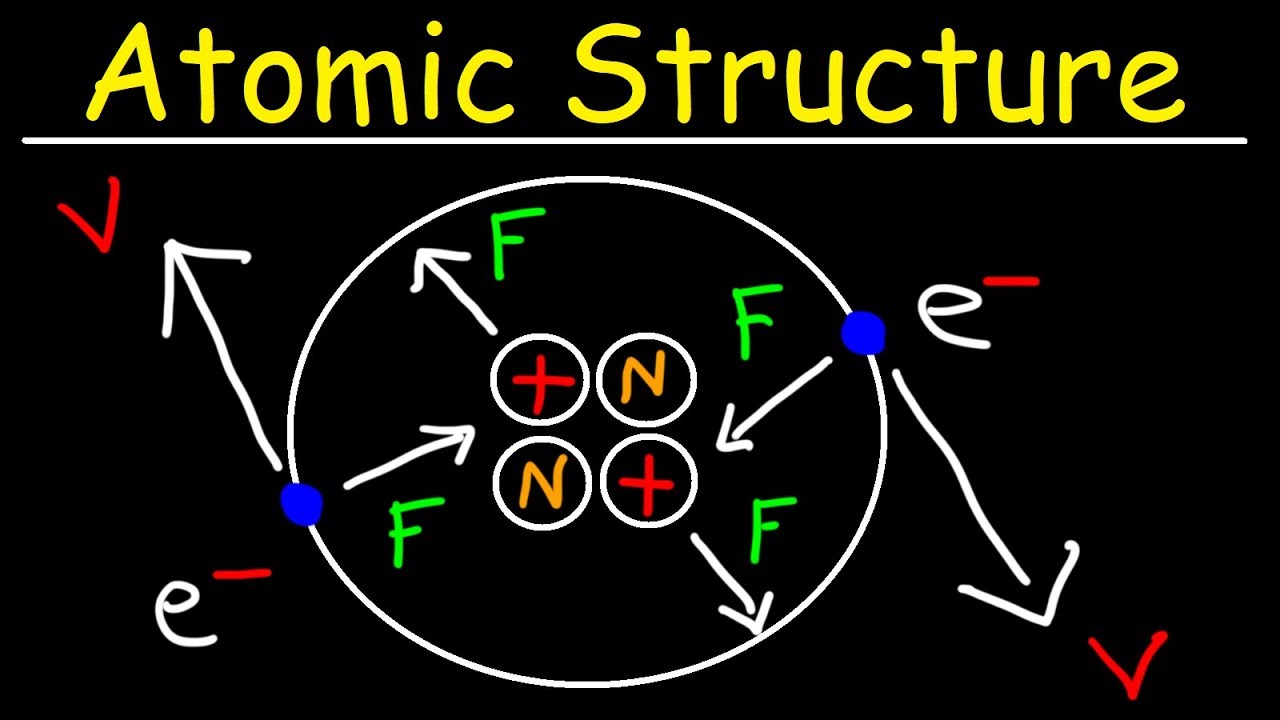
3.4 Subatomic Particles - Mass and Charge
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the world of subatomic particles, exploring their mass, charge, and location within the atom. It introduces the proton, neutron, and electron, highlighting their distinct roles in atomic structure. The proton and neutron make up most of the atom's mass, while electrons carry a negative charge and orbit outside the nucleus. The video also explains key concepts such as nuclear charge, net charge, ions, and mass number. By understanding these particles, we can better comprehend the behavior of elements and their interactions in chemistry.
Takeaways
- 😀 Subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, and electrons) are essential for understanding atomic structure and behavior.
- 😀 Protons are positively charged particles, neutrons are neutral, and electrons are negatively charged.
- 😀 The proton and electron have equal but opposite charges, making them cancel each other out when present in equal numbers.
- 😀 The neutron does not contribute to the charge of an atom but plays a crucial role in the mass of the nucleus.
- 😀 The atomic mass unit (AMU) is used to measure subatomic particle mass, defined as 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
- 😀 The mass of the atom primarily comes from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with electrons contributing negligibly to mass.
- 😀 Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around it, determining atomic structure.
- 😀 The nuclear charge of an atom is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus.
- 😀 The net charge of an atom is calculated by subtracting the number of electrons from protons, leading to a neutral atom when they are equal.
- 😀 Ions are atoms that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net charge different from zero.
- 😀 The mass number of an atom is the sum of its protons and neutrons, indicating its overall mass.
Q & A
What are the three subatomic particles discussed in the script?
-The three subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged, neutrons are neutral, and electrons are negatively charged.
What role does the proton play in an atom?
-The proton is the positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom. It plays a crucial role in defining the atomic number and, therefore, the identity of the element.
