KEKUASAAN REPUBLIK BATAAF DI INDONESIA | Sejarah Indonesia Kelas 11 - Video Pembelajaran
Summary
TLDRThis historical video script delves into the Dutch East India Company's (VOC) eventual dissolution in 1878 and the subsequent colonial governance by the Batavian Republic. It discusses the French invasion of the Netherlands, leading to the formation of the Batavian Republic under Louis Napoleon. The script highlights the political impact on Indonesia, the appointment of Herman Willem Daendels as the Governor-General, and his efforts to modernize and secure Java against British invasions. Daendels' policies in defense, administration, and socio-economic reforms are covered, along with the challenges faced by his successor, Jan Willem Janssens, culminating in the British conquest of Batavia in 1811 and the signing of the Treaty of Tuntang, marking the Dutch defeat and the transfer of Java to British control.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ The Dutch East India Company (VOC) was officially disbanded on December 31, 1878, but this did not end Dutch colonialism and imperialism in Indonesia.
- 🇳🇱 In 1795, French forces invaded the Netherlands, leading to the formation of the Batavian Republic under the leadership of Louis Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte's brother.
- 👑 King William V fled to England, where he issued orders through 'Kew Letters', instructing the Dutch to surrender territories to the British instead of the French.
- 🏰 The British swiftly took control of several territories in Indonesia, including Padang, Ambon, and Aceh, and strengthened their military presence to blockade Batavia.
- 🛡️ The Batavian Republic sought to take over all former VOC territories in the Indonesian archipelago to protect them from British attacks.
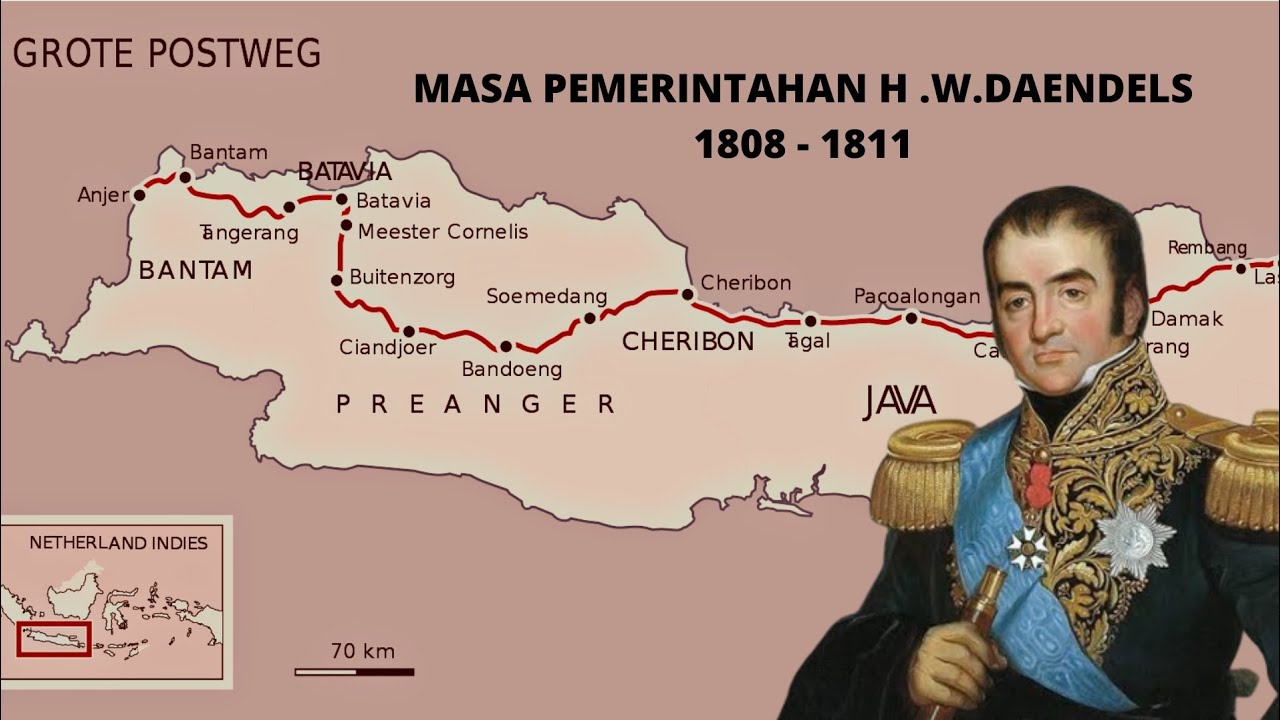
- 🔑 Louis Napoleon appointed Herman Willem Daendels, a young revolutionary, as the Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies from 1808 to 1811, with the main task of preventing British control over Java.
- 🛠️ Daendels implemented policies in defense, security, politics, and social-economic fields, aiming to eliminate feudalism and make the Indonesian society more dynamic and productive.
- 🛤️ One of Daendels' most famous policies was the construction of a 1100 km long road, stretching from Anyer in Banten to Panarukan in East Java.
- 👥 Daendels' policies, particularly the forced labor for road and base construction, led to suffering and impoverishment among the Indonesian people, with many casualties.
- 🏛️ In politics and governance, Daendels reformed the administrative structure, moved the capital from Batavia to Weltevreden (now Menteng, Jakarta), and established courts and regional divisions.
- 💼 Economically, Daendels introduced policies to improve the Dutch government's finances, such as issuing paper money, forming a financial supervisory board, and increasing taxes on private individuals.
- 🏆 Daendels' tenure was marked by authoritarian rule and heavy-handedness, which led to his eventual removal from the position of Governor-General.
Q & A
What was the significance of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) being dissolved on December 31, 1878?
-The dissolution of the VOC marked the end of the Dutch colonial and imperialistic practices in Indonesia, and it led to the governance of Indonesia under the influence of the Batavian Republic.
Why did the French invasion of the Netherlands in 1795 lead to the establishment of the Batavian Republic?
-The French invasion prompted a group known as the 'patriots' who desired a unified Netherlands. This resulted in the formation of the Batavian Republic under the leadership of Louis Napoleon, Napoleon Bonaparte's brother.
