GCSE Chemistry - Allotropes of Carbon - Diamond and Graphite #18
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the distinct structures and properties of carbon's allotropes: diamond and graphite. Diamond, with its tetrahedral bonding, is extremely strong and has a high melting point but is an electrical insulator. Graphite, in contrast, forms hexagonal layers with weaker interlayer bonding, making it softer yet still strong and a good conductor due to delocalized electrons. The video also teases the discussion of graphene and other carbon structures like fullerenes in the next installment.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Allotropes are different structural forms of the same element in the same physical state.
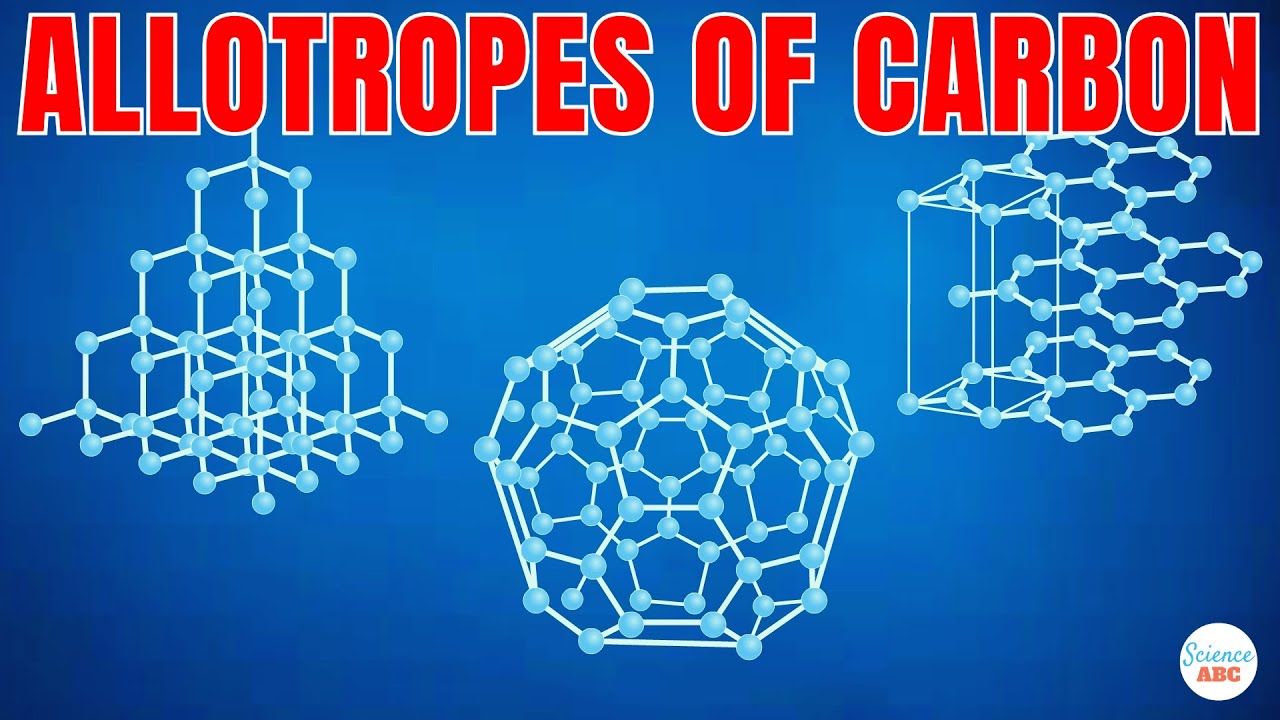
- 💎 Diamond and graphite are two allotropes of carbon, both being giant covalent structures.
- 🔗 In diamond, each carbon atom is tetrahedrally bonded to four other carbon atoms, making it extremely strong.
- 🔥 Diamond has a very high melting point due to the strength of its covalent bonds.
- ⚡ Diamond does not conduct electricity as it lacks free electrons or ions.
- 📜 Graphite's carbon atoms are bonded to only three others, forming hexagonal patterns and layers.
- 📃 The layers in graphite are weakly held together, allowing them to slide over each other, making graphite soft.
- 🔥 Despite its softness, graphite has a high melting point due to the strong covalent bonds within its layers.
- ⚡ Graphite conducts electricity and heat because of the delocalized electrons from each carbon atom's spare bonding capacity.
- 📄 A single layer of graphite is called graphene, which can be isolated for various applications.
- 🔬 Fullerenes and other carbon structures will be discussed in a subsequent video.
Q & A
What are allotropes and how do they relate to carbon?
-Allotropes are different structural forms of the same element in the same physical state. Carbon can exhibit various allotropes in its solid state, such as diamond, graphite, and fullerenes, each with distinct structures and properties.
What is the defining characteristic of giant covalent structures?
-Giant covalent structures are made of a regular lattice of covalently bonded atoms, which gives them strength and stability due to the strong bonds between the atoms.
Why is diamond very hard and has a high melting point?
-Diamond is hard and has a high melting point because each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a strong, regular 3D pattern, requiring a lot of energy to break these bonds.
Does diamond conduct electricity, and if not, why?
-Diamond does not conduct electricity because it lacks free electrons or ions that can move around, as all electrons are involved in strong covalent bonds.
How is the bonding in graphite different from that in diamond?
-In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to only three other carbon atoms, forming hexagonal arrangements that create flat sheets stacked on top of each other with weak forces between the layers.
What makes graphite soft compared to diamond?
-Graphite is softer than diamond because the layers of carbon atoms are held together only by weak forces, allowing them to slide over one another easily.
Why does graphite have a high melting point despite being soft?
-Although graphite is soft, it has a high melting point because the individual layers within the graphite are strongly held together by covalent bonds.
How does the structure of graphite allow it to conduct electricity?
-Each carbon atom in graphite has one spare electron that is not involved in bonding, becoming delocalized and free to move around, which enables graphite to conduct electricity.
What is graphene and how is it related to graphite?
-Graphene is a single layer of graphite, which can be isolated and used to create other structures. It is known for its exceptional strength and electrical conductivity.
What are fullerenes and how do they differ from diamond and graphite?
-Fullerenes are another allotrope of carbon, distinct from diamond and graphite. They consist of carbon atoms arranged in a spherical shape, resembling a soccer ball, and have unique properties different from those of diamond and graphite.
What are the unique properties of graphene that make it useful for various applications?
-Graphene has exceptional properties such as extreme strength, flexibility, and high electrical and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for a wide range of applications from electronics to materials science.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Allotropes of Carbon Explained in Simple Words for Beginners

The Structural Characteristics of CARBON | Carbon Compounds | Grade 9 Science Quarter 2 Week 4-5

1.2 Bonding and 1.3 Structures - Covalent Bonding & Structures

Carbon: The Element of Life

Diamond & Graphite (with exam predictions) - GCSE & IGCSE Chemistry Revision 2024

What Are Giant Chemical Structures | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)