Why is the neutron important in the nucleus of an atom?
-The neutron, while neutral, helps to stabilize the nucleus by contributing to the mass and holding the protons together due to the strong nuclear force.
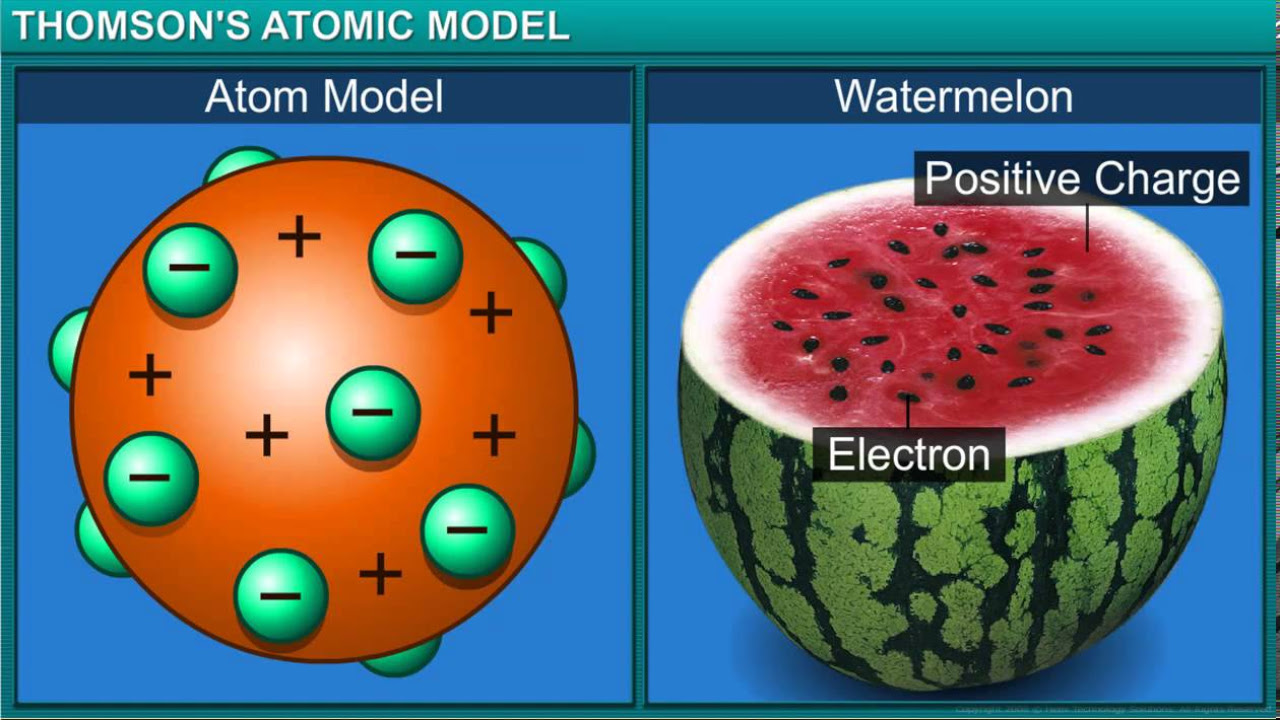
How did J.J. Thomson discover the electron?
-J.J. Thomson discovered the electron through his experiments with cathode ray tubes, which led to the identification of negatively charged particles.
Why is the mass of the electron considered negligible in atomic mass calculations?
-The mass of an electron is extremely small, approximately 1/1836 of a proton's mass, making its contribution to the overall mass of the atom negligible.
What is the concept of the atomic mass unit (AMU), and how is it defined?
-The atomic mass unit (AMU) is a unit used to measure the mass of atoms and subatomic particles. It is defined as 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
What is the difference between the nuclear charge and the net charge of an atom?
-The nuclear charge refers to the total positive charge from the protons in the nucleus. The net charge is the overall charge of the atom, calculated by subtracting the number of electrons from the number of protons.
What happens to the charge of an atom when electrons are added or removed?
-When electrons are added or removed, the atom becomes an ion. If electrons are removed, the atom becomes positively charged (cation); if electrons are added, the atom becomes negatively charged (anion).
How does the concept of mass number relate to atomic structure?
-The mass number of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. It represents the atomic mass of a single atom and is essential for understanding isotopes.
What is an isotope, and how does it relate to mass number?
-An isotope is an atom of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons, leading to a different mass number.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

2 Subatomic Particles

This Is Chemistry: Part 1: What is an Atom?
Chemistry - Atomic Structure - EXPLAINED!

Modelo Atômico de Thomson | Modelo Pudim de Passas | Atomística | Química Geral

3. Qué es el átomo - QUÍMICA (Estructura ATÓMICA)
Chemistry_Class 9th_Chapter 4_Structure of the Atom_Module-Thomson's Atomic Model
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
