?
-Places with more trees, such as forests and hill stations, experience more rain due to the increased transpiration from the plants, which adds more water vapor to the atmosphere.
How does the water cycle demonstrate the continuous movement of water?
-The water cycle demonstrates the continuous movement of water through its various stages: evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, ensuring that water is constantly circulating between the Earth's surface and the atmosphere.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Eureka 18 - Evaporation & Condensation.mov

Kenapa Air Tidak Bisa Habis ? | Siklus Air | Animasi Siklus Hidrologi

Daur Air (Hidrologi) - Daur Biogeokimia - Ekologi - Biologi X
Understanding Evaporation and Evapotranspiration: Key Concepts in Hydrology
#Watercycle process | #hydrologicalcycle| #Watercycle Explanation | #letsgrowup

PROSES TERJADINYA HUJAN (SIKLUS AIR), kelas 3 SD tema 5 subtema 3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)