Au coeur des organes : Le fonctionnement du système nerveux
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the role of sensory organs in stimulating the nervous system. It explains how the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin detect various environmental stimuli, transmitting electrical signals to the brain or spinal cord. These sensory messages are analyzed by the brain, which then sends efferent messages to muscles and organs to execute actions. The script highlights the impact of fatigue, drugs, alcohol, and noise pollution on the nervous system, stressing the importance of caring for our sensory system from childhood to prevent irreversible damage.
Takeaways
- 😀 Our sensory organs (eyes, nose, ears, tongue, skin) are constantly stimulated by the environment and help us perceive the world around us.
- 😀 When a sensory organ is stimulated, it generates electrical nerve messages that travel toward the brain or spinal cord for analysis.
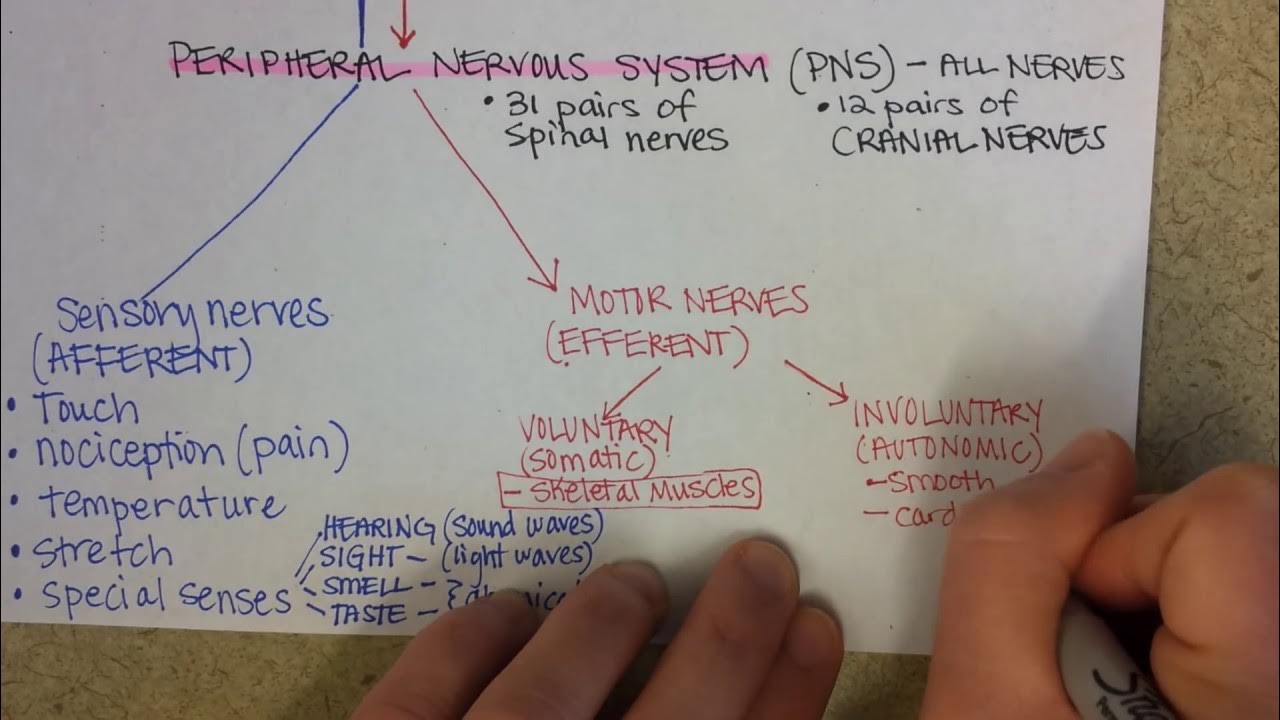
- 😀 These electrical messages are called 'sensory afferent messages' and follow the path of sensory nerves.
- 😀 The brain and spinal cord act as nerve centers that analyze these sensory messages according to which organ generated them.
- 😀 The location where these messages arrive in the brain or spinal cord is specific to each sensory organ (e.g., visual messages go to the back of the brain).
- 😀 This process triggers intense communication within the nerve centers, where new messages are generated and exchanged.
- 😀 The brain can send efferent messages (motor messages) to organs to take action, such as telling muscles to contract.
- 😀 Sensory dysfunctions can occur due to environmental factors, such as loud noises damaging hearing receptors or UV rays harming the eyes and skin.
- 😀 Some dysfunctions, such as hearing damage or sunburn, can be irreversible, so it’s crucial to care for our nervous system from a young age.
- 😀 Fatigue can impair the speed and accuracy of the brain’s analysis of sensory messages and the adaptation of efferent messages to organs.
- 😀 Consumption of drugs and alcohol can disrupt the nervous system, leading to potentially dramatic consequences for the body.
- 😀 Overuse of alcohol, fatigue, or medication can impair motor skills and reaction times, increasing risk in situations like driving.
Q & A
What is the role of sensory organs in the human body?
-Sensory organs like the eyes, nose, ears, tongue, and skin are responsible for detecting stimuli from the environment. They react to light, odors, sound, taste, and touch, which allows the body to interact with and respond to its surroundings.
How do sensory organs transmit information to the brain?
-When a sensory organ is stimulated, it generates electrical nerve messages that travel through sensory nerves towards the brain or spinal cord. These messages are called afferent sensory signals and help in processing the stimuli.
