Het bewegingsapparaat: Inleiding in de skeletspieren
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the anatomy and function of skeletal muscles, highlighting their structure composed of protein filaments like myosin and actin. It explains the three types of muscle contractions: dynamic concentric, static, and dynamic eccentric. The role of motor units and the reflex actions of muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs are also discussed, illustrating how these mechanisms contribute to movement, balance, and muscle coordination.
Takeaways
- 💪 Skeletal muscles are strong and anchored to bones, playing a crucial role in body movement.
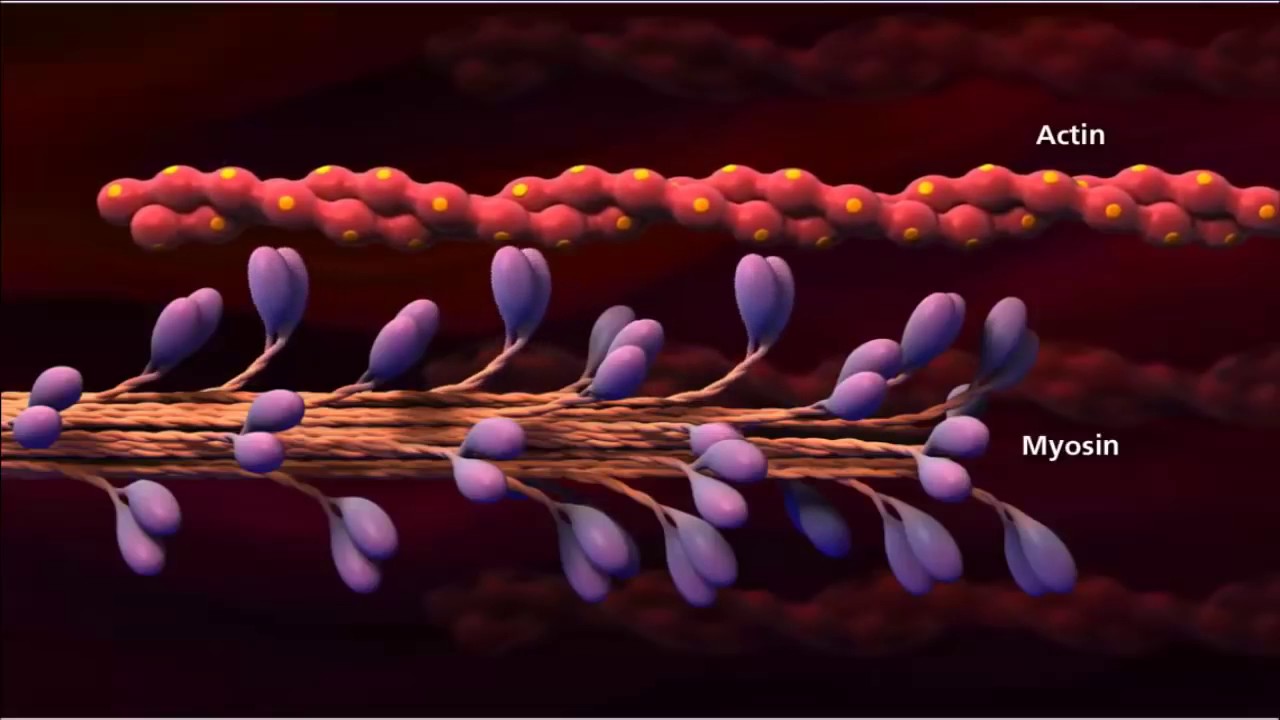
- 🔬 Muscles are composed of a muscle belly with bundles of muscle fibers, which are made up of proteins like sarcomeres, myosin, and actin.
- 🔄 The sliding of actin over myosin, facilitated by bridges, is the fundamental mechanism of muscle contraction.
- 🏃♂️ Skeletal muscles are striated, meaning they have a distinct pattern of bands, and are under voluntary control unlike smooth muscles.
- 🏋️♂️ Muscle contraction can occur in three ways: dynamic concentric (shortening against resistance), static (no change in length), and dynamic eccentric (lengthening under load).
- 💉 Motor units are the connections between motor nerves and muscle fibers, which control muscle contractions in response to nerve impulses.
- 👁️ Proprioceptors, or muscle spindles, are sensory receptors that detect changes in muscle length and play a role in reflexes and maintaining posture.
- 🔁 The muscle stretch reflex, or myotatic reflex, is an automatic response to maintain muscle length and balance, such as in standing or sports movements.
- 🚫 Golgi tendon organs measure muscle tension and can signal the muscle to relax if excessive force is applied, protecting it from damage.
- 🤝 Agonist, antagonist, and synergist muscles work together to facilitate movement, with agonists initiating the movement, antagonists opposing it, and synergists assisting.
- 🔄 Muscles can be classified by their function and the number of joints they cross, such as monoarticular, biarticular, and polyarticular muscles.
Q & A
What are skeletal muscles and how are they anchored?
-Skeletal muscles are strong muscles that are anchored to bones and are part of the muscular system. They are responsible for body movement and are arranged neatly alongside each other, creating clear cross-striations.
What are the main components of skeletal muscles?
-Skeletal muscles are composed of muscle fibers, which in turn consist of myofibrils. Myofibrils are made up of proteins such as myosin and actin, connected by bridges that facilitate muscle contraction.
How do muscle contractions occur in skeletal muscles?