How did the political developments in the Netherlands affect the political situation in Indonesia?
-The political changes in the Netherlands, particularly the establishment of the Batavian Republic, influenced the political situation in Indonesia, leading to the Dutch East Indies coming under the control of the new republic.
What was the main task of Herman Willem Daendels during his tenure as Governor-General in Indonesia from 1808 to 1811?
-Daendels' main task was to defend the island of Java from British control and to eliminate feudalism, making the Indonesian society more dynamic and productive for the benefit of the Batavian Republic.
What was the impact of Daendels' policies on the defense and security of Java?
-Daendels implemented policies such as increasing the number of native troops, forming the Mangkunegara Legion, building new defense fortresses, and establishing naval bases to strengthen Java's defense against British attacks.
What is the significance of the road built by Daendels, stretching over 1100 km from Anyer, Banten to Panarukan, East Java?
-The road built by Daendels was a significant infrastructure project aimed at improving connectivity and facilitating the movement of troops and resources across the island, which was crucial for defense and administration.
How did Daendels' policies in the field of politics and governance change his image among the people?
-Initially seen as a young, democratic, and revolutionary leader, Daendels' image changed to that of a dictator due to his forced labor policies for road and base construction, which brought suffering and poverty to the Indonesian people.
What administrative changes did Daendels implement to streamline the governance of the Dutch East Indies?
-Daendels restructured the administration by forming the Secretariat of State, moving the capital from Batavia to Weltevreden (now Menteng, Jakarta), establishing courts in Batavia and Surabaya, and reorganizing the territory into 23 larger regions called 'keresidenan' and several 'kabupaten'.
What were the economic policies of Daendels aimed at improving the Dutch government's finances?
-Daendels implemented policies such as issuing paper money, forming a financial supervisory board, collecting taxes from private individuals, increasing the cultivation of profitable crops, and compelling the population to sell their produce on the world market.
What was the consequence of Daendels' land sale policy, and how did it affect his tenure as Governor-General?
-Daendels' policy of selling land to private parties, including Chinese and Arab individuals, was controversial as the proceeds were used to enrich himself. This led to his dismissal from the position of Governor-General.
What happened to the Dutch East Indies after the British attacked Batavia in 1811, and how did it affect the Dutch control over the region?
-After the British attack on Batavia in 1811, the Dutch forces under Jan Willem Janssens were unable to defend the city, leading to its capture by the British. This resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Tuntang, where the Dutch acknowledged their defeat and handed over control of Java and surrounding areas to the British.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Mengapa VOC Belanda Bisa Menjajah Nusantara? & Mengapa Akhirnya Runtuh?
Masa Pemerintahan Daendels (1808 - 1811) Di Indonesia || Materi Sejarah Lengkap

Perlawanan Bangsa Indonesia terhadap Penjajah Bangsa Eropa hingga awal abad 20 SEJARAH kelas 11

Perebutan Hegemoni Bangsa Barat Di Indonesia || Sejarah Indonesia Kelas 11 SMA

Sejarah Penjajahan Pemerintahan Belanda Pasca Bubarnya VOC

Sejarah awal masuknya belanda di nusantara
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
