GCSE Biology - What is the Carbon Cycle? What is the Water Cycle? Cycles Explained #88
Summary
TLDRThis script explores Earth's life-sustaining cycles, focusing on the water and carbon cycles. It explains how water evaporates, forms clouds, and returns to Earth as rain, completing the cycle. The carbon cycle is more intricate, involving photosynthesis, respiration, and the transformation of dead organisms into fossil fuels or releasing carbon dioxide through microbial respiration. The script highlights the continuous recycling of atoms and molecules, emphasizing the interconnectedness of life on our planet.
Takeaways
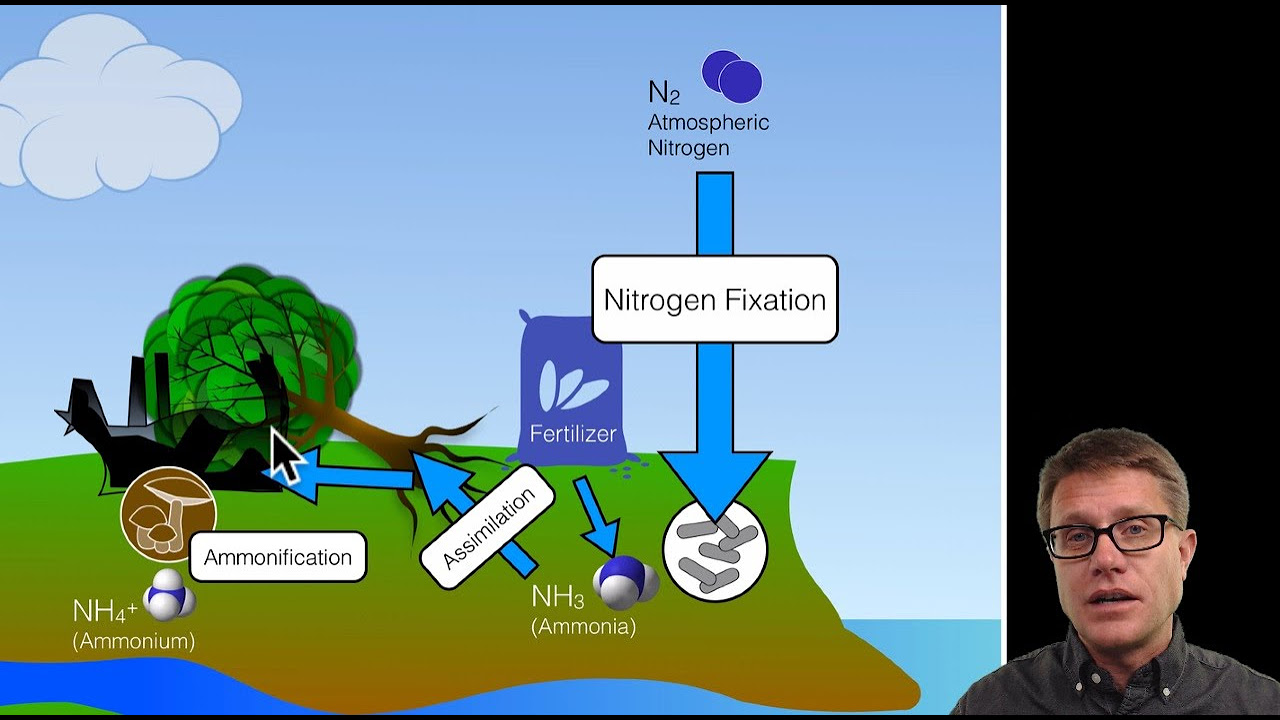
- 🌏 Life on Earth has been sustained for billions of years through the recycling of molecules and atoms, including water, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon.
- 🔁 The recycling process allows atoms to be reused in the creation of various organisms over millions of years.
- 🧬 Humans, like all life forms, are composed of countless atoms that have been part of oceans, volcanoes, other animals, and even other humans.
- 💧 The water cycle involves the evaporation of water from various sources, condensation into clouds, and precipitation back to the Earth's surface.
- ☀️ Solar energy is the driving force behind the evaporation step of the water cycle, turning liquid water into water vapor.
- 🌳 Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere, contributing to the water cycle.
- 🌧️ Precipitation returns water to the Earth, where it can seep into the soil, flow into rivers, or be absorbed by plants, continuing the cycle.
- 🌿 The carbon cycle is more complex and involves various living organisms and carbon storages, including the atmosphere, plants, soil, fossil fuels, and animals.
- 🍃 Photosynthesis is a key process in the carbon cycle, where plants and algae convert carbon dioxide into glucose and other biological molecules.
- 🐛 Decomposition by microorganisms in the soil releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere through respiration.
- 🔥 If dead organisms are not decomposed aerobically, they may form fossil fuels, which, when burned, release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- 🔄 Additional carbon cycle processes include the burning of plants and biofuels, which also release carbon dioxide.
Q & A
What is the significance of recycling atoms and molecules in life on Earth?
-Recycling atoms and molecules is essential for life on Earth because it allows atoms to be reused over and over again, enabling the formation of various organisms over millions of years. This recycling process ensures that essential elements like water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus continue to support life.
How does water transition from liquid on Earth's surface to water vapor in the atmosphere?
-Water transitions from liquid to water vapor through the process of evaporation, where energy from the sun heats water from sources like lakes, oceans, rivers, and even soil and plant leaves, causing it to evaporate and rise into the atmosphere.
What role do clouds play in the water cycle?
-Clouds form when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses. These clouds can then be transported by wind from one region to another, eventually releasing the accumulated water back to Earth as precipitation (rain), thus continuing the water cycle.
What are the main steps of the water cycle described in the transcript?
-The main steps of the water cycle include evaporation (water turning into vapor), condensation (formation of clouds), precipitation (rainfall), and the eventual return of water to the soil, rivers, or uptake by plants, allowing the cycle to start over.
How is carbon stored in the environment, according to the carbon cycle?
-Carbon is stored in five main places: in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide, in plants as biological molecules, in the soil with microorganisms, in fossil fuels underground, and in animals as biological molecules.
What is photosynthesis and its importance in the carbon cycle?
-Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and algae take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into biological molecules like glucose. This process is crucial as it removes carbon dioxide from the air and incorporates it into the food chain.
How does carbon move from plants to animals and back to the atmosphere?
-Carbon moves from plants to animals when animals eat the plants. Both plants and animals release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere through respiration. When they die, carbon can also be released during microbial decomposition.
What happens to carbon in organisms that do not decay in aerobic conditions?
-If organisms do not decay in aerobic conditions (without oxygen), they may gradually be converted into fossil fuels like oil, natural gas, or coal, which can later be burned by humans to release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
What is the significance of fossil fuels in the carbon cycle?
-Fossil fuels represent a significant store of carbon. When burned, they release stored carbon back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide, contributing to the carbon cycle. This process is a major factor in human-induced climate change.
How does the burning of plants and biofuels relate to the carbon cycle?
-Burning plants, such as logs in a fire, or biofuels in an engine, releases carbon stored in these materials back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide, thereby continuing the carbon cycle.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CHU TRÌNH SINH ĐỊA HÓA & SINH QUYỂN | SINH HỌC 12

Cycles of Matter - Earth Science for Kids!

KELAS 10 : MATERI EKOSISTEM BAG. 2 (Daur Biogeokimia)
Biogeochemical Cycles

Biogeochemical Cycles Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur

The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycles: Always Recycle! - Crash Course Ecology #8
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)