What happens after the sensory signals reach the brain or spinal cord?
-Once the afferent sensory signals reach the brain or spinal cord, they are analyzed in specific areas corresponding to the sensory organ they originated from. This rapid analysis triggers communication within the nervous system and generates new messages.
What are efferent messages, and what role do they play in the nervous system?
-Efferent messages are signals sent from the brain or spinal cord to various organs, instructing them to perform specific actions. For example, efferent motor messages direct muscles to contract.
Can you explain how the nervous system can be disrupted?
-The nervous system can be disrupted by excessive exposure to loud noises, ultraviolet rays, or substances like drugs and alcohol. These disruptions can damage sensory receptors and impair the nervous system's ability to process and transmit signals.
What are the consequences of dysfunction in the nervous system?
-Dysfunctions in the nervous system can lead to impaired sensory signal interpretation, slower response times, and less accurate messages being sent to organs. In extreme cases, such dysfunctions can be irreversible.
How does fatigue affect the nervous system?
-Fatigue can slow down the analysis of sensory information and cause less precise interpretation of sensory signals. It can also reduce the efficiency of efferent messages sent to organs, leading to less effective responses.
How do drugs and alcohol affect the nervous system?
-Drugs and alcohol can interfere with the normal functioning of the nervous system. They impair the brain's ability to process sensory signals and generate appropriate responses, potentially leading to serious and sometimes irreversible consequences.
What is the importance of taking care of our nervous system?
-Taking care of our nervous system is essential for maintaining its proper function. Avoiding harmful stimuli, such as loud noises, UV rays, or substance abuse, helps preserve the integrity of sensory receptors and ensures that the nervous system operates efficiently.
What can happen if a person drives while fatigued or intoxicated?
-Driving while fatigued or intoxicated can impair the brain's ability to process sensory information quickly and accurately. This increases the risk of accidents, as the person's response time is slower and their ability to make quick decisions is compromised.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

BAB 2 Sistem Koordinasi Manusia || Sistem Saraf Manusia || IPA SMP/MTs Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka

#Materi UTBK Biologi - Sistem Koordinasi : Syaraf, Indra, Hormon

As grandes vias aferentes e eferentes: Introdução e vias aferentes - Parte 1

Sistem Saraf - Materi IPAS Kelas 6 Kurikulum Merdeka
Nervous System Overview

The Nervous System in 6 Minutes | How Does it Work?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)