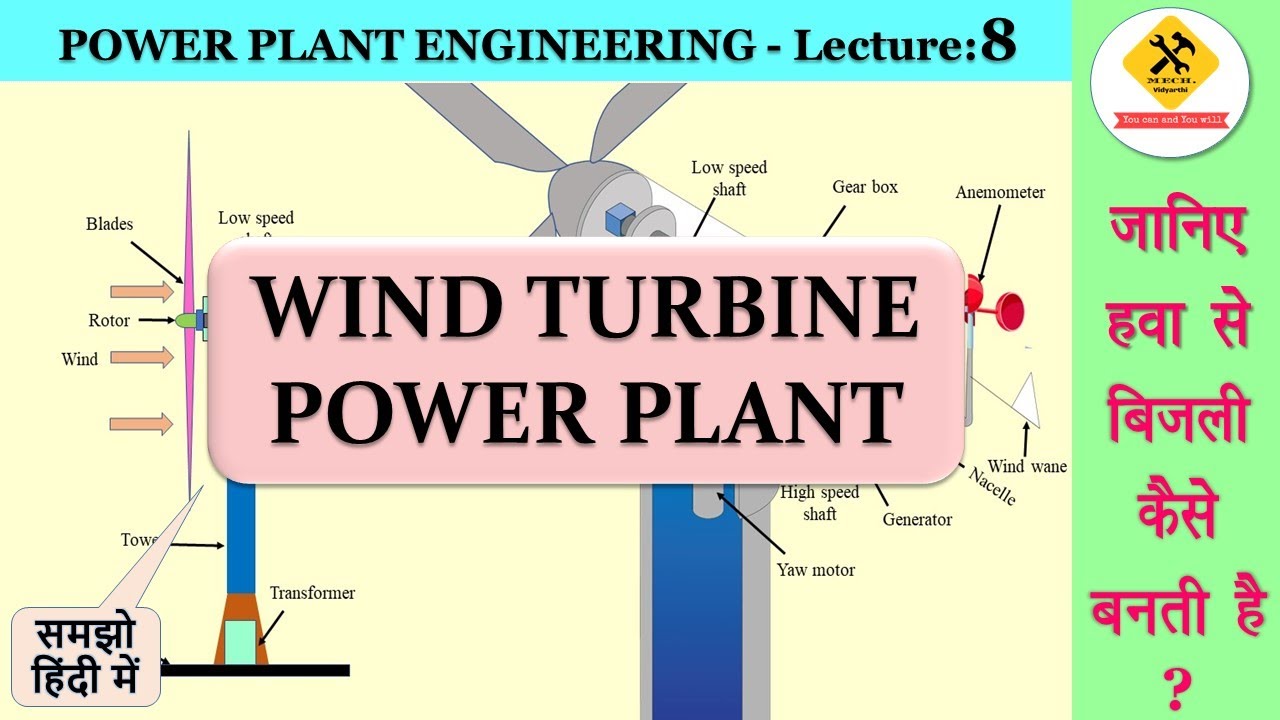
Elettricità. Principi fondamentali, in 10 minuti
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the fundamentals of electricity, including its nature, advantages, and disadvantages. It explains how electricity is generated, transported, and consumed, highlighting concepts like voltage, current, and resistance. The script uses analogies, such as comparing electric circuits to hydraulic systems, to make complex ideas accessible. It also introduces Ohm's law and demonstrates how to calculate current and resistance in a real-life example with a heater. Overall, it provides a comprehensive introduction to the science of electricity, from atomic structure to practical applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electricity involves both static and moving electrical charges and is considered secondary energy because it is derived from other forms of energy.
- 😀 One of the main advantages of electricity is its easy transportability, convertibility into other forms of energy, and its convenience of use (e.g., simply pressing a switch).
- 😀 Electricity does not produce dust or emissions at the consumption point, making it a cleaner energy source compared to fossil fuels.
- 😀 However, electricity has some disadvantages, such as difficulty in storage, partial energy conversion during generation, and pollution from fossil fuel-based production.
- 😀 The generation of electricity from nuclear sources raises concerns regarding radioactive waste and security issues.
- 😀 Atoms, the building blocks of matter, consist of a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons, with the balance of these charges resulting in a neutral charge under normal conditions.
- 😀 Materials that easily lose electrons, such as metals (e.g., silver, copper, aluminum), are called conductors, while those that do not are called insulators (e.g., glass, plastics, wood).
- 😀 Electric current occurs when excess electrons flow from one body (negative charge) to another (positive charge) to restore equilibrium, and is driven by a voltage (difference in electrical potential).
- 😀 Ohm's law states that the current (I) is directly proportional to the voltage (V) and inversely proportional to the resistance (R), expressed as V = R * I.
- 😀 Power (P), measured in watts, is the energy released per unit of time in an electric circuit and is calculated using the formula P = V * I.
- 😀 In a practical example, a 750-watt heater operating at 220 volts will draw a current of 3.4 amperes, and its resistance can be calculated as 64.7 ohms using Ohm's law.
Q & A
What is electricity and what are its main types?
-Electricity refers to the physical phenomena where electrical charges, both static and moving, are involved. It includes static electricity (charge at rest) and dynamic electricity (flowing charges).
Why is electricity considered a secondary form of energy?
-Electricity is considered a secondary form of energy because it is produced from other primary energy sources, like coal, oil, or renewable energy sources, rather than existing naturally in its electrical form.
What are some key advantages of electricity?
-Electricity is easily transportable and distributable, can be converted into other forms of energy like mechanical energy, doesn't produce dust or emissions at the consumption point, and is very convenient to use—just by flipping a switch.
What are the main disadvantages of electricity?
-The main disadvantages include difficulty in storage, partial conversion from primary sources to electricity, pollution from coal and oil-based generation, and the environmental and security risks associated with nuclear power.
How is an atom structured, and how does it relate to electricity?
-Atoms consist of a central nucleus with a positive charge and electrons with a negative charge revolving around it. Electricity involves the movement of electrons, which are transferred between atoms in conductive materials.
What is the difference between conductors and insulators?
-Conductors are materials that allow electrons to flow easily, like metals (e.g., copper, silver, aluminum), while insulators are materials that resist the flow of electrons, like glass, wood, or plastic.
What is voltage, and how is it related to electric current?
-Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two bodies, creating a 'push' for electrons to move. This difference in potential is what causes an electric current to flow through a conductor.
What is Ohm's Law, and how does it relate to current, voltage, and resistance?
-Ohm's Law states that the current in a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to its resistance. Mathematically, V = R * I, where V is voltage, R is resistance, and I is current.
What is electrical power, and how is it calculated?
-Electrical power is the rate at which energy is transferred or used in an electrical circuit. It is calculated as the product of voltage and current: P = V * I, where P is power, V is voltage, and I is current.
How can the power consumed by an electrical appliance be calculated?
-To calculate the power consumed by an appliance, multiply the voltage (V) by the current (I) passing through the appliance. For example, a 750-watt heater running at 220 volts will draw approximately 3.4 amps.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)