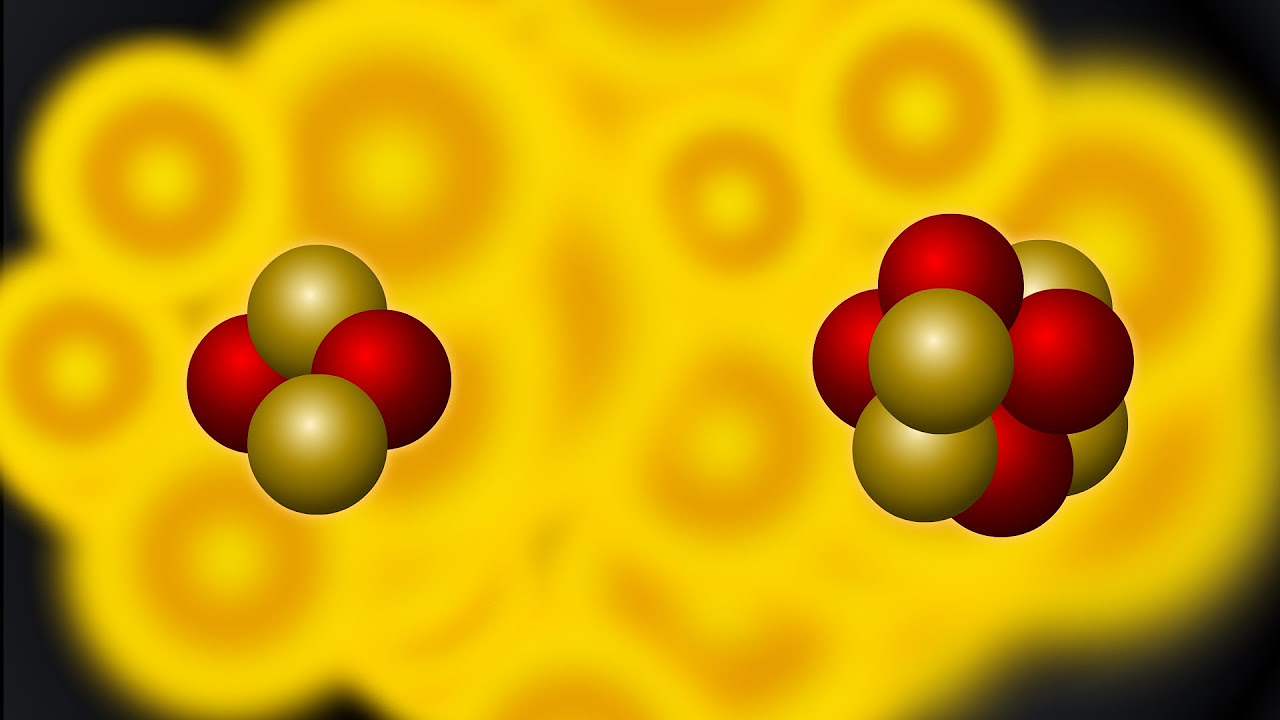
Nuclear Fusion Explained
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the complexities of nuclear fusion, explaining how four protons combine to form a helium nucleus despite the mass difference and Coulomb Barrier. It clarifies that fusion occurs in extreme conditions like the Sun's core and discusses the processes, including the Proton-Proton Chain and CNO Cycle, leading to helium and eventually heavier elements. The video also touches on the potential of fusion as a clean energy source and invites viewers to share their excitement for the future of fusion power.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Nuclear fusion involves combining smaller atomic nuclei to form larger ones, typically occurring in the core of a star.
- 🔬 The term 'nucleus' originally referred to the kernel at the center of a nut but now signifies the center of small entities, like an atom's core.
- ☀️ The Sun primarily fuses hydrogen into helium, a process that is also reflected in the abundance of hydrogen in the universe.
- 💥 Inside the Sun, the extreme heat results in a plasma state where electrons and protons move freely, separate from their atoms.
