The Most Powerful Way to Remember What You Study
Summary
TLDRThis video script introduces spaced repetition, a powerful learning technique that enhances memory retention by spacing study sessions over time. It explains the science behind the spacing effect and the Forgetting Curve, and offers practical advice on implementing this method using both paper flashcards with the Leitner System and digital apps like Anki. The script also highlights the benefits of this approach, such as maximizing learning efficiency and personalizing study intervals.
Takeaways
- 📚 Spaced repetition is a powerful technique to enhance memory retention while reducing study time.
- 🧠 The technique leverages the 'spacing effect,' which helps our brains form stronger connections by spacing out learning sessions.
- 📅 Spaced repetition works by progressively increasing the intervals between study sessions for better retention.
- 💡 Forgetting is an essential part of the learning process; the harder it is to recall information, the stronger the learning.
- 🃏 The Leitner System is a paper-based method for spaced repetition using boxes or bands to organize study intervals.
- 📱 Anki is a highly customizable spaced repetition app with a large community and support for multiple platforms.
- 🖼️ Anki allows users to add media, such as pictures, to flashcards, which can help improve memory retention.
- 🖋️ Other spaced repetition apps include TinyCards, Flashcards Deluxe, Memrise, SuperMemo, and Quizlet.
- 📖 A more detailed explanation of the memory science behind spaced repetition can be found in the accompanying blog post.
- 👕 The video also promotes a College Info Geek t-shirt, designed with input from the community, available for purchase online.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The main focus of the video is to demonstrate how to remember more of what you learn by using a technique called spaced repetition, which involves spacing out study time to improve memory retention.
What is spaced repetition and how does it work?
-Spaced repetition is a learning technique that involves increasing the time intervals between study sessions. It leverages the spacing effect, a memory phenomenon where the brain makes better connections and remembers information more effectively when learning is spaced out over time.
Who is Hermann Ebbinghaus and what did he contribute to memory science?
-Hermann Ebbinghaus was a psychologist who launched the field of memory science in the late-1800s. He conducted an intense study on memory by memorizing long lists of nonsense syllables, which led to the development of the Forgetting Curve and insights into how spacing out memorization efforts can reduce the amount of study time needed.
What is the Forgetting Curve and what does it describe?
-The Forgetting Curve, developed by Hermann Ebbinghaus, describes how memories decay over time. It illustrates the rate at which information is forgotten after the learning period.
Why does the spacing effect enhance learning?
-The spacing effect enhances learning because it allows time for new neural connections to solidify. It also incorporates a degree of forgetting, which makes the retrieval of information more challenging and thus strengthens the learning process.
What is the Leitner System and how does it apply to spaced repetition?
-The Leitner System is a method for organizing flashcards into different boxes representing varying study intervals. Cards graduate to the next box when answered correctly, increasing the time between reviews, while incorrect answers send the card back to the first box. This system maximizes learning through the spacing effect and studies more efficiently by focusing on cards that need more attention.
What is Anki and how does it relate to spaced repetition?
-Anki is a popular spaced repetition app that allows for customizable flashcards and uses an algorithm to schedule reviews based on the difficulty of each card. It tracks individual cards, adjusts the review intervals based on user performance, and is available on multiple platforms.
What are some alternatives to Anki for spaced repetition?
-Alternatives to Anki for spaced repetition include TinyCards, Flashcards Deluxe, Memrise, SuperMemo, Mnemosyne, Eidetic, and Quizlet. These apps offer various features and interfaces for implementing spaced repetition.
How does the video suggest one can use spaced repetition with paper flashcards?
-The video suggests using the Leitner System with paper flashcards for spaced repetition. This involves organizing cards into boxes that represent different study intervals and moving cards through the boxes based on whether they are answered correctly or not.
What is the significance of forgetting in the context of spaced repetition?
-In the context of spaced repetition, forgetting is significant because it allows for the strengthening of learning when the material is revisited. The act of retrieving information after a period of forgetting is what allows learning to build and consolidate, similar to how an exercised muscle grows stronger.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
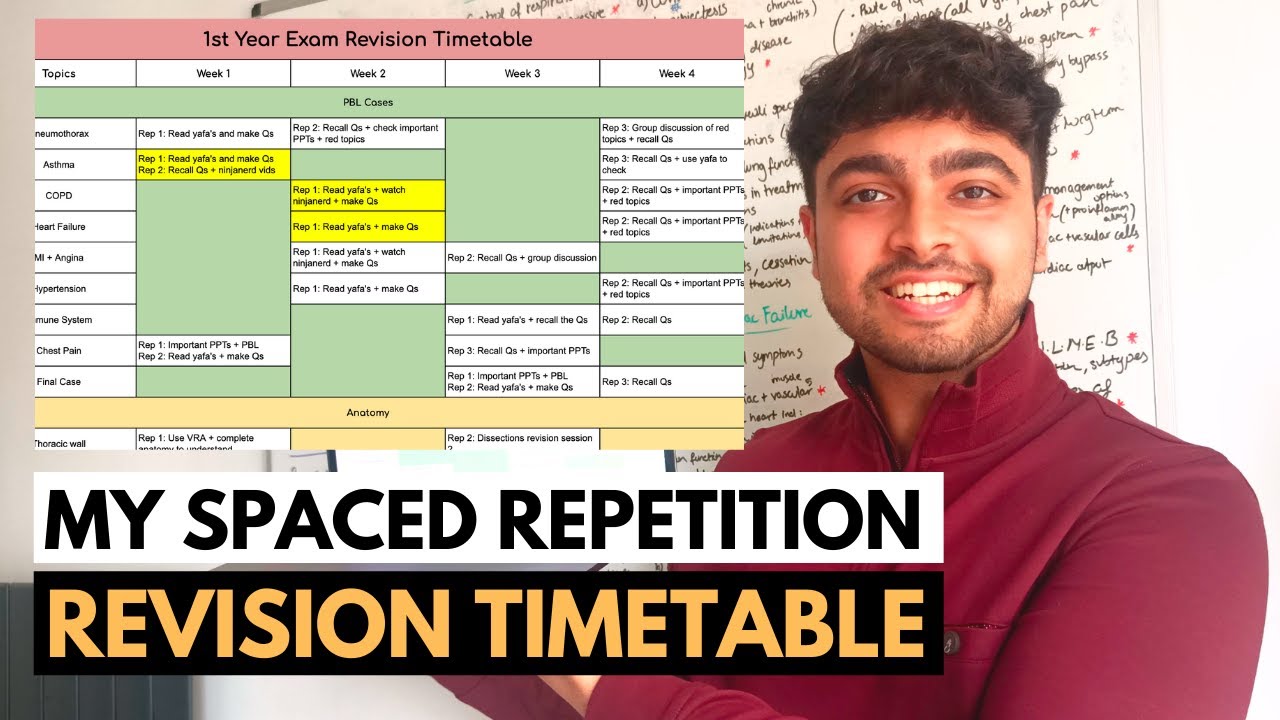
How to Make the PERFECT Revision Timetable with Spaced Repetition
৯৫% ছাত্র এই ভুলটি করে! পড়া মনে রাখার আসল রহস্য Feynman Technique

Spaced repetition in learning theory

Memory: Crash Course Study Skills #3

How to Never Forget What You Study With These PROVEN TECHNIQUES

ഇങ്ങനെ പഠിക്കൂ..! Best Study Methods & Memory Retention Tips | Secretariat Assistant | PSC Padashala
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)