Penguraian Vektor (lanjutan)
Summary
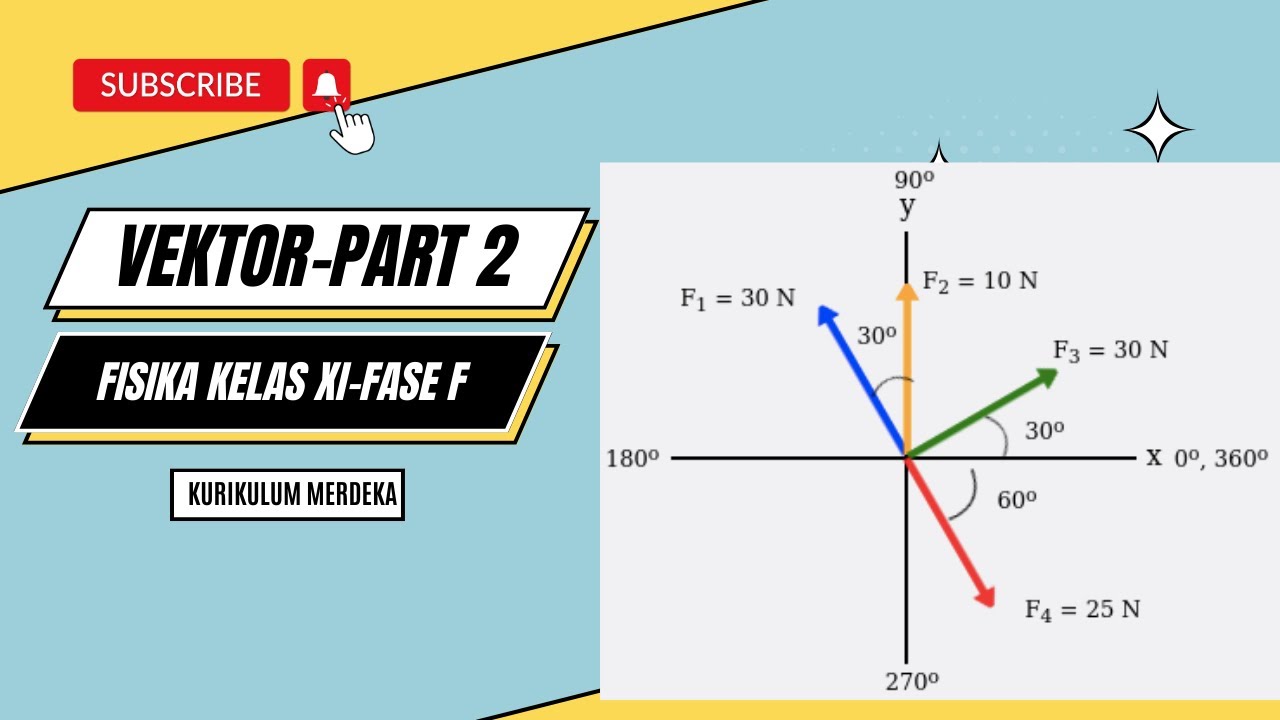
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains the process of vector decomposition, focusing on calculating the magnitude and direction of a resultant vector when its components along the x and y axes are known. Using the Pythagorean theorem, the magnitude is calculated as the square root of the sum of the squares of the components. The direction is determined through the inverse tangent function. The session also includes practical examples, such as finding the magnitude and direction of a vector with components 20 N and 20√3 N, resulting in a 40 N vector at a 60° angle.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video focuses on explaining vector decomposition and related calculations.
- 😀 It covers how to determine the magnitude of a vector when its components are known along the x and y axes.
- 😀 The use of the Pythagorean theorem is emphasized to calculate the resultant vector from its components.
- 😀 The angle between the resultant vector and the x-axis can be calculated using trigonometric functions.
- 😀 The angle θ is calculated using the formula: θ = tan⁻¹(FY / FX).
- 😀 The direction of the vector (positive or negative) depends on the sign of the components along the x and y axes.
- 😀 The video stresses the importance of using a sin, cos, or tan table to find angles for specific trigonometric values.
- 😀 The value of tan(θ) = 1 corresponds to an angle of 45°, which can be verified using a trigonometric table.
- 😀 When dealing with negative values for vector components, one must consider the quadrant in which the vector lies.
- 😀 The script includes a sample problem where the magnitude and direction of a vector are determined from known components (20 N and 20√3 N).
Q & A
What is vector decomposition?
-Vector decomposition is the process of breaking a vector into two or more components along specific axes, often the x and y axes, to make calculations easier.
How is the magnitude of the resultant vector determined from its components?
-The magnitude of the resultant vector can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. If FX and FY are the components along the x and y axes, the magnitude is given by the formula: √(FX² + FY²).
What is the role of the angle in vector decomposition?
-The angle of a vector relative to the x-axis helps determine the direction of the vector. This can be found using trigonometric functions like tangent, where the angle θ = tan⁻¹(FY / FX).
How can we find the angle of a vector given its components?
-The angle θ can be found by using the inverse tangent (tan⁻¹) of the ratio of the y-component to the x-component, i.e., θ = tan⁻¹(FY / FX).
What does a result of 1 for the tangent value indicate about the angle?
-If the tangent value of an angle is 1, it means the angle is 45°. This is because tan(45°) = 1.
What happens if the components of the vector are negative?
-If the components of the vector are negative, the direction of the vector will be opposite to the positive axis, either along the negative x or y axis, depending on which component is negative.
How do we handle vectors in different quadrants?
-For vectors in different quadrants, we use the signs of the components (positive or negative) to determine the direction and adjust the angle accordingly. The angle can still be found using the inverse tangent, but the quadrant will affect the sign of the result.
What is the relationship between the magnitude of the resultant force and the vector components?
-The magnitude of the resultant force is the vector sum of the components. In cases of vector decomposition, the magnitude of the resultant force is the square root of the sum of the squares of the components along the x and y axes.
How does the direction of the resultant vector change if the components change?
-The direction of the resultant vector changes as the relative magnitudes of the x and y components change. If the x-component increases or decreases relative to the y-component, the direction (angle) relative to the x-axis also changes.
In the example problem, how is the magnitude of the resultant force calculated?
-In the example problem, the magnitude of the resultant force is calculated by squaring the components along the x and y axes, summing them, and then taking the square root of the result. For components FX = 20 N and FY = 20√3 N, the magnitude is √(20² + (20√3)²) = 40 N.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)