- 🚫 The Coulomb Barrier prevents atomic nuclei from easily combining due to their mutual repulsion as positively charged particles.
- 🌐 The Sun uses its immense gravity to overcome the Coulomb Barrier and force protons to combine, initiating nuclear fusion.
- 🤔 While the concept of nuclear fusion is straightforward, the actual processes are complex and involve various nuclear reactions.
- ⚛️ Neutrons can decay into protons and vice versa, with the transformation influenced by rest-energy and kinetic energy.
- 💡 Fusion in stars like the Sun occurs through processes such as the Proton-Proton Chain and the CNO Cycle, both releasing light and neutrinos.
- 🌌 The Sun will eventually transition from fusing hydrogen to helium to fusing helium into carbon through the Triple-Alpha Process.
- 🔬 Neutron capture, a process where a nucleus absorbs a neutron that later decays into a proton, plays a role in the creation of heavier elements in stars.
Q & A
What is nuclear fusion and why is it significant in the context of the video?
-Nuclear fusion is a process where smaller atomic nuclei combine to form larger ones, typically occurring in the core of a star. It is significant in the video as it explains the fundamental process that powers stars like our Sun and has potential implications for clean energy production.
What is the difference between a hydrogen gas molecule, a hydrogen atom, and a hydrogen nucleus?
-A hydrogen gas molecule (H2) consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded together. A hydrogen atom consists of one proton and one electron. A hydrogen nucleus, on the other hand, refers to just the proton at the center of a hydrogen atom, without any electrons.
What is plasma and how is it related to the conditions inside the Sun?
-Plasma is a state of matter similar to gas but with ionized atoms, meaning the electrons are separated from the nuclei. Inside the Sun, the high temperature causes hydrogen atoms to lose their electrons, resulting in a plasma of freely moving electrons and protons.
What is the Coulomb Barrier and why is it significant in the context of nuclear fusion?
-The Coulomb Barrier refers to the electrostatic repulsion between positively charged atomic nuclei. It is significant in nuclear fusion because overcoming this barrier is necessary for nuclei to come close enough to fuse together.
How does the Sun use gravity to overcome the Coulomb Barrier and facilitate fusion?
-The Sun's immense mass generates a strong gravitational force that compresses the protons, overcoming the Coulomb Barrier and allowing them to come close enough for fusion to occur.
What is the role of neutrons in nuclear fusion reactions?
-Neutrons can help stabilize the nucleus by balancing the repulsive forces between protons. They can decay into protons, releasing energy, and are necessary for the formation of heavier elements through processes like neutron capture.
What are the Proton-Proton Chain and the CNO Cycle, and how do they differ?
-The Proton-Proton Chain and the CNO Cycle are two different processes by which stars convert hydrogen into helium through fusion. The Proton-Proton Chain is the dominant process in stars like the Sun, adding protons one at a time and creating neutrons through decay. The CNO Cycle, on the other hand, involves carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen as catalysts and is more prevalent in more massive stars.
What is the Triple-Alpha Process and why is it important for star evolution?
-The Triple-Alpha Process is a nuclear reaction where three helium nuclei (alpha particles) combine to form a carbon nucleus. It is important for star evolution because it allows stars to create heavier elements after they have exhausted their hydrogen fuel.
What are neutrinos and why are they produced during nuclear fusion in stars?
-Neutrinos are elementary particles with very small mass and no electric charge, which can pass through matter with minimal interaction. They are produced during nuclear fusion in stars as a byproduct of certain reactions, carrying away energy from the reactions.
What is the significance of the conservation laws in nuclear reactions, as mentioned in the video?
-The conservation laws—of energy, momentum, and charge—are fundamental principles that must be obeyed during nuclear reactions. They ensure that the total amount of each quantity remains constant before and after the reaction, even though rest mass can be converted into energy.
How does the video script relate to the potential of fusion power as a clean energy source?
-The video script discusses the process of nuclear fusion, which is the same process that powers stars and has the potential to be harnessed as a clean and virtually limitless energy source on Earth, if the technical challenges can be overcome.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)