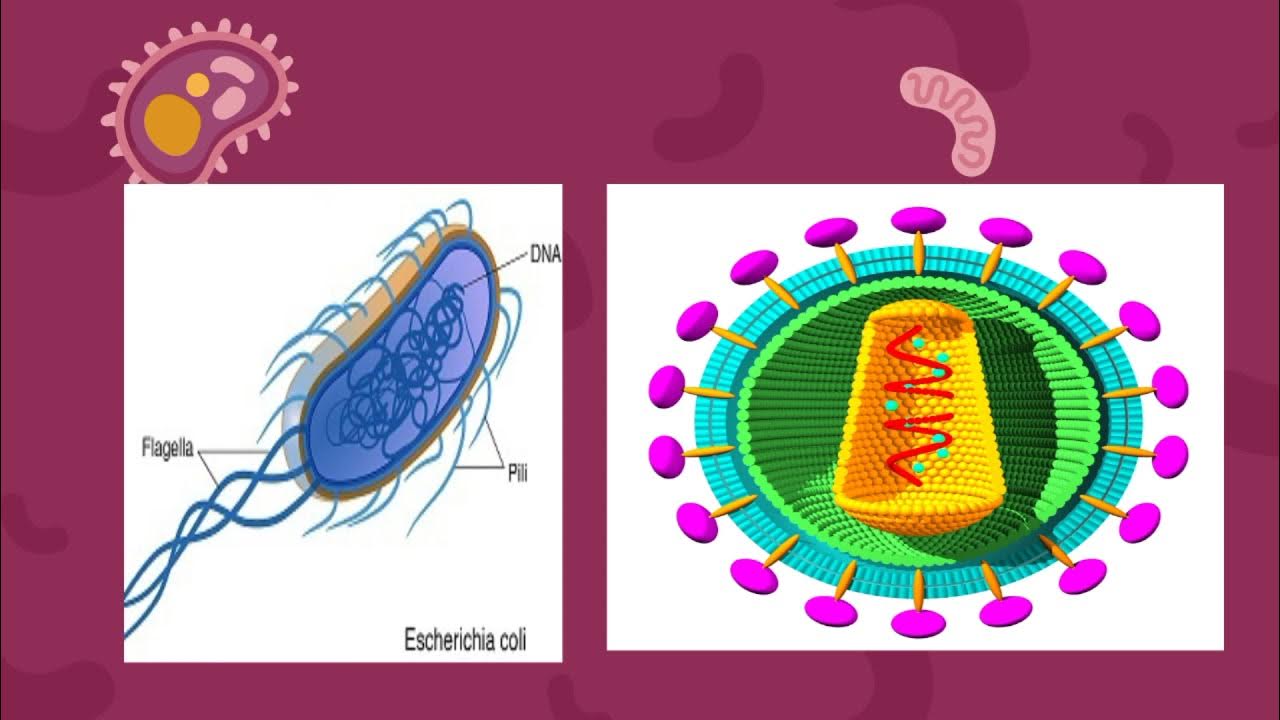
GENETIKA MIKROORGANISME. OH JADI INI BEDA ANTARA DNA DAN RNA YA?
Summary
TLDRThis transcript explores the fundamental concepts of genetics, focusing on microorganisms. It explains the structure and function of DNA, RNA, and chromosomes, emphasizing their role in genetic inheritance and cell replication. Key details include the structure of nucleotides, the process of DNA replication (semi-conservative model), and the differences between DNA and RNA. The script also touches on gene expression, microbial genetics, and the replication process in prokaryotic cells like E. coli. Overall, it provides a detailed yet accessible explanation of genetic principles essential for understanding microbial genetics and their applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Genetics is the study of inheritance, focusing on genes, DNA, and chromosomes.
- 😀 DNA is a macromolecule made up of nucleotides, which consist of a nitrogen base, deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
- 😀 The nitrogen bases in DNA are classified into two categories: purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine).
- 😀 DNA is double-stranded, with two chains held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogen bases (A-T, G-C).
- 😀 Nucleotides in DNA are connected by phosphodiester bonds, linking the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the sugar of another.
- 😀 DNA replication follows a semi-conservative model, where each new DNA strand contains one parent strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- 😀 mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are types of RNA involved in protein synthesis, with mRNA carrying genetic information, tRNA transporting amino acids, and rRNA forming part of the ribosome.
- 😀 RNA differs from DNA in that it is single-stranded, contains ribose sugar, and uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
- 😀 The process of DNA replication involves several enzymes: helicase unwinds the DNA, primase adds RNA primers, and DNA polymerase synthesizes the new strand.
- 😀 DNA replication includes the formation of Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, which are later joined by DNA ligase.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the genetics of microorganisms?
-The main focus is on understanding the inheritance of hereditary traits through genes, DNA, and chromosomes, which are crucial for passing genetic information from parent to offspring.
What are the components of a gene?
-A gene consists of DNA, which is a macromolecule made up of repeating units called nucleotides. These nucleotides are composed of nitrogen bases, deoxyribose sugar, and phosphate groups.
How does the structure of DNA contribute to its function?
-DNA's structure as a double helix with complementary nitrogen base pairing (Adenine with Thymine, Guanine with Cytosine) allows it to store genetic information and replicate accurately. The double-stranded structure is crucial for stability and replication.
What is the difference between purines and pyrimidines in DNA?
-Purines include Adenine (A) and Guanine (G), while pyrimidines include Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C). Purines are larger, containing two carbon-nitrogen rings, while pyrimidines have a single ring structure.
What bonds are involved in the DNA structure?
-DNA structure involves hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogen bases, phosphodiester bonds linking nucleotides, and glycosidic bonds between the nitrogen bases and the pentose sugar.
How does RNA differ from DNA?
-RNA is a single-stranded molecule, unlike DNA, which is double-stranded. RNA contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose and uses Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T) as a nitrogen base.
What are the three types of RNA involved in protein synthesis?
-The three types of RNA involved in protein synthesis are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries the genetic code, tRNA transports amino acids, and rRNA is a part of the ribosome where protein synthesis occurs.
What is the significance of the semi-conservative model of DNA replication?
-The semi-conservative model of DNA replication means that each new DNA molecule consists of one strand from the original DNA and one newly synthesized strand, ensuring genetic continuity and reducing errors.
What are Okazaki fragments and why are they important?
-Okazaki fragments are short DNA segments formed on the lagging strand during DNA replication. They are important because they allow the replication process to occur in a 5' to 3' direction despite the lagging strand being synthesized in the opposite direction.
What enzymes are involved in DNA replication, and what are their functions?
-Key enzymes involved in DNA replication include helicase (which unwinds the DNA), primase (which synthesizes RNA primers), DNA polymerase (which adds nucleotides), and DNA ligase (which joins Okazaki fragments).
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)