Reaksi Fusi
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the concept of fusion energy, explaining how hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process. It highlights the potential of fusion as an almost limitless energy source, contrasting it with the dangers and inefficiencies of fossil fuels and nuclear energy. Despite its promise, the script points out the challenges, including the difficulty of obtaining the necessary isotopes, such as tritium, and the high cost of building fusion reactors. However, if successful, fusion could provide a clean, abundant energy source with minimal environmental impact.
Takeaways
- 😀 Solar energy is one of the key sources of energy for humanity, along with fossil fuels and nuclear energy.
- 😀 While solar power has almost unlimited energy potential, it faces challenges such as storage on cloudy days and the lack of efficient batteries.
- 😀 Fusion energy, the process of combining small particles like hydrogen, releases energy by forming helium, a more stable atom.
- 😀 Fusion reactions occur at extremely high temperatures and pressures, creating conditions where particles can combine to form heavier atoms.
- 😀 The process of fusion involves the combination of hydrogen atoms to create deuterium and eventually heavier helium isotopes, releasing significant amounts of energy.
- 😀 Nuclear fusion reactions have the potential to produce massive energy with little to no waste, unlike fossil fuels or nuclear fission.
- 😀 Deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen, can be found in seawater and is a viable fuel for fusion reactions, while tritium, another required isotope, is scarce and radioactive.
- 😀 Tritium is hard to find and only about 20kg exist globally, making it difficult to rely solely on it for fusion energy production.
- 😀 Helium-3, another isotope of helium, may serve as a potential replacement for tritium in fusion reactions, offering a safer alternative.
- 😀 Unlike nuclear reactors, fusion reactors are safer since a failure would result in the plasma cooling down and stopping the reaction, preventing catastrophic outcomes.
- 😀 Despite the immense potential of fusion energy, the technology is currently too costly to be commercially viable, though the long-term benefits may justify the investment.
Q & A
What are some common sources of energy mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions several sources of energy, including fossil fuel combustion, nuclear fission, and solar panels.
What are the drawbacks of fossil fuels and nuclear energy as energy sources?
-Fossil fuels produce toxic waste, and nuclear energy generates radioactive waste, which is hazardous. Additionally, there is no battery technology capable of storing solar energy on cloudy days.
Why is solar energy considered almost unlimited?
-Solar energy is considered almost unlimited because the Sun generates an immense amount of energy that can potentially be harnessed.
What is nuclear fusion and how does it work?
-Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two very small particles, such as hydrogen, to form helium. This reaction releases kinetic energy and stabilizes the new atom. However, fusion requires extremely high temperatures and pressures to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between the positively charged hydrogen atoms.
Why is nuclear fusion called a thermonuclear reaction?
-Nuclear fusion is called a thermonuclear reaction because it requires very high temperatures and pressures to spontaneously occur, which are characteristic of nuclear reactions involving heat.
What are the key isotopes involved in nuclear fusion?
-The key isotopes mentioned in the script are deuterium and tritium. Deuterium can be found in seawater, while tritium is rarer and radioactive.
How is fusion energy different from nuclear fission in terms of safety?
-Fusion energy is much safer than nuclear fission. If a fusion reactor fails, the plasma will simply spread and cool down, causing the reaction to stop. Unlike nuclear fission, there is no risk of a meltdown or catastrophic release of energy.
What environmental risks are associated with tritium?
-Tritium is a radioactive substance that can combine with oxygen to form radioactive water, which poses a potential environmental threat.
What are the challenges associated with developing fusion energy?
-The main challenges include the extremely high costs of building fusion reactors, the difficulty in obtaining sufficient tritium, and the need for new materials or isotopes like helium-3 to replace tritium.
Why might fusion energy still be considered valuable despite its high costs?
-Fusion energy, although expensive to produce, offers immense long-term benefits as it provides nearly limitless energy without harmful waste, making it highly efficient and environmentally friendly in the future.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

21.4 Nuclear Fission and Fusion

Birth of stars | Stars, black holes and galaxies | Cosmology & Astronomy | Khan Academy

Nuclear Fusion Explained

How Stars Turn MATTER into ENERGY | Nuclear Fusion
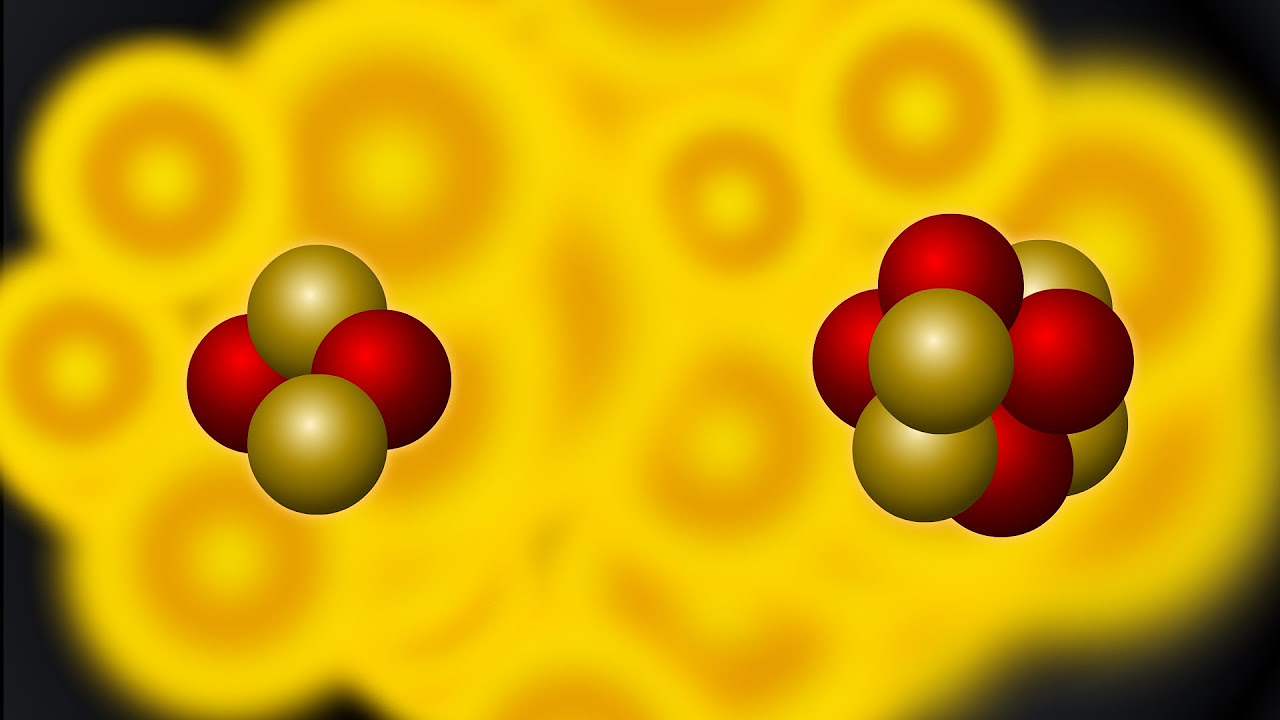
Nuclear Fusion | Fusion energy explained with Hydrogen atom example | Physics animation video

Bersinar milyaran tahun, dari mana asal energi matahari?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)