Farmakokinetika Obat
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses pharmacokinetics, the process of how a drug enters, moves through, and exits the body. It covers four key stages: absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Each stage is explained in detail, including the different routes of drug administration such as oral, sublingual, rectal, and injection. The video also highlights the factors that influence drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism, including blood flow, protein binding, and genetic factors. Finally, the video addresses how drugs are excreted through the kidneys, lungs, and bile, offering an insightful overview of pharmacokinetics.
Takeaways
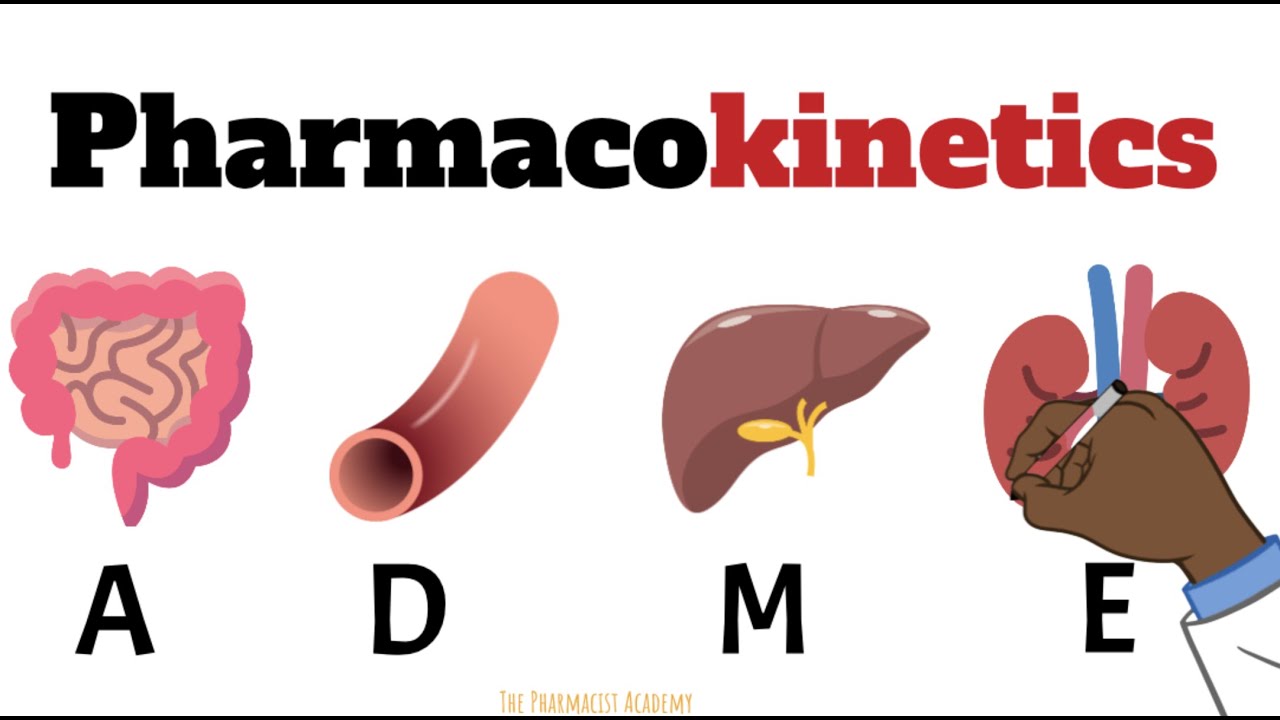
- 😀 Pharmacokinetics refers to the processes of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs in the body.
- 😀 Absorption is the process by which a drug enters the bloodstream, and it varies based on the method of administration (oral, sublingual, rectal, etc.).
- 😀 Sublingual administration allows drugs to bypass the stomach and liver, directly entering circulation through the mouth's mucous membranes.
- 😀 Oral drugs are mostly absorbed in the small intestine, with some exceptions like alcohol and aspirin, which are absorbed more rapidly in the stomach.
- 😀 Rectal administration is used for both local and systemic effects, with drugs bypassing the liver in this process.
- 😀 Topical administration involves applying drugs to the skin, where they are absorbed through the skin into the bloodstream.
- 😀 Inhalation administration involves inhaling drugs into the lungs, which allows rapid absorption into the bloodstream, especially for drugs targeting the lungs.
- 😀 Parenteral administration (injection) provides rapid drug action by directly introducing drugs into the body through veins, muscles, or under the skin.
- 😀 Drug distribution depends on blood flow, organ size, and protein binding, with organs like the heart, liver, and kidneys receiving drugs first.
- 😀 Metabolism, mainly occurring in the liver, converts drugs into water-soluble forms for easier excretion. This process is influenced by genetics, age, environment, and disease conditions.
- 😀 Excretion of drugs primarily occurs through the kidneys in urine, but it can also occur through the lungs or bile into the intestines and feces.
Q & A
What is pharmacokinetics?
-Pharmacokinetics is the study of how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. It focuses on the processes that affect the movement of drugs through the body from entry to elimination.
What are the main processes involved in pharmacokinetics?
-The main processes involved in pharmacokinetics are absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. These processes describe how a drug enters, spreads throughout, is altered by, and is eventually removed from the body.
How does drug absorption occur?
-Drug absorption is the process through which a drug enters the bloodstream. This can happen through various routes such as sublingual, oral, rectal, topical, inhalation, or parenteral, each with its own characteristics and speed of absorption.
What is the difference between sublingual and oral drug administration?
-Sublingual administration involves placing a drug under the tongue where it is absorbed directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. In contrast, oral administration involves swallowing the drug, which is typically absorbed in the stomach or small intestine.
What factors influence the distribution of a drug in the body?
-Factors influencing drug distribution include blood flow to organs (e.g., heart, liver, kidneys), the permeability of capillaries (blood vessels), and the drug's ability to bind to proteins in the blood. These factors determine how well the drug reaches various tissues in the body.
Why do drugs need to be metabolized in the body?
-Drugs need to be metabolized to become more water-soluble, which facilitates their elimination from the body. Metabolism typically occurs in the liver but can also take place in other organs like the intestines and kidneys.
What factors can affect the metabolism of a drug?
-Factors affecting drug metabolism include genetic variations (some people metabolize drugs faster or slower), health conditions (e.g., liver diseases), environmental factors (e.g., smoking or stress), and age (e.g., infants versus adults).
How are drugs excreted from the body?
-Drugs are excreted from the body mainly through the kidneys (in urine), lungs (in exhaled gases), and bile (in feces). The kidneys filter out drugs from the bloodstream, while bile helps eliminate drugs through the digestive system.
What is the role of protein binding in drug distribution?
-When a drug binds to proteins in the blood, it becomes inactive and unable to exert its therapeutic effect. This protein binding influences how much of the drug is free to interact with target tissues and how it is distributed throughout the body.
What are the different types of parenteral drug administration?
-Parenteral drug administration includes various routes such as intravenous (into a vein), subcutaneous (under the skin), and intramuscular (into a muscle). These methods are used when rapid action is needed or when the patient is unable to take drugs orally.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)