Inside the Cell Membrane
Summary
TLDRThe Amoeba Sisters explore the concept of osmosis through an egg lab, demonstrating how the egg's membrane mimics a cell's semi-permeability. They delve into the importance of surface area to volume ratios in cells, emphasizing the cell membrane's structure, including the phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, and proteins. Highlighting the role of glycoproteins in cell signaling and disease resistance, the video educates on the fundamental aspects of cell biology.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The script discusses an educational lab involving eggs soaked in vinegar to model osmosis and cell membrane function.
- 🥚 The eggshell is removed through soaking in vinegar, leaving behind the egg white which acts as a semi-permeable membrane similar to a cell membrane.
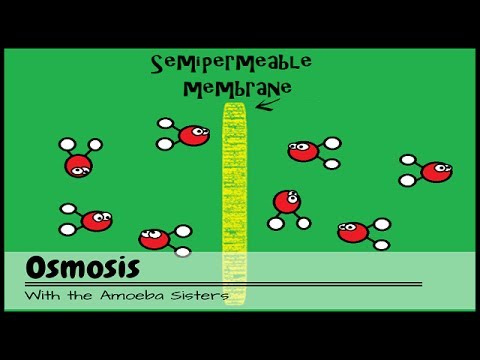
- 🌊 Osmosis is the process where water moves through a semi-permeable membrane, which can be demonstrated using the egg model.
- 📏 The importance of surface area to volume ratio in cells is highlighted, explaining why cells cannot be as large as a chicken egg.
- 📊 A mathematical comparison is made between smaller and larger cube models to illustrate the difference in surface area to volume ratios.
- 🧬 The cell membrane's structure is described as being critical for cell function, with the Fluid Mosaic Model being a key concept.
- 💊 Cholesterol in the cell membrane plays a role in maintaining fluidity and preventing the membrane from becoming too packed or too fluid.
- 🌀 Phospholipids form the phospholipid bilayer, with polar heads and nonpolar tails, contributing to the semi-permeable nature of the cell membrane.
- 🔄 The fluidity of the cell membrane is emphasized, allowing for the movement of its components, including phospholipids and proteins.
- 🛡️ Proteins, both peripheral and integral, serve various functions in the cell membrane, including transport and cell signaling.
- 🦠 Glycoproteins and glycolipids on the cell membrane are important for cell recognition and immune response, with relevance to diseases like HIV.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the egg lab described in the script?
-The egg lab is designed to model osmosis by using the egg white's membrane to mimic a cell membrane, which is semi-permeable, allowing students to explore different scenarios of water and solute movement across the membrane.
Why are raw eggs used in the egg lab instead of hardboiled eggs?
-Raw eggs are used because the shell can be removed after soaking in vinegar, revealing the egg white's membrane which acts as a model for a semi-permeable cell membrane. Hardboiled eggs have a solidified interior and would not serve this purpose.
What is the significance of the cell membrane's semi-permeability in biological processes?
-The semi-permeability of the cell membrane is crucial for controlling the movement of substances into and out of the cell, including nutrients, waste products, and molecules necessary for metabolic processes.
Why can't a body cell be as large as a chicken egg?
-A body cell can't be as large as a chicken egg because the surface area to volume ratio decreases with increasing size, which would reduce the efficiency of nutrient intake and waste removal, essential for cell function.
What is the ratio of surface area to volume in the smaller cube model mentioned in the script?
-In the smaller cube model, the surface area to volume ratio is 6:1, indicating that the surface area is six times greater than the volume.
How does the cell membrane's structure contribute to its functionality?
-The cell membrane's structure, often described by the Fluid Mosaic Model, allows for flexibility and selective permeability due to the movement of its components, such as phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins.
What is unique about the structure of a phospholipid in the context of the cell membrane?
-A phospholipid is unique because it has a polar head that is hydrophilic (attracts water) and a nonpolar tail that is hydrophobic (repels water), allowing it to form a bilayer that separates the cell's interior from its exterior.
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
-Cholesterol in the cell membrane acts as a regulator of fluidity, preventing the phospholipids from packing too closely together in cold temperatures and from becoming too fluid in warm temperatures.
How do integral proteins differ from peripheral proteins in the cell membrane?
-Integral proteins span the entire cell membrane and are often involved in transport, while peripheral proteins are loosely attached to the membrane's periphery and can have various functions, such as enzymatic activity or attachment to the cytoskeleton.
Why are glycoproteins and glycolipids important for cell recognition and signaling?
-Glycoproteins and glycolipids are important for cell recognition and signaling because they can identify the cell as belonging to the organism, aid in self/non-self recognition, and are involved in various cell signaling processes, including immune response.
How does the HIV virus exploit the CD4 glycoprotein?
-The HIV virus exploits the CD4 glycoprotein by using it as a binding site to attach to Helper T cells, which it can then infect, highlighting the importance of cell surface proteins in both immune function and pathogen interaction.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)