Kohlberg’s 6 Stages of Moral Development
Summary
TLDRThis script explores Lawrence Kohlberg's six stages of moral development through three levels: pre-conventional, conventional, and post-conventional. It uses a schoolyard fight scenario to illustrate how individuals at different stages might react and justify their actions. The Heinz dilemma is presented to challenge viewers' moral reasoning, inviting them to consider the complexities of justice, compassion, and social norms in ethical decision-making.
Takeaways
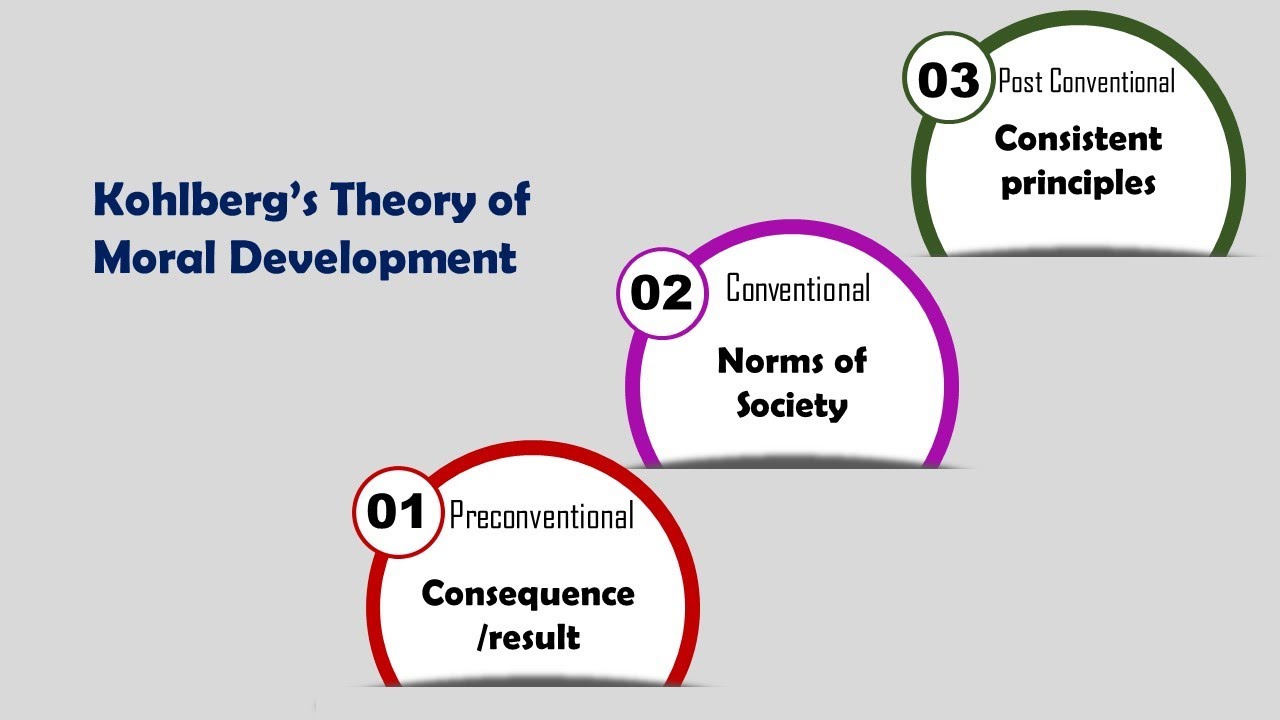
- 📚 Lawrence Kohlberg's theory outlines six stages of moral development across three levels: pre-conventional, conventional, and post-conventional.
- 👦 At stage one, moral reasoning is based on obedience and the fear of punishment, exemplified by Finn's hesitation to intervene in a fight due to potential punishment.
- 🤔 Stage two is characterized by self-interest, as seen with Mary who helps Tom with the expectation of reciprocation, weighing the risks and benefits.
- 👥 At stage three, conformity and interpersonal accord influence moral judgments, like Betty's decision to not intervene in the fight to fit in with the crowd.
- 👮♂️ Stage four values authority and social order, demonstrated by the teacher's immediate action to stop the fight, prioritizing rules and order.
- 📜 In stage five, individuals like Jessie understand rules as a social contract, questioning the purpose and fairness of rules, and considering the broader implications.
- 🌟 Stage six is guided by universal ethical principles, with the headmaster emphasizing justice and compassion as the highest moral principles, even when it means breaking rules.
- 🧒 The pre-conventional level (stages one and two) is common among children, focusing on direct consequences rather than social norms.
- 👩🎓 The conventional level (stages three and four) is prevalent during adolescence and adulthood, where morality is centered around societal norms and rules.
- 🤓 The post-conventional level (stages five and six) is less common, where individuals may act against societal norms or rules if they conflict with personal morality.
- 🔍 Kohlberg's theory was developed based on Piaget's cognitive development theory and was tested through interviews with boys aged 10 to 16 about hypothetical moral dilemmas.
- 💊 The Heinz dilemma is a famous moral scenario used by Kohlberg to explore moral reasoning, asking whether stealing a drug to save a life is justified and how love or stranger status might affect the decision.
Q & A
What are the three levels of moral development according to Lawrence Kohlberg's theory?
-The three levels of moral development according to Kohlberg's theory are pre-conventional, conventional, and post-conventional.
What is the primary concern of individuals at stage one of Kohlberg's theory?
-At stage one, individuals are primarily concerned with obedience and punishment, making moral judgments based on the direct consequences they expect for themselves.
How does Mary's decision to intervene in the fight reflect stage two of Kohlberg's theory?
-Mary's decision to intervene reflects stage two, where she is motivated by self-interest, considering the potential for reciprocity and the personal benefits of helping Tom.
Why does Betty decide not to intervene in the fight according to stage three?
-Betty decides not to intervene because at stage three, she is guided by interpersonal accord and conformity, valuing the opinions of others and the desire to fit in with the community's ethics.
What does the teacher's reaction to the fight indicate about his moral development stage?
-The teacher's reaction indicates that he is at stage four, where he values authority and the maintenance of social order, emphasizing the importance of following rules to prevent chaos.
How does Jessie's perspective on the school rules differ from the others?
-Jessie's perspective differs as she is at stage five, understanding rules as a social contract and questioning whether they serve the right purpose, rather than accepting them as strict orders.
What is the headmaster's approach to moral reasoning at the post-conventional level?
-The headmaster's approach at the post-conventional level is guided by universal ethical principles, particularly justice and compassion, which he believes should underpin all rules and actions.
Why did Kohlberg base his work on Piaget's theory of cognitive development?
-Kohlberg based his work on Piaget's theory because it provided a foundation for understanding how individuals develop cognitively, which he then applied to the development of moral reasoning.
What is the Heinz dilemma and why is it significant in Kohlberg's research?
-The Heinz dilemma is a moral dilemma used by Kohlberg to test his theory, presenting a situation where Heinz must decide whether to steal a life-saving drug. It is significant because it allows Kohlberg to analyze how individuals justify their decisions based on their stage of moral development.
How can the Heinz dilemma be used to understand different stages of moral development?
-The Heinz dilemma can be used to understand different stages of moral development by examining how individuals justify their decisions. For example, those at the pre-conventional level might focus on the direct consequences, while those at the post-conventional level might consider universal ethical principles.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development (Moral Dilemmas)

Kohlberg's Stages of Moral Development

Kohlberg’s Six Stages of Moral Development (Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development)

Kohlberg moral development | Individuals and Society | MCAT | Khan Academy

Perempuan berzinah harus dirajam demi hukum: Standar moralnya apa?

Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development Explained!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)