Carrying Capacity simple explanation | Ecological Carrying Capacity
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the concept of carrying capacity, defining it as the maximum number of a species a habitat can support without degradation. It illustrates the concept with examples, including how it applies to human populations and the IPAT equation, which factors in population size, affluence, and technology to assess human impact on the environment. The video emphasizes the dynamic nature of carrying capacity, highlighting its importance in measuring sustainability and the need for balance between resource availability and consumption habits.
Takeaways
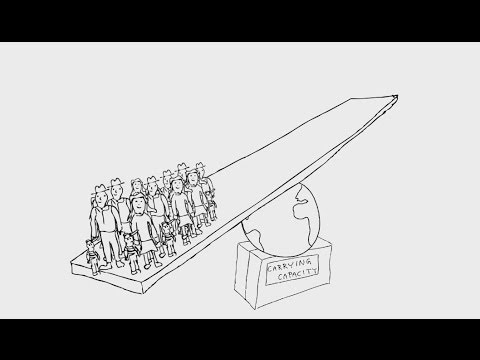
- 🌿 Carrying Capacity is defined as the maximum number of a species that an environment can support without being degraded.
- 📐 The concept of carrying capacity is visualized by the capacity to hold or contain, like the maximum volume a flask can hold.
- 🐑 Historically, carrying capacity was first applied to simple environments like the number of livestock sustainable on grazing land.
- 🌱 The term 'carrying capacity' has evolved to include the impact of unsustainable human consumption and production on the environment.
- 🌍 The imbalance of human activities on the environment is evident in issues like greenhouse gas emissions, endangered species, and deforestation.
- 🔢 Carrying capacity varies for each species due to specific needs for food, shelter, and competition with other species.
- 🐄 An example given is grazing land that can support a certain number of sheep, but increasing their numbers can exceed the land's capacity.
- 🧬 The concept was later applied to human populations, noting that human consumption habits are highly variable and more complex to predict.
- 📉 The IPAT equation was introduced to understand human impact on the environment, considering population size, affluence, and technology.
- 🔗 The IPAT equation (I = P * A * T) shows that impact is the product of population, affluence, and technology, and these factors are interdependent.
- 🔄 Carrying capacity is not static; it changes over time due to varying conditions and resource availability, as well as evolving consumption habits.
Q & A
What is the definition of carrying capacity?
-Carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of individuals of one or more species that can be supported by a particular habitat or environment without degrading it.
How is the concept of carrying capacity visualized in the script?
-The script uses the example of a flask to visualize carrying capacity, asking how many people can join a subgroup, to which the answer is 256 people, similar to the flask's maximum holding ability of one liter.
How did the concept of carrying capacity originally apply to?
-Carrying capacity was originally applied to relatively simple population environments, such as determining the number of sheep or cattle that could be maintained on grazing land without degrading it.
What is the relationship between unsustainable consumption and production and the concept of carrying capacity?
-Globally, unsustainable consumption and production threaten to exceed the capacity of nature to sustain life forms, which is directly related to the concept of carrying capacity as it highlights the imbalance between what nature can support and what humans consume.
Why is the carrying capacity different for each species in a habitat?
-The carrying capacity is different for each species in a habitat due to their particular food, shelter, and social requirements, as well as competition from other species that may have similar requirements.
Can you give an example of how carrying capacity is exceeded?
-An example given in the script is grazing land for five sheep. If the number of sheep is gradually increased to ten, twenty, and so on, the pasture can no longer support the population, indicating that the carrying capacity has been exceeded.
How was the concept of carrying capacity applied to human populations in the 1960s?
-In the 1960s, it was noted that human consumption habits are much more variable than those of other animal species, making it more difficult to predict the carrying capacity of the Earth for human beings.
What is the IPAT equation and how does it relate to human carrying capacity?
-The IPAT equation is I = P * A * T, where I stands for the impact of any population, P for population size, A for affluence or per-capita consumption, and T for technologies used in production and consumption. It points out that the carrying capacity for humans is a function of these three characteristics.
Why are the factors in the IPAT equation not independent?
-The factors in the IPAT equation are not independent because decreasing the population size alone will not reduce impact if affluence levels and technologies are not also managed, as all three factors collectively determine the overall impact.
How does carrying capacity relate to sustainability?
-Carrying capacity is a measure of sustainability as it reflects the balance between the conditions and resources available in a specific area and the consumption habits of the species considered, which are always changing over time.
What is the significance of understanding carrying capacity in the context of the current environmental challenges?
-Understanding carrying capacity is crucial in the context of environmental challenges as it helps identify the limits of what ecosystems can support, thus guiding sustainable practices to prevent degradation and ensure the long-term viability of habitats.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)