-Muscle contractions occur when actin filaments slide over myosin filaments due to the action of myosin bridges, causing the muscle to shorten and generate force.
What is the role of the motor unit in skeletal muscles?
-A motor unit is a single motor nerve and all the muscle fibers it innervates. It plays a crucial role in controlling muscle contractions, with the motor nerve sending signals that cause the muscle fibers to contract.
What are the three types of muscle contractions mentioned in the script?
-The three types of muscle contractions are dynamic concentric (where the muscle overcomes resistance and shortens), static (where the muscle contracts but the length remains the same), and dynamic eccentric (where the muscle lengthens under resistance).
How does the musculus biceps brachii demonstrate static muscle contraction?
-The musculus biceps brachii demonstrates static muscle contraction by exerting force without changing its length, such as when holding a weight at a fixed position.
What is the function of muscle spindles in skeletal muscles?
-Muscle spindles are proprioceptive sensors sensitive to length and changes in muscle length. They provide feedback to the central nervous system, which helps in maintaining posture and balance.
What is the purpose of the muscle stretch reflex?
-The muscle stretch reflex, or myotatic reflex, helps to maintain a constant muscle length by quickly contracting the muscle in response to a sudden stretch, ensuring stability and balance.
What are antagonist muscles and how do they function?
-Antagonist muscles are those that have the opposite action to the agonist muscles. They work together with agonist muscles to control movement by relaxing while the agonist contracts, allowing for smooth and coordinated motion.
What is meant by monoarticular, biarticular, and polyarticular muscles?
-Monoarticular muscles cross only one joint, biarticular muscles cross two joints, and polyarticular muscles cross over two or more joints, each playing a specific role in movement and support across different joints.
What is the significance of the muscle's ability to fully contract and extend?
-The ability of a muscle to fully contract and extend is important for its functionality. If a muscle is insufficiently active and cannot fully contract, it may not be able to generate the maximum movement output in multiple joints simultaneously, affecting the overall range of motion and strength.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Muscle Contraction - Cross Bridge Cycle, Animation.

How Your Muscles Work
3. Muscle contraction detail Concept Cell Biology

Struktur Otot Rangka : Pita A, Pita I, Aktin, Miosin, Troponin, Tropomiosin, Garis Z, Garis A, dll.

Cellule musculaire : organisation - SVT - SANTÉ Term spé #7 - Mathrix

Contração muscular - dublado
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)